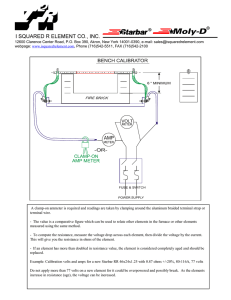
TECH TIP - LED RESISTOR CALCULATION LEDs typically operate
advertisement

TECH TIP - LED RESISTOR CALCULATION LEDs typically operate on about 2 volts DC. To operate them on higher voltages, you must wire a resistor in series with them to drop the voltage to their operating voltage. You connect the ANODE of the LED to one lead of the resistor and the other lead of the resistor to the positive (+) voltage source. The LED anode is typically the long lead on the LED. Connect the short lead of the LED to the negative voltage source. See the wiring diagram below. If you connect the LED up backwards, then it will not light up. Simply reverse the connections on the LED. In general, LEDs operate on about 2 volts DC and at 20 mA. You can check the specific specifications of your LED for its voltage and current requirements, but the 2 volt/20mA rule of thumb will work for most cases. Use the Ohm’s Law formula V=IR to calculate your resistance value. For example, to operate on 12 volts, the calculation would be: V= 12 volts (supply voltage) – 2 volts (LED operating voltage) = 10 volts I= (current), assume 20 mA (convert the current to amps, so it would be .02 amp) R= 10 divided by .02 = 500 ohms. You can choose any standard value resistor close to the calculated value as it is not absolutely critical to be exact. Since 470 ohms is a standard value, you could choose it as your resistance value. Below is a chart for common voltages and the required resistor. VOLTAGE 3 vdc 6 vdc 9 vdc 12 vdc 15 vdc 24 vdc 120 VAC* RESISTOR (1/4 watt or ½ watt) 47 ohms 220 ohms 330 ohms 470 ohms 680 ohms 1100 ohms 5.6K ohms (plus a 1N4007 diode) *Note: for an AC voltage, you will need to include a diode, such as a 1N4007, in series with the resistor. LEDs do not operate very long on AC voltages. DC SOURCE VOLTAGE WIRING DIAGRAM: Anode (long lead) + DC VOLTAGE SOURCE RESISTOR - LED AC SOURCE VOLTAGE WIRING DIAGRAM: Anode (long lead) + AC VOLTAGE SOURCE - DIODE RESISTOR LED