Circuits Review
advertisement

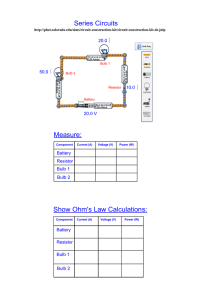
Circuits Practice Date: 11/12/2009 Version #: 0 Name: ____________________________ 1. When checked with a voltmeter, an old 6 V lantern battery shows the expected reading of 6.0 V. However, the battery fails to light a low resistance light bulb. Identify the property of the battery that must have changed as it aged. Explain why this change to the property results in the bulb no longer lighting. (4.00) A 12 V battery transfers 33 C of charge to an external circuit in 7.5 s. 2. What current flows through the circuit? (2.00 marks) 3. A student is instructed to determine the amount of charge flowing past a point in a circuit of unknown resistance during an experiment. What equipment will permit the student to do this? A. voltmeter B. ammeter, voltmeter C. ammeter, stopwatch D. voltmeter, stopwatch 4. Current is a measure of A. the number of charges stored in a cell. B. the amount of energy given to a charged object. C. the charge passing a point in a circuit in a given time. D. the resistance to the flow of charged particles in a circuit. 5. Electric current could be defined as the: A. speed of electrons B. energy of electrons C. total charge D. total charge per second 6. Which of the following is a correct statement? A. The current in a typical resistor is directly proportional to the applied voltage. B. The current in a typical resistor is inversely proportional to the applied voltage. C. The total current into a junction is less than the total current out of the junction. D. The total current into a junction is greater than the total current out of the junction. 7. In which of the following circuits is the voltmeter placed correctly to measure the terminal voltage of the battery, and the ammeter placed correctly to measure the current through the light bulb ( )? A. B. C. D. 8. Which parallel circuit diagram shows meters placed correctly for an experiment in which terminal voltage and current are measured? A. B. C. D. 9. Which one of the following shows the correct placement of an ammeter and a voltmeter to determine the power output of resistor R1? A. B. C. D. 10. Which of the following represents the correct placement of a voltmeter (V) and an ammeter (A) in a circuit? A. B. C. D. 11. The circuit diagram below shows a uniform resistance wire 1.000 m long with a potential difference of 8.32 V between its ends. What is the decrease in electrical energy of an electron as it travels from 'B' to 'C' (4.00 marks) 12. The diagram shows a potentiometer. What is the potential difference between points X and Y? A. 18 V B. 24 V C. 54 V D. 72 V 13. Which arrangement of four identical resistors has the highest equivalent resistance? A. B. C. D. 14. What is the equivalent resistance of the following circuit segment? A. 2 Ω B. 3 Ω C. 9 Ω D. 12 Ω 15. What happens to the total resistance of a circuit as one more resistor is added in parallel? A. The total resistance decreases. B. The total resistance increases. C. The total resistance becomes zero. D. The total resistance does not change. 16. For which of the following arrangements of three 5.0 Ω resistors is the equivalent resistance 3.3 Ω? A. B. C. D. 17. Which of the following arrangements would draw the largest current when connected to the same potential difference? All resistors have the same value. A. B. C. D. Use the following diagram to answer questions 18 - 18 18. What is the total resistance in the circuit? (3.00 marks) 19. What is the voltage of the power supply shown in the diagram? A. 12 V B. 19 V C. 21 V D. 27 V 20. In the circuit below, the current through the 3.0 Ω resistor is 1.0 A. What is the current through the 9.0 Ω resistor? A. 1.0 A B. 1.5 A C. 2.0 A D. 3.0 A 21. Three ammeters are located in an electric circuit as shown. If A1 reads 8 A and A2 reads 2 A, what is the reading on A3? A. 16 A B. 6 A C. 5 A D. 4 A C. 16 A D. 20 A C. 4.0 A D. 6.0 A 22. Calculate the current through the 9.0 Ω resistor. A. 4.0 A B. 12 A 23. Calculate the current through the ammeter. A. 1.0 A B. 2.0 A 24. In the above circuit, what is the effect on bulbs X an Y after the switch S is opened? A. Bulb X is dimmer and Bulb Y is dimmer B. Bulb X is dimmer and Bulb Y is brighter C. Bulb X is brighter and Bulb Y is dimmer D. Bulb X is brighter and Bulb Y is brighter 25. A string of Christmas lights consists of 8 identical bulbs in series connected to a 120 V source. a) What is the potential difference across each bulb? b) If one bulb is removed while the string is still plugged in, what is the potential difference across the empty socket? (4.00 marks) 26. A circuit is made from two resistors and a light bulb as shown on the left. A short time later a copper wire is connected across points X and Y as shown on the right diagram. What is the current through the light bulb and what happens to the brightness of the bulb when the wire is connected? CURRENT BRIGHTNESS OF BULB dimmer A. 0.64 A brighter B. 0.64 A dimmer C. 1.10 A 1.10 A brighter D. 27. In the circuit below, what is the current through the 2.0 Ω resistor? A. 9.5 A B. 10 A C. 12 A D. 13 A 28. In the circuit below, resistor R1 dissipates 0.40 W. Resistors R2 and R3 are identical. What is the resistance of R2? (7.00 marks) 29. In the circuit shown, the current through meter A is: A. 0.67 A B. 0.86 A C. 1.0 A D. 1.5 A 30. In the diagram, the current through ammeter A is 1 A. Resistor B has a resistance of A. 9 Ω B. 6 Ω C. 3 Ω D. 1/3 Ω 31. Each of the two cells shown is connected to an external 6.00 Ω resistor. With supporting calculations, state which cell delivers the greater power to the 6.00 Ω resistor. (7 marks) 32. A certain dry cell has an EMF of 1.500 V. When it is connected in series with a 1.20 Ω resistance, the current through it is 0.870 A. What is the internal resistance of the dry cell? A. zero B. 0.38 Ω C. 0.52 Ω D. 1.72 Ω 33. What is the combined terminal voltage for the cells in the given circuit? A. B. C. D. 29 V 36 V 48 V 60 V 34. What is the battery's terminal voltage in the circuit below? A. 0.40 V B. 5.6 V C. 6.0 V D. 6.4 V 35. A battery is being charged by a 2.0 A current as shown in the diagram below. What is the terminal voltage of this battery? A. 1.4 V B. 4.1 V C. 5.5 V D. 6.9 V 36. When a resistor is added in parallel with the 4.0 Ω resistor in the circuit shown below, what happens to the voltage across the 5.0 Ω resistor and to the terminal voltage of the battery? A. B. C. D. Voltage Across 5.0 Ω increases increases decreases decreases Terminal Voltage decreases increases decreases increases 37. What is the current through the battery shown in the circuit below? A. 0.17 A B. 0.50 A C. 1.5 A D. 2.0 A 38. The above diagram shows two different resistors connected in parallel across a 12.0 V battery. What is the power dissipated by resistor R2? A. 18 W B. 54 W C. 81 W D. 160 W 39. The following diagram shows part of a complete circuit. What is the power dissipated in one of the 20 Ω resistors? A. 16 W B. 25 W C. 33 W D. 99 W 40. In the DC circuit shown below, how much current is necessary to deliver an output of 100 kW at an output voltage of 120 kV? A. 0.042 A B. 0.83 A C. 17 A D. 42 A 41. Explain why a 6.0 V battery feels warm to the touch when it is being used to run a low resistance light bulb. (4.00 marks) 42. What is the resistance of a light bulb rated 150 W at 220 V? A. 0.0031 Ω B. 0.68 Ω C. 1.5 Ω D. 320 Ω 43. The power input to certain transmission lines is 8.5 x 107 W. If the input voltage is 2.4 x 105 V and the total resistance of the lines is 1.9 Ω, how much power is "lost" in the form of heat because of the resistance of the lines? (4.00 marks) 44. Stepping up a voltage means the induced electromotive force for transmission must A. stay the same B. decrease C. increase D. not enough information given 45. What is the efficiency of transmission if 30 000 W of power is delivered over 2 Ω at 500 V? A. 0.4% B. 24% C. 76% D. 99%