Economic Flow and Economic Growth - McGraw-Hill
advertisement

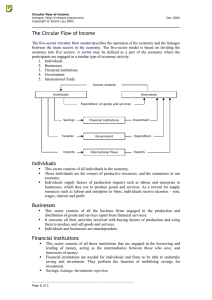
netw rks There’s More Online! GRAPHIC ORGANIZER Economic Sectors CHART Circular Flow of Economic Activity GRAPH Consumer Expenditures VIDEO Lesson 2 Economic Flow and Economic Growth ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why and how do people make economic choices? It Matters Because People of all ages and from every part of the country contribute to the U.S. economy. PHOTO: (tl) Ariel Skelley/Getty Images; (tc) Ross Harrison Koty/Getty Images; (tr) Digital Vision/PunchStock NGSSS covered in “The Circular Flow Model” SS.7.E.2.1 Explain how federal, state, and local taxes support the economy as a function of the United States government. LA.7.1.6.1 The student will use new vocabulary that is introduced and taught directly. LA.7.1.7.3 The student will determine the main idea or essential message in grade-level or higher texts through inferring, paraphrasing, summarizing, and identifying relevant details. Reading HELP DESK Taking Notes: Identifying As you read the lesson, complete a diagram identifying the four sectors of the economy. LA.7.1.7.3 The Circular Flow Model GUIDING QUESTION Why do resources, goods, and services flow in a circular pattern in a market system? How can you understand what goes on in a country’s economy? Economists like to use models to show how things work. A model is a graph or diagram used to explain something. Demand and supply curves are models. In this lesson we will study another one, the circular flow model. This model shows how resources, goods and services, and money flow between businesses and consumers. The model has a circular shape because the flows it shows have no beginning or end. For example, you might have a job in a bookstore. You use the income you earn to purchase a book. The bookstore uses that money to pay your wages, and so on. As you can see, the money flows in a circular pattern. The circular flow model has four parts. Two parts are markets where buying and selling take place. Two parts are sectors, or categories, that stand for the two main groups of participants in the markets. These are the people and businesses that are active in the economy. We will start by looking at the two markets. Economic Sectors Content Vocabulary • circular flow model • economic growth • factor market • productivity • product market • specialization Lesson 2 487 The Factor and the Product Markets The first market is the factor market. This is where factors of production are bought and sold. When people go to work, they sell their labor in the factor market. Capital resources like machines and tools are also bought and sold in the factor market, as are natural resources like oil and timber. The product market is where goods and services are offered for sale. You can think of this market as one big store where all products and services are sold. All exchanges of goods and services take place in the product market. The Consumer Sector and Business Sector Economists think of the buyers in the economy as being divided into four groups called sectors. To keep the diagram simple, the circular flow model shown here has only two sectors: the consumer sector and the business sector. The two sectors not shown are the government sector and the foreign sector. After you have learned how the first two sectors operate, these other sectors will be discussed. Consumers take part in both the factor and the product markets. When consumers go to work, they sell their labor in the factor market. When they get paid, they take that money to the product market, where they buy goods and services. To earn more income, they return to the factor market and sell their labor again. CHART SKILLS This simple model of the circular flow of economic activity shows how the business and consumer sectors interact in the factor market and the product market. CRITICAL THINKING 1 Analyzing Visuals What happens in the product market? CIRCULAR FLOW OF ECONOMIC ACTIVITY PRODUCT MARKETS $ $ Goods and Services Purchased Goods and Services Sold BUSINESS SECTOR CONSUMER SECTOR Labor, Land, Capital and Entrepreneurship Inputs for Production 2 Explaining How do consumers get the income they need to buy products? $ FACTOR MARKETS $ = Flow of dollars = Flow of goods & services Reading HELP DESK Content Vocabulary (cont.) • division of labor • human capital 488 The American Economy circular flow model a model showing how goods, services, and money flow among sectors and markets in the American economy Academic Vocabulary sector a category, or a part of a whole factor market a market where productive resources are bought and sold By doing their weekly grocery shopping, this family is participating in the product market. The average American family spends more than 12 percent of its income on food. ▲ PHOTO: Ariel Skelley/Getty Images CRITICAL THINKING Finding the Main Idea This family is acting as what sector of the economy? The business sector represents all the companies that produce goods and services. This sector is also active in both markets. Businesses sell goods and services in the product market. They use the money they receive from these sales to buy land, labor, and capital in the factor market. The Circular Flow If you look at the whole diagram, you can see that the loop representing money always flows in the clockwise direction. Starting with the consumer sector, money flows through the product market to the business sector. Money then flows through the factor market back to the consumer sector. The loop representing goods, services, and factors of production flows in the opposite direction. The key feature of the model is to show that money flows in one direction while the products and productive resources flow in the opposite direction. This is precisely what happens in real life. For example, suppose you purchase a bottle of water from a vending machine. You put the money in, and the water bottle comes out. The money and the product you buy flow in opposite directions. The circular flow model also shows something else. It shows that markets link the consumer and business sectors. You probably will never set foot in the factory that makes some of your favorite products. However, you still interact with that factory when you buy its products at the store. product market a market where goods and services are for sale Reading Strategy: Paraphrasing Describe in your own words the circular flow of economic activity. Use real-life examples of each sector you describe. LA.7.1.7.3 Lesson 2 489 PHOTO: Ross Harrison Koty/Getty Images The government is a big spender. This single military fighter costs more than $15 million. The Government and Foreign Sectors ▲ CRITICAL THINKING Making Connections How does the factor market connect the consumer sector and the government sector? Florida CONNECTION Government Spending Florida has a gross domestic product (GDP) of $737 billion. State government spending accounts for nearly 13 percent of Florida’s GDP. The largest portion of Florida’s spending goes to education (26 percent), followed by health care (18 percent). Reading HELP DESK Academic Vocabulary comprise to be made up of 490 The American Economy The simplified circular flow model does not show the government and foreign sectors. Both of these sectors are important, but adding them to the model would make it more difficult to understand. The government sector is comprised, or made up, of units of the federal, state, and local governments. These units go to the product market to buy goods and services, just as people in the consumer sector do. Sometimes the government sells goods and services to earn income. For example, state universities charge tuition. Such charges are not enough to fund the government, though. Instead, governments use taxes and borrowing to get the money they need to operate. The foreign sector is made up of all the people and businesses in other countries. They act in both U.S. markets. Businesses in other countries buy raw materials in U.S. factor markets. They also sell their goods and services to consumers in U.S. product markets. In recent years, about 15 percent of the goods and services we in the United States buy have come from foreign countries. Also, about 13 percent of the things we produce are sold outside the United States. PROGRESS CHECK Applying Where and how have you participated in the product market? economic growth the increase in a country’s total output of goods and services over time productivity the degree to which resources are being used efficiently to produce goods and services Promoting Economic Growth NGSSS covered in “Promoting Economic Growth” GUIDING QUESTION How can nations create and promote economic growth? SS.7.E.1.3 Review the concepts of supply and demand, choice, scarcity, and opportunity cost as they relate to the development of the mixed market economy in the United States. SS.7.E.3.4 Compare and contrast the standard of living in various countries today to that of the United States using gross domestic product (GDP) per capita as an indicator. The United States has experienced a clear upward trend in GDP over the past 50 years. This reflects our nation’s steady economic growth. Economic growth is the increase in a country’s total output of goods and services over time. Whenever GDP goes up from one year to the next, it means the economy has grown. Government and business leaders work hard to promote economic growth. Why? Because when the economy grows, the nation’s wealth increases. This also helps improve the standard of living. Two things are needed for economic growth. The first is additional resources. The second is increased productivity. Additional Productive Resources PHOTO: Digital Vision/PunchStock Increasing Productivity Productivity is a measure of how efficiently resources are used to create products. Productivity goes up when more products are made with the same amount of factors of production in the same amount of time. Productivity goes down if fewer products are created using the same amount of the factors of production or more time. Suppose a factory that has made 1,000 computers each week begins to make 1,100 a week with the same number of workers. In that case, its productivity has increased. The automobile assembly line is a good example of the division of labor. Each worker stays in one place and performs a single task to assemble, or put to together, a car. The car is assembled piece by piece as it moves down the line. The use of the assembly line in manufacturing led to a rise in productivity and a reduction in costs. ▲ As you know, the four factors of production are used to make goods and provide services. If a country were to run out of these factors, increasing production would be much more difficult and perhaps impossible. This would cause economic growth to slow or even to stop. One key resource, land, is in limited supply. Only so much oil is under the ground, and it may run out someday. There is only so much timber to be cut, so it is important to plant new trees regularly. Also, our country has a limited amount of freshwater, so it is important to use it wisely and keep it clean. When we work to save or preserve our trees, fields, streams, and other natural resources, we are helping lay a foundation for future economic growth. Economic growth also needs a growing population or one that is becoming more productive. This takes us to the next requirement for growth—productivity. CRITICAL THINKING Drawing Conclusions How do you think the use of assembly lines in manufacturing affected the country’s economic growth? 21st Century SKILLS Write a Research Report Automaker Henry Ford pioneered the use of assembly lines in automobile manufacturing in 1913. Research the ways in which the assembly line changed how Americans made and bought cars. In your report, include details on how these changes affected autoworkers. specialization when people, businesses, regions, and/or nations concentrate on goods and services that they can produce better than anyone else division of labor the breaking down of a job into separate, smaller tasks to be performed individually human capital the sum of people’s knowledge and skills that can be used to create products Over the years, there have been two key changes in how products are made. These are specialization and the division of labor. Both improve productivity. Specialization occurs when people, businesses, regions, or countries concentrate on goods or services that they can produce more efficiently than anyone else. For example, a region that has a mild climate and fertile land will specialize in farming. A person who has good mechanical skills might specialize in car repair. By specializing, each becomes more efficient—or productive. Specialization by people leads to another development that increases productivity: division of labor. Division of labor means breaking down a job into separate, smaller tasks that are done by different workers. This improves productivity—which increases economic growth. Businesses always strive to be more productive because their goal is to make more money. They may increase productivity in different ways. One way is to improve production methods. For example, a factory might invent a new process that results in less waste of a costly resource. Businesses can also use new and better information technology. Computers, for example, let one person do work that was once performed by several people. Production can also be improved by using higher-quality factors of production. This is especially true of one factor of production: labor. When economists talk about the quality of labor, they use the term human capital. Human capital refers to the knowledge, skills, and experience that workers can draw on to create products. How can we improve human capital? Three key factors are education, training, and experience. As workers gain more of these, the quality of their work improves and they become more productive. As you know, greater productivity leads to economic growth and a higher standard of living. PROGRESS CHECK Synthesizing How do people benefit from economic growth? LESSON 2 REVIEW Review Vocabulary 1. What is the difference between a factor market and a product market? LA.7.1.6.1 2. What do the terms specialization and division of labor mean? How is each related to productivity? LA.7.1.6.1 Answer the Guiding Questions 3. Identifying What roles does government play in the circular flow model? SS.7.E.2.1 492 The American Economy 4. Analyzing How do you think specialization is related to differences in GDP between one country and another? SS.7.E.3.4 5. EXPOSITORY WRITING Suppose you manufactured a product that required a scarce natural resource that was rising in cost. Describe how increased productivity might help you avoid passing on rising costs to your consumers in the form of higher prices. SS.7.E.1.3