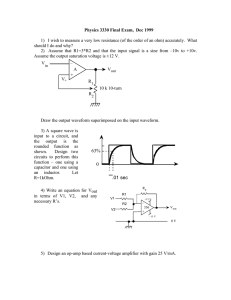
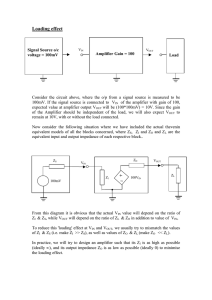
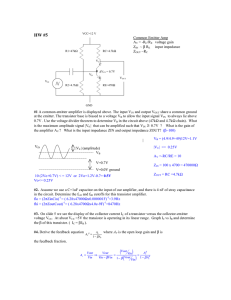
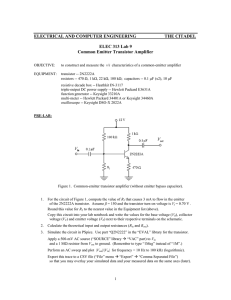
Lab #9, Common-emitter transistor amplifier
advertisement

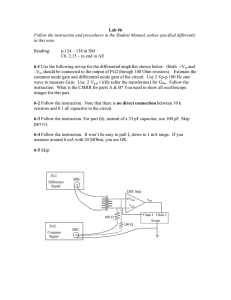
ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING THE CITADEL ELEC 313 Lab 9 Common Emitter Transistor Amplifier OBJECTIVE: to construct and measure the v/i characteristics of a common-emitter amplifier EQUIPMENT: transistor -- 2N2222A resistors -- 100 kΩ , 22 kΩ , 1 kΩ , 470 Ω ; capacitors -- 0.1 F, 10 F resistive decade box -- Heathkit IN-3117 or General Radio Co. 1434-N triple-output DC power supply -- Hewlett Packard E3631A function generator -- Hewlett Packard 33120A multi-meter -- Hewlett Packard 34401A or Fluke 8010A oscilloscope -- Agilent 54622D PRE-LAB: Figure 1. Common-emitter transistor amplifier (without emitter bypass capacitor). 1. For the circuit of Figure 1, compute the value of R2 that causes 3 mA to flow in the emitter of the 2N2222A transistor. Assume β = 150 and the transistor turn-on voltage is Vf = 0.70 V . Round this value for R2 to the nearest value in the Equipment list (above). Copy this circuit into your lab notebook and write the values for the base voltage (VB), collector voltage (VC) and emitter voltage (VE) next to their respective terminals on the schematic. 2. Calculate the theoretical input and output resistances (Rin and Rout). 3. Simulate the circuit in PSpice. Use part “Q2N2222” in the “EVAL” library for the transistor. Apply a 50-mV AC source (“SOURCE” library “VAC” part) to Vin and a 1 M resistor from Vout to ground. (Remember to type “1Meg” instead of “1M”.) Perform an AC sweep to plot |Vout| for frequency = 100 Hz to 1 MHz (logarithmic). Print out this plot and paste/staple it into your lab notebook. Note the gain Av of the amplifier at f = 30 kHz. (Calculate it and write it on your plot.) 4. Add a 10-F capacitor from the emitter to ground and repeat the PSpice analysis. Print out this new plot and paste/staple it into your lab notebook. Note the new gain Av of the amplifier at f = 30 kHz. (Calculate it and write it on your plot.) 1 PROCEDURE: 1. Construct the circuit of Figure 1 (without the emitter bypass capacitor). 2. Measure and record the DC voltage at each terminal of the transistor (VB, VC, VE). 3. Connect the output of the function generator to Vin . Set the function generator to output a sine wave at a frequency of 30 kHz. Connect Channel 1 of the oscilloscope to Vin and Channel 2 to Vout . 4. Set the Vin to 500 mVpp as measured on the oscilloscope. Record the peak-to-peak amplitude of the output waveform, Vout . Note if the waveform Vout is inverted with respect to the waveform Vin . 5. Connect the decade resistance box to the output. Adjust its resistance until Vout reads as one-half the open-circuit value of Vout (measured in step 4). Record this value as the output resistance of the amplifier, Rout . 6. Disconnect the function generator from Vin . Remove the decade box from the output and reconnect it between the function generator and the circuit input (i.e. reconnect it in series with the function generator). 7. Adjust the resistive decade box so that the new measured Vin (after the decade box) is one-half the open circuit value of Vin (from step 4). Record this resistance as the input resistance Rin . 8. Remove the decade resistance box and reconnect the function generator directly to Vin . 9. Slowly increase the amplitude of the generator while observing the output waveform. Record the values of Vin and Vout at which the waveform begins to clip. 10. Insert the 10-F capacitor (emitter bypass capacitor), from the emitter to ground. Ensure that the arrow (or “–” symbol) on the electrolytic capacitor is pointed towards ground. 11. Repeat steps 2–4 with Vin set to its minimum value (100 mV pp). 12. Complete the Data Analysis section before leaving the lab. DATA ANALYSIS: 1. Compute percent error for VB, VC, VE (vs. pre-lab calculations). 2. Calculate the gain (Av) of the common-emitter amplifier with and without the bypass capacitor. QUESTIONS: 1. Do your values for Av without the bypass capacitor, Av with the bypass capacitor, Rin, and Rout match theory/simulation? Why or why not? 2. How/why do Procedure steps #6 and #8 accurately measure the input and output resistances? 3. What causes Vout to clip for high values of Vin ? 4. What is the effect of the bypass capacitor on (a) the DC voltages and (b) the gain of the transistor? LAB REPORT: Complete your lab report in the format requested by your instructor. See Lab #1 for a complete list of requirements. 2