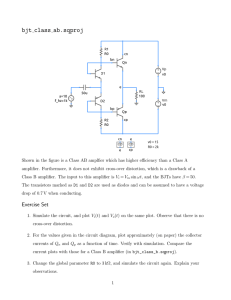
OCL class AB amplifier
advertisement

THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EN107/1 EN107: OCL Class AB Power Amplifier Objective 1. To study the circuit performance of an OCL amplifier. 2. To study the effects of biasing on cross-over distortion of a class AB amplifier. Apparatus 1. OCL class AB amplifier 2. C.R.O. 3. Audio signal generator 4. Twin 30V/2A D.C. power supply 5. One set of headphones Introduction: An OCL amplifier is a push-pull amplifier that requires neither transformer nor output capacitor. Instead, the amplifier requires a twin D.C. power supply and a matched pair of complementary transistors at the output stage. As shown in Fig. 1, the cross-over distortion, which is an inherent characteristic of a push-pull amplifier circuit, is due to the non-linearity of the input characteristics of the output transistors at the cross-over point at which neither transistor is being turned on. The result is that a dead zone appears in the output waveform. This type of distortion can be heard as harmonic noise superimposed on the output signal, and it can be minimized or even eliminated by providing a suitable amount of bias voltage to the output transistors. A class AB amplifier is a modified form of class B push-pull amplifier where each output transistor is provided with a small amount of bias just sufficient to allow each device to conduct slightly in order to minimize the cross-over distortion. THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering a) c) ib1 ib1 Dead zone Cross-over point vb1 vb2 0 θ π θ 0 θ π π 2π ωt θ ib2 ib2 b) EN107/2 vi π ωt Fig. 1 a) input characteristic b) input voltage waveform c) input current waveform of the push-pull transistor amplifier without bias voltage. Circuit Fig. 2 shows the circuit of the OCL amplifier used. The circuit is classified into two stages a) the pre-amplifier stage and b) the driver and the output stage. In the pre-amplifier stage, a differential amplifier is used in which negative feedback is fed to the base of Q2 while the input signal is fed to the base of Q1. The difference between these two voltages is amplified and fed to the input of the next stage, the driver, via the base of Q3. The driver transistor Q3 has the collector load composed of Q8, R2, R15 and R17 (the rubber diode). The potential drop across the rubber diode is used to bias the transistors in the output stage to operate in class AB mode. THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EN107/3 By turning R17 (a rotary potentiometer) the biasing current to the output transistors can be reduced to completely cutoff (ie. Class B). For class AB operation, a moderate biasing current (or quiescent current) is required. Two Darlington pairs of complementary symmetry transistors are used in the output stage. R7 and R8 are inserted to provide a convenient way of observing the current waveforms and measuring the average D.C. current in Q4, Q6 and Q5, Q7. Procedure 1. Do not connect power to the OCL amplifier. 2. Reset the OCL amplifier by i. Turn R17 counterclockwise to the end (Class B) ii. Switch SW1 to select the 15 Ω load 3. Plug the headphone into the phono socket. 4. Connect the signal generator to the I/P of the amplifier. For this experiment, the maximum I/P voltage is about 1 Vpp. However please set it to minimum at the moment. Monitor I/P with oscilloscope CH1. Monitor O/P with CH2. 5. Before connecting the D.C. power supply, select the tracking mode (series mode). The maximum output current will not exceed 1 A for this experiment. Please limit the output current accordingly (both +15V & -15V supplies) and then set the outputs to 15 V. 6. Switch off the power supply and connect it to the amplifier. 7. Now turn on the supply. 8. Set the signal generator frequency to 1 kHz. Gradually increase its amplitude until a 20 Vpp voltage is seen on the output (H). 9. Observe and record voltage waveforms with oscilloscope at (B), (C), R7, R8 and (H). Note also the DC Levels with respect to GND (0V). THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EN107/4 Notes: When measuring waveforms across R7 & R8, use ONE probe only. The other probe must be disconnected from the circuit. (B) DC voltage = 0.792 V (R7) (C) DC voltage = 0.704 V ( R8 ) (H) DC voltage = 0.08 V THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EN107/5 10. Monitor O/P again. Check if you can identify the cross-over distortion. 11. Gradually reduce Vin until a significant cross-over distortion is seen in Vout and record the waveform (~ 2Vpp). 12. Reduce Vin to minimum before switching SW1. Now switch to headphone and put on the headphone. Slowly increase Vin until the volume is at a comfortable level. 13. Turn R17 to and from between Class B and Class AB. Check if you can sense the cross-over distortion. Caution: keep the supply current below 0.5 A. 14. Repeat (13) with different volume levels (be careful – do not turn on too loud) and various frequencies. Comment on the sensitivity of the human ear to cross-over distortion. Caution: remember to reduce Vin before changing the input frequency. Input frequency Comment 20 Hz 7.25 Vpp, distortion heard 100 Hz 7.19 Vpp, distortion heard 500 Hz 2.25 Vpp, distortion heard 2 kHz 2.19 Vpp, distortion heard 10 kHz 1.63 Vpp, cannot tell distortion from signal 15 kHz Inaudible THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EN107/6 15. Reset the OCL amplifier as in (2). Setup the signal generator as in (8). 16. Monitor both Vin and Vout with oscilloscope. a) Calculate the voltage gain Av of the circuit where AV = Vin = 0.813 Vpp Vout Vin Vout = 19.9 Vpp Av = 24.48 b) Measure the average D.C. supply currents. Derive it from the D.C. voltage across R7 and R8. Voltage across R7 = 0.205 V current = 0.205 A Voltage across R8 = 0.199 V current = 0.199 A c) Calculate the output power Pout where Pout = 2 Vout (r.m.s ) RL Pout = 3.3 W d) Calculate the efficiency η of the output stage where P P η = out = out η = 0.54 Pd .c. Vd .c. I d .c. 17. Reduce Vin to minimum. Turn R17 such that the supply current (quiescent current) is about 0.1 A. 18. Adjust Vin to give 20 Vpp output. Repeat (16). Vin = 0.794 Vpp Vout = 20.2 Vpp Av = 25.44 Voltage across R7 = 0.233 V current = 0.233 A Voltage across R8 = 0.226 V current = 0.226 A Pout = 3.4 W η = 0.49 19. Vary input frequencies from 100 Hz to 40 kHz and plot the gain-frequency response of the circuit using dB and log frequency. Determine the bandwidth of the amplifier. THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EN107/7 Frequency Vin Vout Av Av in decibel 100 Hz 0.8 20.3 25.38 28.09 150 Hz 0.8 20.3 25.38 28.09 250 Hz 0.8 20.3 25.38 28.09 400 Hz 0.8 20.3 25.38 28.09 630 Hz 0.8 20.3 25.38 28.09 1 kHz 0.8 20.2 25.25 28.05 1.5 kHz 0.8 19.9 24.88 27.92 2.5 kHz 0.79 19.4 24.56 27.80 4 kHz 0.79 18.6 23.54 27.44 6.3 kHz 0.79 17.5 22.15 26.91 10 kHz 0.78 15 19.23 25.68 15 kHz 0.78 12.4 15.90 24.03 25 kHz 0.78 8.4 10.77 20.64 40 kHz 0.78 5.9 7.56 20.88 Bandwidth = 12 kHz 20. Record the serial number of the OCL amplifier. Serial no. 14 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EN107/8 Problems for further study: 1. Explain why rubber diode was used to provide base emitter bias for the output transistors instead of a resistor. 2. Describe how this amplifier can be modified to work with a single D.C. power supply and compare the gain bandwidth of these two circuits. PREAMP DRIVER OUTPUT R13 +15V 390 C1 220u B R3 1k R21 13k Q3 Q2SA1015 R1 150p R24 R25 Q2SC1815 Q1 I/P 1.5k Q2SC1815 Q2 RUBBER DIODE R5 510 Tune R17 to vary the quiescent current. SW1 R20 180 R2 1.1k SPDT R6 510 R17 1K Q5 QTIP32C R18 R19 15 Q7 QMJ2955 F1 Fuse 1 GND R10 560 H Q8 QTIP31C C5 100u R11 2.2k Q6 Q2N3055 R15 4.3k C14 47u R12 10k F Q4 QTIP31C 33k C3 3.3u C8 10n R7 1 560 33k R23 1k C17 470u 2 C4 R16 D1 1N5819 V2 15V C2 100u C16 220u 6.8k R9 6.8k R22 13k R4 2.2k R14 C V3 D2 15V 1N5819 C18 470u 390 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of OCL amplifier circuit ---END--- G R8 1 -15V J1 1 2 3 PhoneJack