Unit 2 - Electrical Quantities and Ohm`s Law
advertisement
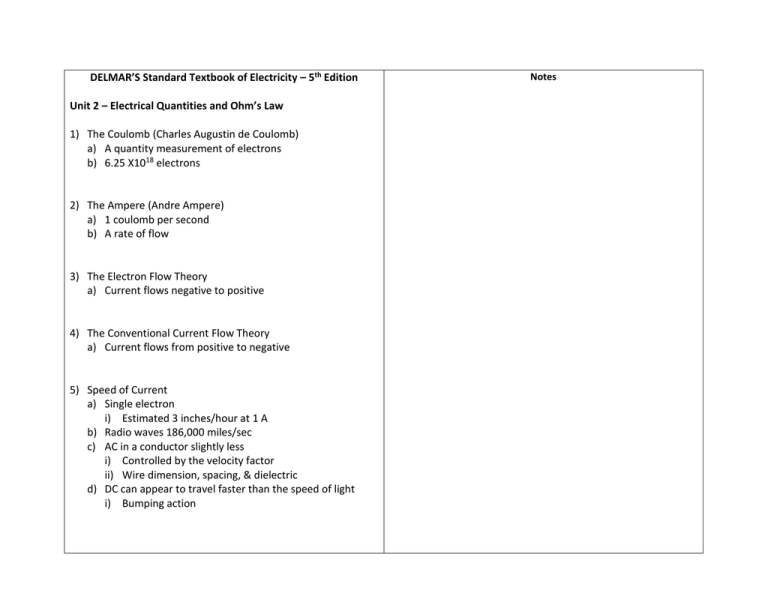
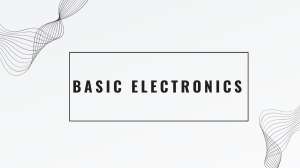
DELMAR’S Standard Textbook of Electricity – 5th Edition Unit 2 – Electrical Quantities and Ohm’s Law 1) The Coulomb (Charles Augustin de Coulomb) a) A quantity measurement of electrons b) 6.25 X1018 electrons 2) The Ampere (Andre Ampere) a) 1 coulomb per second b) A rate of flow 3) The Electron Flow Theory a) Current flows negative to positive 4) The Conventional Current Flow Theory a) Current flows from positive to negative 5) Speed of Current a) Single electron i) Estimated 3 inches/hour at 1 A b) Radio waves 186,000 miles/sec c) AC in a conductor slightly less i) Controlled by the velocity factor ii) Wire dimension, spacing, & dielectric d) DC can appear to travel faster than the speed of light i) Bumping action Notes 6) Basic Electrical Circuits a) Three requirements i) Source ii) Path iii) Load 7) The Volt (Alessandro Volta) a) Unit of electrical potential b) Potential difference between two points c) The “Push” analogous to pressure d) Potential necessary to cause one coulomb to do 1 joule of work 8) The Ohm (Georg S. Ohm) a) Unit of resistance to current flow b) Resistance present when 1 volt causes 1 amp to flow 9) The Watt (James Watt) a) Unit of electrical power b) Measure of the power being used in a circuit 10) Other Measures of Power a) Horsepower (hp) i) 1 hp = 550 ft-lbs/sec or 33000 ft-lbs/min ii) 1 hp = 746 Watts b) British thermal unit (Btu) i) Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water 1 degree Farenheit c) Calorie i) Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius d) Joule i) SI (Systems Internationale) equivalent of the Watt ii) A force of 1 newton acting through 1 meter (mechanical power) iii) Amount of work done by 1 Coulomb flowing because of a voltage of 1 Volt for 1 second (1 joule = 1 wattsecond) 11) Ohm’s Law a) Describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a DC Circuit b) 1 volt of pressure will cause a current of 1 ampere to flow through a resistance of 1 Ohm c) Ohm’s Law variants d) E = IR, R = E/I, I = E/R 12) Metric Prefixes a) Part of the SI (System Internationale) system b) Common prefixes include milli, micro, nano, pico, Kilo, and Mega i) Mega, Kilo, Units . milli, micro, nano, pico ii) Groupings of 3’s