Test 3/Chapter 8 Sample Questions
advertisement

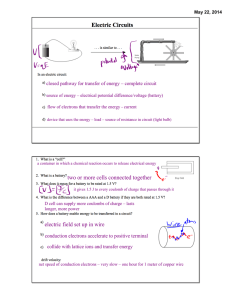
PHS 112 Test 3 Review Chapter 8 All matter is made up of atoms and all atoms contain charged particles. Name the positive particle. Name the negative particle. Which particle is lighter and tends to move more easily? positive: proton; negative: electron; the electron is much lighter and easier to move. How does rubbing a balloon across my hair give the balloon a negative charge? What charge does my hair end up with? Is there a current? The rubber in the balloon holds on to electrons more tightly than my hair. When rubbed together the rubber gains electrons from my hair leaving my hair with a positive charge. These are static charges that can have high voltages but are not flowing as a current. The equations for gravitational force and for electrical force are very similar. What can electrical forces do that gravitational forces cannot? Electrical forces can repel when the charges have the same sign. Gravity always attracts. True (T/F) All of the positive particles are identical and all of the negative particles are identical. True (T/F) The charge of one negative particle exactly balances the charge of one positive particle. The unit we use for the amount of charge is Coulombs. Current does not flow well through tap water. Water is not a good conductor. Current does flow well through water when salt (charge) is present. True. Related to Coulomb’s Law (T/F) The greater the amount of charge, the greater the attraction/repulsion between charges will be. 0.04 Newtons or 1/25 of a newton. Coulomb’s law shows us that the attraction between charges follows the inverse square rule like gravity does. So 5 times the distance is 1/52 the amount of attraction. What do we know about the sign(s) of the two charges? The signs must be opposite for the interaction to be an attraction. If two charges have an attractive force of 1N when 1 foot apart, what will the attraction be if they are 5 feet apart? When a negatively charged balloon sticks to the wall, it has caused the charges in the wall to rearrange. This is called polarization. What are the units for electric potential and for electric potential energy? Also review units for power, energy, and work. Look for these in your textbook. What is the voltage of a battery that does 60J of work on 10C charge? 6 Even when there is a very high voltage, there isn’t much energy if the charge is small. For electricity to flow around a circuit requires a push or pressure known as voltage. What are the units for current and resistance? Look for these in your textbook. Which type of current flows both ways around a circuit? (Flows first one way and then the other. Cannot flow both ways at the same time.) ac or alternating current Which type of current flows in one direction? dc or direct current Does the wire have a net charge? No. Electrons are flowing into and out of the wire at the same speed. Do most of the electrons in the wire stay in the wire? Electrons move through a wire fairly slowly. It would take some time for a direct current to replace the electrons in a wire with different electrons (and depend on the length of the wire). Alternating current changes direction rapidly enough that few of the electrons leave the wire. They move back and forth within the wire. What properties of a wire increase the resistance? Length, cross sectional area (diameter), identity of conductor, temperature What is the voltage across a 10 Ohm resister with a current of 5 amperes? How much current is in a 60-W light bulb connected to 120 V? 50 volts 0.5 ampere What is the combined resistance of a pair of 1 Ohm resisters connected in series? 2 Ohms. In a parallel circuit these to resistances would not "combine" since they would be on separate pathways. False (T/F) When connected in parallel, if one bulb burns out they all go out.