Copyright © 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
Science Physics Electromagnetic Blizzard Bag 2014 - 2015
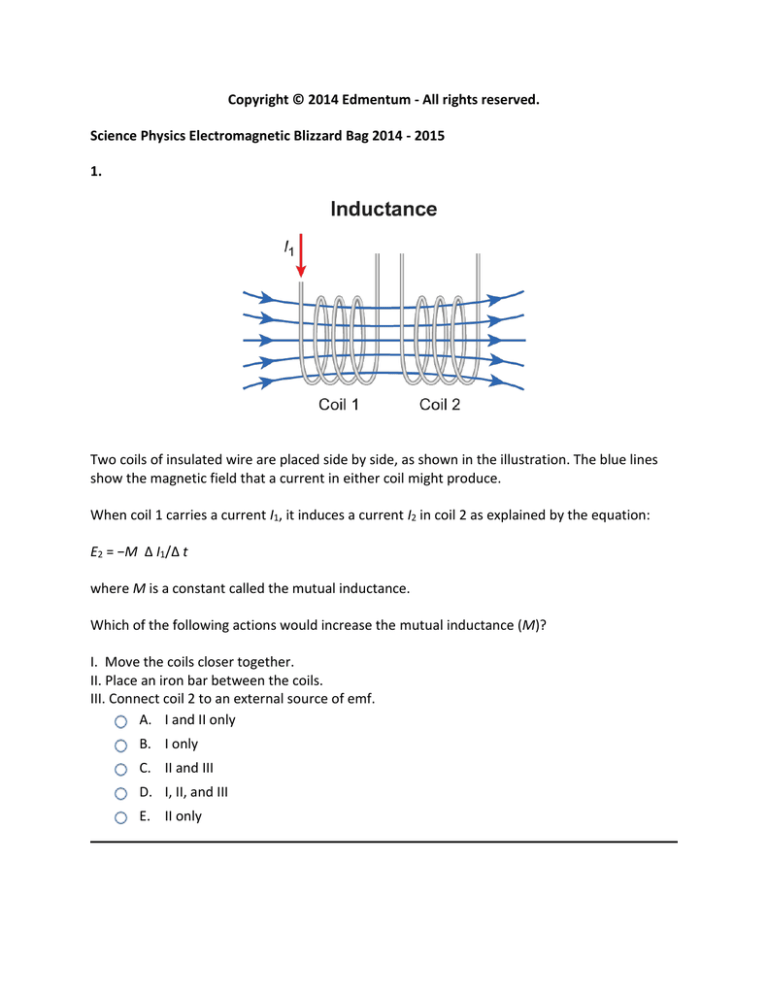
1.
Two coils of insulated wire are placed side by side, as shown in the illustration. The blue lines
show the magnetic field that a current in either coil might produce.
When coil 1 carries a current I1, it induces a current I2 in coil 2 as explained by the equation:
E2 = −M Δ I1/Δ t
where M is a constant called the mutual inductance.
Which of the following actions would increase the mutual inductance (M)?
I. Move the coils closer together.
II. Place an iron bar between the coils.
III. Connect coil 2 to an external source of emf.
A. I and II only
B. I only
C. II and III
D. I, II, and III
E. II only
2. According to Maxwell's fourth equation, a magnetic field will be produced by...
I. a static electric field.
II. a changing electric field.
III. an electric current.
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. II only
D. III only
E. I, II, and III
3.
In this transformer, two insulated wire coils (the primary coil and the secondary coil) are
wrapped around a laminated iron core. When current flows through the primary coil, the
transformer acts to induce a current in the secondary coil through magnetic flux.
If the two coils were interwoven tightly along one edge of the bar, rather than separated
among two edges, the effect of the transformer would...
A. be only minimally effective in inducing current.
B. be about the same.
C. change from decreasing the voltage to increasing the voltage.
D. change from increasing the voltage to decreasing the voltage.
E. be about 10 times more effective in inducing current.
4. What best describes how an alternator works?
A. A stationary magnet induces a current in moving wire coils.
B. An electric current in wire coils is used to create an electromagnet.
C. A stationary magnet induces a current in stationary wire coils.
D. Magnets around a current-carrying wire change DC to AC.
E. A moving magnet induces current in stationary wire coils.
5.
A wire carries a current straight down into the ground. When viewed from above, in what
direction are the magnetic field lines surrounding the wire?
A.
Straight lines with vectors pointing right
B.
Concentric circles with vectors pointing counterclockwise
C.
Concentric circles with vectors pointing clockwise
D.
Straight lines with vectors pointing left
E. Straight lines with vectors pointing into the ground
6. A scientist uses a spectrometer to produce light across the visible spectrum, which ranges in
wavelength from about 400 nm to 750 nm. The light produced at 400 nm is colored _______
and has a wavelength of _________.
A. white; 1.5 x 1015 Hz
B. red; 7.5 x 1014 Hz
C. violet; 3.4 x 1016 Hz
D. green; 2.4 x 1012 Hz
E. violet; 7.5 x 1014 Hz
7.
As illustrated in the diagram, a circular loop of wire of area A = 0.20 m2 is parallel to a uniform
magnetic field B of strength 2.0 T. Gradually the loop of wire is lifted so that it becomes
perpendicular to the field. How does the magnetic flux through the loop change during its
movement?
A. from 0.40 Wb to 0
B. from 0.10 Wb to 0.40 Wb
C. from 0 to 0.10 Wb
D. from 0 to 0.40 Wb
E. from 0.10 Wb to 0.20 Wb
8. A thin, 24-cm long solenoid carries a current of 0.70 A and has 650 turns of wire. What is the
magnetic field near the center of the solenoid?
A. 3.8 × 10–4 T
B. 1.2 × 10–3 T
C. 4.8 × 10–3 T
D. 1.9 × 10–4 T
E. 2.4 × 10–3 T
9.
A battery delivers 8.0 A though a wire that runs for 0.050 m between the poles of a magnet.
The wire is perpendicular to a magnetic field averaging 0.30 T. In this situation, what is the
magnitude and direction of the force that the magnet exerts on the wire due to the current
flowing in it?
A. 0.060 N; up
B. 0.12 N; up
C. 0 N
D. 0.12 N; down
E. 0.060 N; down
10. A long straight wire carries a current of 45 A. At what distance from the wire will the
magnetic field due to this current have the same strength as the magnetic field of the Earth?
(Note: Use a value of 5.0 × 10–5 T for Earth's magnetic field.)
A. 1.8 cm
B. 9.0 cm
C. 0.9 cm
D. 90 cm
E. 18 cm
11.
A tightly-wound coil of wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field that is pointing away from the
observer, as shown in the illustration. Which of the following events would induce an
alternating current in the coil, meaning a current that alternates between traveling in clockwise
and counterclockwise directions?
I. rotational movement of the coil (i.e., spinning it like a top through the field)
II. increasing and decreasing the strength, but not the direction, of the field
III. alternating the direction of the field between pointing away from the observer and toward
the observer
A. II only
B. I and II only
C. I, II, and III
D. II and III only
E. I and III only
12. What variables, if any, affect the speed of electromagnetic radiation through empty space?
A. the ratio of the strengths of the electric field (E) and magnetic field (B) that make
up the radiation
B. the frequency or wavelength of the radiation
C. the angle between the electric field and magnetic field of the radiation
D. the intensity of the radiation
E. no variables (the speed is a constant)
13.
The diagram illustrates certain parts of an AC electric generator. The armature, along with the
wire loop it holds, is placed on an axle that can rotate freely.
What else is needed for the generator to produce AC current?
I. a permanent magnetic field through the armature and wire loop
II. an energy source to turn the axle either clockwise or counterclockwise
III. an energy source to turn the axle in alternating clockwise and counterclockwise directions
A. III only
B. I and III only
C. I and II only
D. I only
E. II only
14.
The figure shows magnetic field lines for a bar magnet. Which statements are true about the
magnetic field at points a and b?
I. The field is stronger at point a than at point b.
II. The field is the same strength at points a and b.
III. The field has the same direction at points a and b.
A. II only
B. II and III
C. I and III
D. III only
E. I only
15.
As shown in the illustration, a person is holding a bar magnet just below a loop of electrical
wiring. The person begins to move the magnet up and down inside the wire loop. Which of the
following actions, if any, would change the induced current in the wire?
I. Increase the speed at which the magnet moves up and down.
II. Tightly wrap more loops of wire around the existing loop.
III. Change the angle at which the magnet is moved through the loop.
A. I and II only
B. I, II, and III
C. I and III only
D. No current is induced in the wire.
E. III only