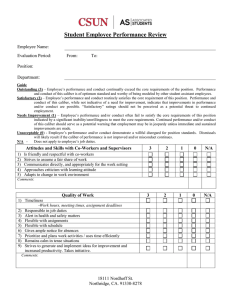
0 46 2 54 01811 18 . . / . . cm cm in in cal = ⇒
advertisement

Forensics Lab Activity Using a Vernier Caliper to Measure “Brass” Name ____________________ Per ____ Date _____________ When a bullet casing (commonly called “brass”) is found at a crime scene, someone has to measure it to determine what caliber it is. This measurement is often done using a vernier caliper. Once measured in centimeters using a Caliber: The diameter of a projectile or the bore of vernier caliper, the measurement is converted to a firearm; expressed in hundredths of an inch (example .30 cal.) in the United States and in either inches (to determine US caliber) or metric millimeters (example 5.56mm) in Europe, millimeters (to determine metric caliber). Asia, etc. US caliber is expressed in hundredths of an inch (.30 cal is read as “30 caliber”) while metric caliber is expressed in millimeters (9mm is read as “nine millimeter”). In this activity, you will first practice converting from centimeters to inches and millimeters. Once proficient in converting, you will be presented with a collection of empty (unprimed) brass to measure to determine caliber. Converting from Centimeters to Inches Given that 2.54 cm = 1 inch, one simply needs to divide a measurement in centimeters by 2.54 to convert to inches. In ballistics, such conversions are rounded to 2 decimal places. Ex: to convert a measurement of 0.46cm to US caliber… 0.46cm . in ⇒ .18 cal = 01811 2.54cm / in Practice on this conversion process is offered in Table 1. Convert each of the centimeter measurements shown in Column 1 to inches (Column 2; show 4 decimal places) and then to US caliber (Column 3). Table 1 Measurement (cm) 0.22 0.36 0.42 0.77 0.85 inches US caliber Converting from Centimeters to Millimeters As previously practiced, converting from centimeters to millimeters is simply a matter of shifting the decimal place one position to the right. Ex: to convert a measurement of 0.46cm to metric caliber… 0.46 cm = 4.6 mm Practice on this conversion process is offered in Table 2. Convert each of the centimeter measurements shown in Column 1 to metric caliber (Column 2). Table 2 Measurement (cm) 0.22 metric caliber 0.43 0.57 Table 3 below lists some common calibers. Convert the given data to complete the table. Table 3 US caliber .17 metric caliber .22 .223 .25 .30 .357 .38 .45 .50 7 7.65 9 10 Forensics Lab Activity Using a Vernier Caliper to Measure “Brass” Name _____________________ Per ____ Date ______________ Measuring Brass Obtain a set of brass samples from your instructor. For each lettered brass (there should be two samples of each) Measure the inside diameter (ID) of the mouth. Rotate the brass 90o Measure the inside diameter of the mouth again. Repeat steps 1 – 3 for the second sample. Average the four measurements. Convert the average to both inches and millimeters. Using the information in Table 3, determine the caliber of the sample. Repeat steps 1 – 7 for all lettered samples. Sample A Trial Who ID (cm) 1 2 3 4 Sample B Trial ave in mm convert to caliber Sample C Trial Who 1 2 3 4 in mm caliber ID (cm) Sample D Trial Who 1 2 3 4 ave convert to ID (cm) 1 2 3 4 ave convert to Who in mm caliber ave convert to in mm caliber ID (cm) Sample E Trial Who ID (cm) 1 2 3 4 Sample F Trial ave in mm convert to caliber Sample G Trial Who ID (cm) Sample H Trial ID (cm) ave in mm convert to caliber Who 1 2 3 4 in mm caliber ID (cm) Sample J Trial Who 1 2 3 4 ave convert to Who 1 2 3 4 ave Sample I Trial in mm caliber 1 2 3 4 convert to ID (cm) 1 2 3 4 ave convert to Who in mm caliber ave convert to in mm caliber ID (cm)