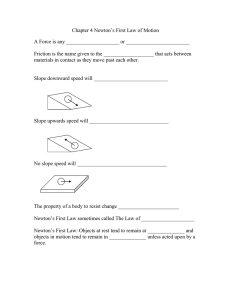
1.6 x 10 20600 1.231 x 10 0.00109
advertisement

UNIT I - REVIEW I. Good things to know • names and uses of lab equipment • safety rules and safety symbols • graphing: independent variable, dependent variable; directly proportional and inversely proportional graph, and equations for these relationships • pure science, applied science, technology, chemistry • scientific method: variables, hypothesis, experiment, data, theory • accuracy vs. precision • observation vs. inference; qualitative vs. quantitative observation • SI system; 5 base units; 1 cm3 = 1 mL; 1 dm3 = 1 L II. How many sig figs in the following number? 1 1) 0.003 3 2) 10.0 2 3) 550 5 4) 310.01 2 5) 0.0023 5 6) 0.29104 3 7) 84.2 1 8) 800 1 9) 100 3 10) 1.20 III. Calculate the following. Be sure your answer has the correct number of sig figs. 1) (4.0 x 1028) (4.4783 x 1014) = 2) (5.3 x 10-26) (5.12 x 1015) = 43 1.79132 x 10 = 1.8 x 10 3) 43 = 2.7136 x 10-10 = 2.7 x 10-10 7.02 x10 −72 = 1.595454x10-52 − 20 4.4 x10 4) 9.02 x1017 = 2.05598 x 104 13 4.3872 x10 1.6 x 10-52 5) 7) 20,600 5.1348 x1030 (13,430)(0.0235) = 0.001089522 = 1.23103 x 1060 6) − 34 3 6.012 x10 6.938 x10 (40.01)(7240.01) ( )( 456.30 + 1107.284 + 263.388 = ) 1.231 x 1060 0.00109 8) 9) 1826.972 1826.97 3.200 + 0.03892 + 0.45653 = 3.69545 3.695 10.20 - 1.201 = 8.999 9.00 IV. Convert the following into decimal notation: 1) 9.10 x 10-3 0.00910 2) 4.00 x 106 4,0θ0,000 V. Convert the following into scientific notation: 1) 4,750,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 4.75 x 1039 2) 0.000 000 000 000 000 003 40 3.40 x 10-18 UNIT I - REVIEW VI. Answer the following questions. Use the given conversion factors: DEFINITIONS APPROXIMATIONS 1 ton = 2000 lbs 1 inch = 2.54 cm 16 oz = 1 lb 1 liter = 1.06 qts 1 gal = 4 qts 1 km = 0.6214 mi 1 foot = 12 in 1 kg = 2.2046 lbs 1) What is the volume of this solid? 2) What is the area of this rectangle? 32.0 mm 3.40 cm 9.6 mm 93.4 mm 7.23 cm V=lwh = (93.4mm)(9.6mm)(32.0mm) = 29,000mm 3 A=lw = (7.23cm)(3.40cm) = 24.6cm2 3) 687 mg = ? kg 7) 21.0 mi = ? km 1kg 687 mg ∗ 6 = 6.87 x10 −4 kg 10 mg 21.0mi ∗ 4) 80.10 km = ? um 8) 50.0 lbs = ? kg 9 80.10km ∗ 10 um = 8.010 x1010 um 1km 50.0lbs ∗ 1km = 33.8km 0.6214mi 1kg = 22.7 kg 2.2046lbs 5) 4.01 x 105 J = ? kJ 9) 65.0 in = ? m 1kJ 4.01x10 5 J ∗ 3 = 401kJ 10 J 65.0in ∗ 6) 2.730 dm3 = ? cm3 2.730dm 3 ∗ 103 cm 3 = 2730cm 3 3 1dm 2.54cm 1m ∗ 2 = 1.65m 1in 10 cm 10) 20.0 cm2 = ? m2 20.0cm 2 ∗ 1m 2 = 0.00200m 2 4 2 10 cm 11) A condor has a wingspan of 305 cm. What is this wingspan in feet? 12) Many candy bars have 9g of fat per bar. If during a chocolate attack you ate one pack of candy (6 bars), how many ounces of fat have you ingested? 6bars ∗ 9 gfat 1kg 2.2046lbs 16oz ∗ ∗ ∗ = 1.9oz 1bar 103 g 1kg 1lb 13) In Europe, gasoline is sold by the liter. If Mr. V’s 1990 Honda Accord has a 14.0 gallon gas tank, how many liters of gas would it require? If the price of gas at the Speedway is $1.65 per gallon, what is the price per liter? How much will it cost to fill the tank completely? 14.0 gal ∗ ( ) 4qts 1L $1.65 1gal 1.06qts $0.44 ∗ = 52.8 L ∗ ∗ = (52.8 L) $0.44 = $23.23 L L 1gal 1.06qts gal 4qts 1L 14) You are in Paris and want to buy some peaches for lunch. The sign on the fruit stand says that peaches cost 4.00 euros per kilogram. Assuming that there are 1.14 euros to the dollar, calculate the cost of a pound of peaches in dollars. 1.00lbs ∗ 1kg 4∉ $1 ∗ ∗ = $1.59 2.2046lbs 1kg 1.14 ∉ UNIT I - REVIEW VII. Graphing After doing an experiment on the effect of temperature on the time for dissolving a sugar cube, you obtain the following data: Temp (oC) 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 time (s) 68.1 64.9 61.7 58.5 55.3 52.1 48.9 45.7 42.5 39.3 36.1 32.9 29.7 26.5 23.3 20.1 1. Graph the data on the sheet of graph paper provided. Be sure to properly title the graph and label your axes. Neither 2. Is this directly proportional, inversely proportional, or neither? 3. Draw a best-fit line through your data. Choose two points which fall on the line and use them to find the slope. slope = y 2 − y1 36.1 − 68.1 = = −0.64 x 2 − x1 70 − 20 4. Choose one of the two points you used and find the equation for the line. Be sure to express your equation in in the form: y = mx+b. Rewrite this equation substituting “T” for x, and “t” for y. 68.1 = (−0.64)(20) + b → 68.1 = −12.8 + b → b = 80.9 t = −0.64T + 80.9 5. What should the dissolving time be at a temperature of 5oC? t = −0.64(5) + 80.9 = 77.7 s 6. Estimate the time required to dissolve a sugar cube in boiling water (100oC). t = −0.64(100) + 80.9 = 16.9 s 7. Describe what you think would happen to the data (and therefore the graph) if there were already 3 sugar cubes dissolved in the beaker before performing the experiment. All the values would increase Temperature vs. Dissolving Time for a Sugar Cube proportionally new line (#7) time (s) Temp (oC) UNIT I - REVIEW