Airport Technical Services Training Modules
advertisement

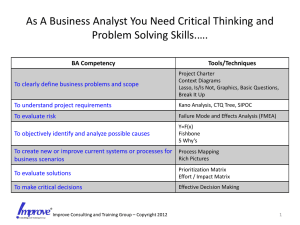
NO. COURSE OBJECTIVE COURSE OUTLINE DURATION 14 Airfield Ground Lighting i) AGL products/ system characteristics and maintenance principles ii) AGL compliance requirements and international standards set by ICAO and FAA iii) How to conduct product evaluation and audits iv) Maintenance procedures and and documentation v) Maintenance Plan and schedule preparation following knowledge AGL Products : Inset Fittings, Elevated Fittings, Transformers AGL Products : CCR’s, PAPI’s, Control Systems, Power Supplies AGL Product Maintenance Approach Systems, Runway Systems, Taxiway Systems AGL Product Training, CCR, Primary Circuit Checks AGL Product Training, Isolating Transformer Checks, Light Fitting Alignment AGL Product Maintenance Inset & Elevated fitting Maintenance AGL Product & Systems Fault Finding & Maintenance techniques Planned Maintenance & programming Operational Maintenance planning procedures Facilities & Safety, evaluation & report 5 working days 15 Automotive Workshop Safety i) To provide participants with an understanding of Auotmotive workshop safety, legal requirements and employee responsibilities • • • • • Automotive in automotive workshop Tools and equipment safety, OSHA 1994 Legal requirements and employee responsibilities Penalties and General written policy Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and control 2 working days 16 Fire Truck Maintenance This course is to provide an understanding on : i) The purpose, construction, and operation of airport firetrucks ii) Trouble- shooting and repair works • • • • • • • Industrial Automated System Fire Trucks specifications Identified and describe the function of an airports fire trucks Test the serviceability of the truck main components Troubleshooting and diagnostic method component repair and installation Electrical and pneumatics diagram 3 working days 17 Motor Starters and Equipment i) Familirization with starting motors and variable speed drive principles, etc ii) Strong knowledge on schematic diagrams, control appratus, and electrical motors in accordance with actual safety regulations • Control and Power Circuit, Protection Devices, Control ElementS and Electrical Motors • Selection of Starting Methods: * Direct on line starting (D.O.L) * Star-Delta * Starting by Eliminating of Stator Resistances * Starting by Autotransformer * Asynchronous Motor with two speeds of rotation * Electronics Starter (Alistart 3) * Various Starting Methods 2 working days 18 Trouble Shooting in Industrial Automation i) To understand, diagnose and troubleshoot an automated system ii) To understand and carry out simple programming • • • • Diagnosis and troubleshooting Industrial Automated System Functioning of a sequential system Function description of an installation Command looping * Input program, preactuator, actuator control looping * Sensor, input program • Troubleshooting method * Study of the installation files, electrical diagram * Input/output addressing 2 working days 19 Predictive Maintenance using Vibration Analysis i) Understand the concept of predictive maintenance and the ability to apply the vibration analysis method ii) Identify and understand the different sources of vibration in running machines • • • • • • • • • 2 working days 20 Baggage Handling System i) Familiarize participants on the fundamentals of operating an airport’s Baggage Handling System (BHS) to maximize airport operational effectiveness and efficiency and minize operational and maintenance costs Introduction Planning Your Routine Repairs How to establish Six Step Preventive Maintenance Program How to establish a Six Step Preventive Maintenance Program How to implement a Predictive Maintenance System Motion Economy. How to Work Smarter Cleaning, Inspecting and Lubricating Equipment General view of maintenance Definition of Predictive Maintenance Introduction to Machinery Vibration Monitoring and Analysis Vibration Measurement Terminology Technical components of Predictive Maintenance Vibration analysis in case examples Imbalance, Misalignment, Mechanical looseness Rolling element bearings Gear, Belts, Motors and Resonance Airport Technical Services Training Modules 5 working days MALAYSIA AIRPORTS CONSULTANCY SERVICES SDN BHD (375245-X) Target Audience Capacity : : Manager (Engineering Team) Executive (Engineering Team) Supervisor (Engineering Team) Minimum 10 pax Maximum 25 pax (Formerly known as Malaysia Airports Management and Technical Services Sdn. Bhd.) Malaysia Airports Corporate Office, Persiaran Korporat KLIA, 64000 KLIA, Sepang, Selangor, Malaysia. D/L : +603 8777 7410/ 7408 • G/L : +603-8777 7000 • Fax : +603-8777 7550 E-mail : macs@malaysiaairports.com.my • Website : www.malaysiaairports.com.my Airport Technical Services Training Modules MALAYSIA AIRPORTS CONSULTANCY SERVICES SDN BHD (MACS) Airports depend on a wide variety of sophisticated technological systems to function effectively. These systems range from the aeronautical ground lighting systems that guide aircraft landings to the baggage handling system that separates and loads baggage onto aircraft. These systems are complex and highly technical, and require personnel with the right knowledge and skills to operate. NO. Malaysia Airports Consultancy Services (MACS) offers a comprehensive range of Airport Technical Services training modules to equip participants with the requisite technical skills and know-how to become qualified and highly competent Airport technical modules personnel able to ensure the technical side of airport operations function as smoothly as possible. NO. 1 2 COURSE Effective Supervisory Skills Facilities Maitenance Management OBJECTIVE Upon completion of this program, the trainees are expected to : • Understand the purpose and functions of a supervisor • Have an enhanced awareness of a supervisor’s responsibilities and expectations in today’s world • Develop more effective people skills in handling subordinates • Be able to exercise alternatives for handling team decisions • Understand the various levels of empowerment- Empowerment vs Capability • Build employee morale via positive approach to correcting errors and use of delegation in improving employee productivity • Manage change and resolve conflicts respectfully • React to and discuss major changes occurring in organization. i) Demonstrate an understanding of troubleshooting technques to identify issues regarding facilities and equipment ii) Participate in gathering information related to repair and maitenance of facilities and equipment to be used as inputs during maitenance analysis 3 Failure Modes and Effect Analysis i) ii) iii) iv) Defining Failure Mode and Effect Analysis Identifying the benefits of using FMEA Learn the steps in carrying out an FMEA How to create typical FMEA design and process v) Prioritize Potential Failures according to Risk and Drive actions to eliminate/ reduce their likelihood of occurence vi) Translate this analysis into effective product/ process contol by addressing critical characteristics of product /process through process control vii) Develop a Control Plan - written depscription of system for controlling production parts and processes COURSE OUTLINE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. DURATION Introduction • Overview, Objectives and Airport Level of Service (LOS), Terminal Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Functions and responsibiltiies of a supervisor Human Relations and Communication The 5 foudnations of Leadership and Supervision Fundamental Principles of Leadership Laws of Motivation Critical Characteristics ofLeadership Effective Task delgation Improving Employee Work Habits Improving Employee Performance Problem employees and employe problems Dealing with Employee Complains Motivating and Inspiring Staff Handling Work Conflicts Building productive teams Managing Change- Effective Change Management, OD Interventions and Employee Involvement 2 working days Overview Repair Programs Equipment malfunctions Six big equipment-related wasters Advantages of repairing own machines Preventive maintenance database requirements Approaches to improving machine reliability Steps in trouble-shooting for causes Seven Points For Root Cause Analysis (RCA) : Description of breakdown: i. Define the physical phenomena of the breakdown. iii. Organize the details of the breakdown by using the ‘3W2H’ ( what, when, where, how, how much) tool. iv. Work as a team, respecting each other’s expertise and knowledge, v. Consider every possible cause of the breakdown. vi. Verify all logical causes and eliminate all illogical ones. vii. If determined that the cause of the breakdown was human error, separate that cause from the physical causes. viii. The latent causes of industrial failures How to identify them and what actions to take? ix. Tools for data collections and trends analysis. 3 working days INTRODUCTION TO FMEA QUALITY PLANNING & TYPES OF FMEA STEPS OF ANALYSIS & CREATING A FMEA • Create & Design FMEA • Creating A Process FMEA • Learn & select the appropriate FMEA • Understanding the importance of FMEA in Manufacturing • Applying the FMEA Methodology to your own case FMEA PRACTICAL PROCESS REVIEW OF KEY TERMS FMEA IMPLEMENTATION REVIEW OF PROCESS FLOW CHART PROCESS CONTROL PLAN NO. COURSE 4 Air Conditioning Maintenance i) This course is designed to ensure participants are able to gain the technical knowledge required in air conditioning maintenance • • • • • • • Introduction - Operating conditions Pump-down and Charging Service diagnosis and repairs Electrical fault finding and controls Chiller installation and features AHU - element and controls Course condition - real case studies 2 working days Air Conditioning Technology i) This course is an entry levelo course to prepare participants to locate faults and carry out basic maintenance works on air-conditioners • Units and measurements • Refrigeration and air conditioning * Fumdamental principles * Refrigeration cycle * Pressure Enthalphy Chart * Factors effecting refrigeration system • Types of systems • Psychrometrics • Air Handling System • Component of refrigereting 2 working days Introduction to PLB Layout Introduction to VGDS Layout LB’s Safety Procedures Operations PLB & VGDS Care & Periodics Maintenance Sistem Calibration Worthiness Checks 5 working days Introduction to Pavement Fundamental of Pavement Construction Defination of Pavement Pavement Design Pavement Classification Pavement Materials Rigid & Flexible Method of Construction Type of Equipments Distress in Airport Pavement, Its defination & effect, component and its charecteristics Distress Factors and Remedial Processes Pavement Situation Case Studies Inspection & Maintenance SOP Site Visits 2 working days Electricity Economics – regulation & Deregulation Market Operation - LV & HT Electricity Supply Industry & Malaysian Grid Code Power System Operation Basics Load forecasting and demand curves System planning and expansion Unit commitment & Intergration Strategy Frequency regulation & economic dispatch Basic system protection practices for safety operation Network switching & isolation SCADA and Energy Management Systems Defence & Restoration Plans Interchange Evaluations Switch gears Operation 5 working days 5 6 7 8 2 working days Passenger Loading Bridges OBJECTIVE This course is designed to help participants gain the following knowledge : i) Knowledge and skills needed for operational worthiness and ensure readiness of the Passesnger Loading Bridge ii) Learn the best pracitices to minimize downturn and ensure service reliability iii) Understand concepts of Airside Safety and Aerodome Rules and Regulations Airport Pavement i) Management System This course provides participants with the following knowledge regarding Pavement Management: • Co-ordination, design, construction, maitenance and evaluation activities • Making efficient use of existing knowledge and practices ii) Plan all work activities and services necesary to provide, operate and maintain airfield pavements in a safe and cost-effective manner Electrical Power System This course provides participants with the following : i) insight on the various equipment types in a typical high voltagee substation and how they contribute to overall system reliability ii) Learn and understand the practical aspects related to the various phases in engineering and design, project implementation, comissioning and maintenance iii) Understanding contractual requirements and technical compliances required iv) Experienced instructors who have encountered and solved serious issues with electrical power systems COURSE OUTLINE COURSE OBJECTIVE COURSE OUTLINE DURATION 9 Electrical for non-electrical Personal i) ii) iii) iv) Adherence to electrical safety precautions Identify types of fuses, circuit breakers Read and interpret electrical drawings Measure voltage, current, resistance in circuits and components v) identify types of electrical AC motors vi) Read and interpret circuit diagrams for starters vii) Wire up different types of starters viii) Trouble - shoot fault in starting system • Safety precaution in Handling 415 volts 3 phase and 230 volts single phase. • Basic electrical circuit, current, resistance, voltage & power calculations. • Measurement of current, resistance, voltage, insulation and etc. • Principle construction and operation of AC motors • Principle of starters for AC motors • Trouble shooting in Electrical AC motors • Common fault and rectification • Practical exercises using multimeters, series, parallel, seriesparallel circuits. 3 working days 10 Sensor in Industry Process Control, Selection and Sizing i) To be able to undestand the operating principles for different types of sensors ii) To understand the principle of regulation loop and role of each component and setting effects • Role and Control system in automation system • Different types of loop, ie. Open and close • Functional description and field application * PT 100 probe * J, K, type Thermal Convector * Notion of analogue and digital convector * Control power point • Setting and Sensor Selection • Sensor and Industrial Application 2 working days 11 Sensor in Industry Process Control, Selection and Sizing i) To be able to understand the general structure of a PLC, how its set up in an automated system, and how to carry out simple programming on the PLC ii) To equip a programmer with advanced techniques typically found in larger or more complex control operations • PLC Structure * Power supply, I/o interface, * The bus, The network, The memories, * Extension racks, wiring, Program language • Programming and Industrial language • Arithmetic; Word manipulation, Functions • Process control and data acquisition * Intro to process control and data acquisition * Transducers * Transmitters * Data acquisition theory * Analog–to-digital conversation, operational amplifiers 4 working days 12 Electro Pneumatic i) • • • • • 4 working days DURATION To provide an introduction to AGL products/ system characteristics and maintenance principles, as well as related international standards established by ICAO and FAA • • • • • • • • • • • • 13 ElectroHydraulics For participants to: i) Understand the functions of the main hydraulic components and trouble shoot hydraulic circuits ii) Understand the main parts of electrohydraulic circuits in order to improve settings and trouble-shooting ability Introduction and Applicable Standards & Safety Intoduction to AGL Airfield and Electrical Safety AGL Series Circuit Approach Lighting Systems: Introduction, Categories and Design Principles Approach Lighting Systems: Design and Application Runway Lighting Systems: Introduction, International Categories Runway Lighting Systems: Design and Application PAPI & APAPI: Design & Application Constant Current Regulators: Principles of Operation & Types Taxiway Systems: Design and Application (Taxiway & Apron Edge, Centreline) Taxiway Systems: Design and Application (Taxiway Lead On/ Off, Hold & Stop Bars) Surface Movement Guidance: Signs-Design and Application and Basic Principles of SMGCS Remote Control & Monitoring Systems: Design and Application-Simple & CAT 1) Remote Control & Monitoring Systems: Design and Application-SMGCS & CAT II/III) Introduction to Main & Standby Power: Design and Application Introduction to Service Manuals, Planned & Preventive Maintenance • Principles of hydraulics and electro control • Hydraulic fluids, power supply unit and electrical components used in electro-hydraulics • Symbols, valves, cylinders and accumulators • Design, Constructions and troubleshooting of hydraulic control circuits • Logic functions in electro-pneumatics • Process sequential control in electro-pneumatics 2 working days