lst week notes
advertisement
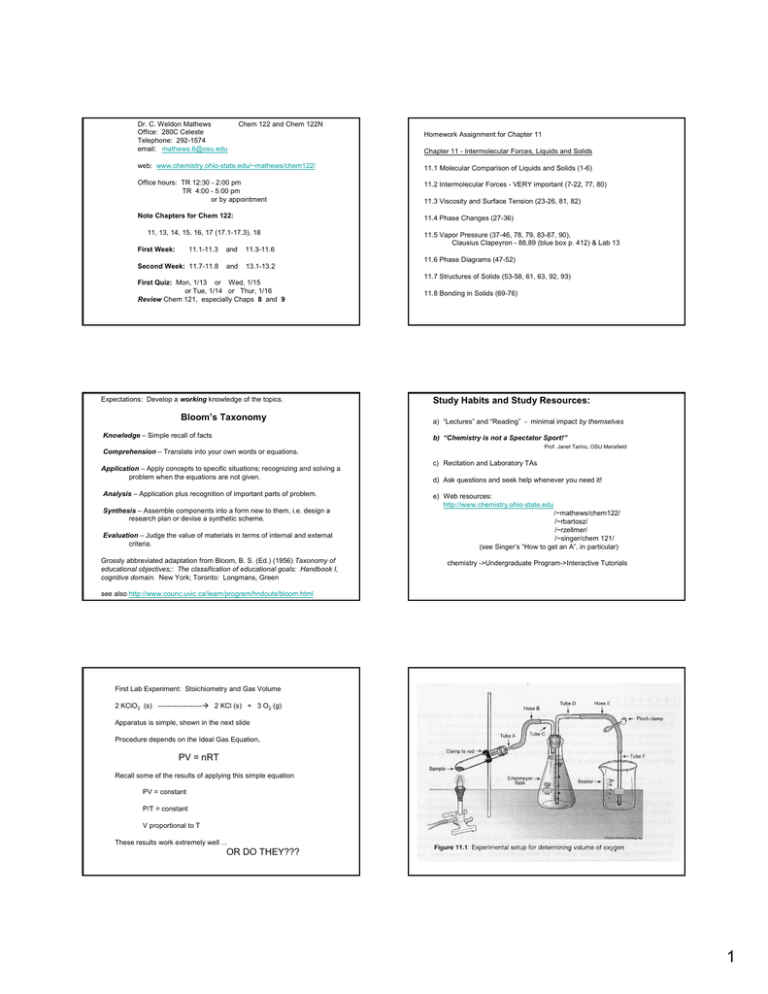
Dr. C. Weldon Mathews
Office: 280C Celeste
Telephone: 292-1574
email: mathews.6@osu.edu
Chem 122 and Chem 122N
Homework Assignment for Chapter 11
Chapter 11 - Intermolecular Forces, Liquids and Solids
web: www.chemistry.ohio-state.edu/~mathews/chem122/
11.1 Molecular Comparison of Liquids and Solids (1-6)
Office hours: TR 12:30 - 2:00 pm
TR 4:00 - 5:00 pm
or by appointment
11.2 Intermolecular Forces - VERY important (7-22, 77, 80)
Note Chapters for Chem 122:
11.4 Phase Changes (27-36)
11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 (17.1-17.3), 18
First Week:
11.1-11.3
and
11.3-11.6
Second Week: 11.7-11.8
and
13.1-13.2
First Quiz: Mon, 1/13 or Wed, 1/15
or Tue, 1/14 or Thur, 1/16
Review Chem 121, especially Chaps 8 and 9
Expectations: Develop a working knowledge of the topics.
Bloom’s Taxonomy
Knowledge – Simple recall of facts
11.3 Viscosity and Surface Tension (23-26, 81, 82)
11.5 Vapor Pressure (37-46, 78, 79, 83-87, 90),
Clausius Clapeyron - 88,89 (blue box p. 412) & Lab 13
11.6 Phase Diagrams (47-52)
11.7 Structures of Solids (53-58, 61, 63, 92, 93)
11.8 Bonding in Solids (69-76)
Study Habits and Study Resources:
a) “Lectures” and “Reading” - minimal impact by themselves
b) “Chemistry is not a Spectator Sport!”
Prof. Janet Tarino, OSU Mansfield
Comprehension – Translate into your own words or equations.
Application – Apply concepts to specific situations; recognizing and solving a
problem when the equations are not given.
Analysis – Application plus recognition of important parts of problem.
Synthesis – Assemble components into a form new to them, i.e. design a
research plan or devise a synthetic scheme.
Evaluation – Judge the value of materials in terms of internal and external
criteria.
Grossly abbreviated adaptation from Bloom, B. S. (Ed.) (1956) Taxonomy of
educational objectives;: The classification of educational goals: Handbook I,
cognitive domain. New York; Toronto: Longmans, Green
c) Recitation and Laboratory TAs
d) Ask questions and seek help whenever you need it!
e) Web resources:
http://www.chemistry.ohio-state.edu
/~mathews/chem122/
/~rbartosz/
/~rzellmer/
/~singer/chem 121/
(see Singer’s “How to get an A”, in particular)
chemistry ->Undergraduate Program->Interactive Tutorials
see also http://www.counc.uvic.ca/learn/program/hndouts/bloom.html
First Lab Experiment: Stoichiometry and Gas Volume
2 KClO3 (s) -------------------Æ 2 KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g)
Apparatus is simple, shown in the next slide
Procedure depends on the Ideal Gas Equation,
PV = nRT
Recall some of the results of applying this simple equation
PV = constant
P/T = constant
V proportional to T
These results work extremely well ...
OR DO THEY???
1
Notice the nice, regular behavior predicted by the ideal gas equation.
This is a typical plot of the dependence of Volume on Temperature—note limits.
This plot for
SO2 is a more
representative
one of real
systems!!!
And this one includes a realistic one for Volume as a function of Temperature!
van der Waals Equation:
{P + a (n2/V2) } { V – nb } = nRT
2
Intermolecular Forces -- forces between molecules -are now going to be considered.
Note that previous chapters concentrated on Intramolecular
Forces, those within the molecule.
Important ones:
ion-ion
similar to atomic systems
ion-dipole
(recall properties of dipoles)
dipole-dipole
dipole-induced dipole
Note that the (normal) BP is the temperature at which the liquid is in equilibrium
with vapor (gas) of the substance at 760 torr (1.00 atm).
London Dispersion Forces:
induced dipole-induced dipole
polarizability
dipole
dipole
3
Recall that dipole moment = |charge| X separation = q r
ion
dipole
initial interactions of two
spherically symmetric
atoms (zero dipole)
generates
induced dipole - induced dipole
interactions
Contact area is also important:
n-Pentane has more surface area than Neopentane
4
Relative Energies
molecule
F2
polarizability
1.3
molecular wt.
predict the
37
Cl2
Br2
4.6
6.7
71
160
I2
10.2
254
d-d
d-id
disp
Ar
0
0
50
58
N2
0
0
2.6
C6H6
0
0
1086
16
C3H8
0.0008
0.09
528
HCl
22
6
106
CH2Cl2
106
33
570
SO2
114
20
205
CH4
trends in the boiling points
The website is up for Chem 122; and a slightly different one is available for
Chem 122N.
Only
OnlyONE
ONE
tt
http://www.chemistry.ohio-state.edu/~mathews
H2O
190
11
38
HCN
1277
46
111
Intermolecular Forces -- forces between molecules -are now going to be considered.
Note that previous chapters concentrated on Intramolecular
forces -- those within the molecule.
Important ones:
gets you to either of them.
ion-ion
similar to atomic systems
The direct URLs are
ion-dipole
(recall properties of dipoles)
http://www.chemistry.ohio-state.edu/~mathews/chem122
http://www.chemistry.ohio-state.edu/~mathews/chem122n
dipole-dipole
dipole-induced dipole
Recall FIRST QUIZ for 2:30 section is on Mon, Jan 13 or Wed, Jan 15
for 6:30 section is on Tue, Jan 14 or Thur, Jan 16
In all cases the quiz will be through the previous week’s classes.
NOTE Addition to Syllabus: I may give additional quizzes during lecture.
If I do, their scores will be added to the posted value of 1000 pts.
London Dispersion Forces:
induced dipole-induced dipole
polarizability
and
Hydrogen Bonding
5
Water provides our best model for Hydrogen Bonding.
Water is also
unusual in the
relative densities
of liquid and solid.
Hydrogen Bonding MUST involve H-F , H-O, or H-N bonds interacting
with the lone pairs of another first row atom, usually F, O, or N
Properties of Liquids:
Viscosity—the resistance to flow
oil, water, gasoline, molasses, (glass !!!)
Surface Tension – tendency to minimize the surface area
compare water, mercury
http://quest.arc.nasa.gov/space/teachers/mg/9tension.html
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/surten.html
Cohesive forces—bind similar molecules together
Adhesive forces – bind a substance to a surface
Capillary action results when these two are not equal
Soap reduces the surface tension, permitting one
material to ‘wet’ another more easily
6
Excerpt from http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/surten.html
Surface Tension Examples
Walking on water
Floating a needle
Don't touch the tent!
Rationale
for
Surface
Tension
Soaps and detergents
Clinical test for jaundice
Normal urine has a surface tension of about 66 dynes/cm but if bile is present
(a test for jaundice), it drops to about 55. In the Hay test, powdered sulfur is
sprinkled on the urine surface. It will float on normal urine, but sink if the S.T.
is lowered by the bile.
Washing with cold water vs hot water
Surface tension with soaps and/or disinfectants
Can you think of another?
See, for example: http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/surten.html
Excerpt from http://quest.arc.nasa.gov/space/teachers/mg/9tension.html
1. Make a surface tension-propelled paper
boat by cutting a small piece of paper in the
adjacent shape and floating it on clean water.
Touch a small amount of liquid soap to the
water in the hole at the back of the boat.
2. Design an experiment to test whether the
temperature of a liquid has any effect on
surface tension.
3. Try floating needles on water and observe
what happens when liquid soap is added.
See also Exercise 11.4 and the above Fig 11.18 on page 407
7
The same
picture is
useful to
rationalize
Vapor
Pressure
8
Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
See the side bar on page 412 and Figure 11.23, as well as probs. 11.88-11.90.
ln P =
ln
− ∆H vap
R
+C
∆Hvap 1 1
P2
−
=−
P1
R T2 T1
9
To access WebCT:
For help with WebCT:
The link is actually: https://webct.mps.ohio-state.edu. Do NOT forget the "s"
• Let's hope you were successful logging in. If not . . .
Click on WebCT (if this is new to you, read through the instructions below)
• What do you have on your computer? The use of WebCT requires:
1) Netscape 4.X or Internet Explorer 4.X or above. Older browsers,
and the AOL browser are incompatible with WebCT.
2) Adobe Acrobat Reader (we use PDF files) - at least version 4 free
from http://www.adobe.com/products/acrobat/readstep.html.
3) Unicomp sells CD-ROMs with above software and many plugins
for $5 contains both Mac and Windows software. 4) Netscape, plugins and other software also downloadable free from OIT
http://softwaretogo.osu.edu/
If you are having problems, first try another browser. This site runs on
Netscape Navigator, so try Microsoft Internet Explorer. Many students have
had trouble using AOL in the past so that may give you problems.
For help with your password or other Internet login difficulties --- NOT
WebCT!
Call 8-HELP for assistance 7 AM to 10 PM, Monday through Friday or
Go to http://www.oit.ohio-state.edu/ and click on Help Desk or Activate OSU
Internet Username/Change Password.
• Send a pleasant e-mail to webcthelp@mps.ohio-state.edu. Indicate
the type of problem you are having (copy the error message if you
can). Include your full name and OSU name.n ID and the course
(Chemistry 122 or 122N - Mathews). Make sure the return address
on your e-mail is correct.
Do not mention WebCT to these people as their job is only the OSU main
system.
10
11