CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
Using a digital output gyroscope such as the ADXRS450
eliminates the need for analog-to-digital conversion, reducing
system cost and real estate. The ADXRS450 communicates via
an SPI interface. The circuits that follow demonstrate how to
implement a hardware setup to enable this communication.
The ADXRS450 is a digital output gyroscope intended for use
in medical, industrial, instrumentation, stabilization, and other
high performance applications. This gyroscope is highly robust
to shock and vibration and is, therefore, an appropriate choice
for applications in harsh environments.
3.3V
3.3V
0.1µF
0.1µF
75
3.3V
3.3V
DACVDD
73
74
AVDD
AVDD DACREF
69
0.1µF
0.1µF
68
26
54
27
VREF
IOVDD
IOVDD
LVDD
5.5V
UART
1
62
2
61
3
DAC0
10
P1.0/T1/SPM0/PLAI[0]
10kΩ
3
U
0.1µF
VADJ
1
AD8034
P1.1/SPM1.PLAI[1]
2
10µF
4
20kΩ
10kΩ
VADJ
ADUC7026
6
PDD
3.3V
P1.5/SPM5/PLAI[5]/IRQ3
0.1µF
1kΩ
GND
SW2
37
SW3
20
P1.6/SPM6/PLAI[6]
RST
P2.7/PWM1L/MS3
58
16
57
5
52
15
48
MOSI
4
470µH
67
ADXRS450
8
VX
57
71
72
25
9
DIODE:
MA27728
CP5
9
1µF
2
NC
3
NC
10
NC
12
NC
CS
IOGND DGND REFGND DACGND AGND AGND IOGND ADCNEG
28
1µF
MISO
VADJ
BM/P0.0/CMPOUT/PLAI[7]/MS0
R
1kΩ
53
1
DVDD
14
AVDD
SCLK
PSS AVSS DVSS
7
11
13
D
0.1µF,
30V
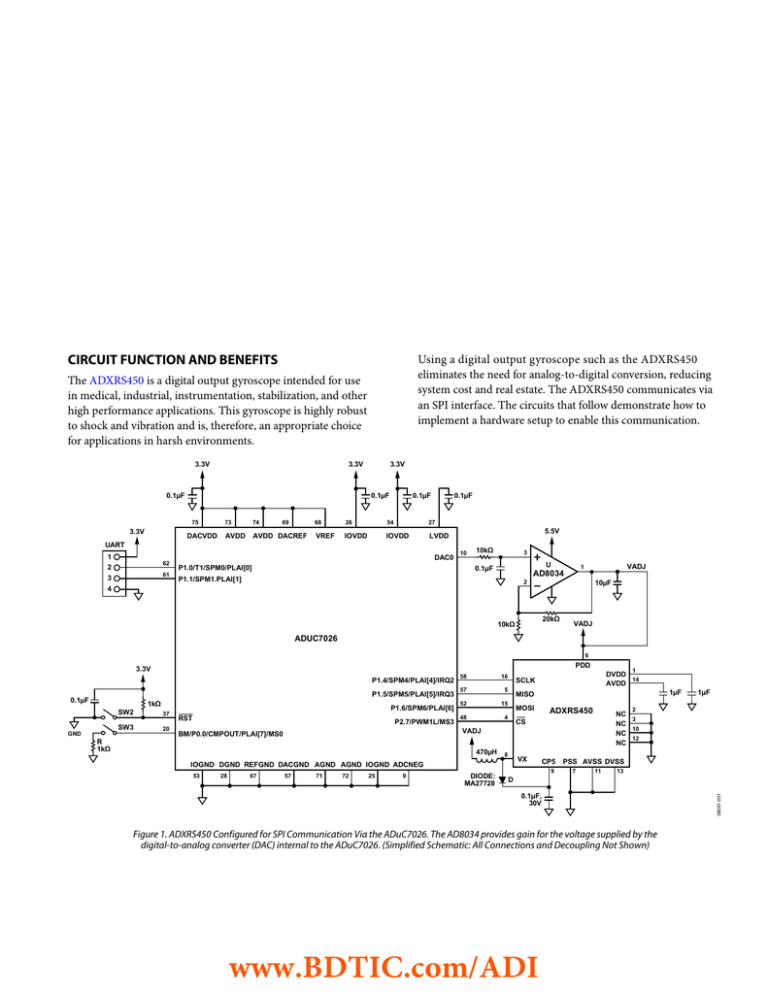
Figure 1. ADXRS450 Configured for SPI Communication Via the ADuC7026. The AD8034 provides gain for the voltage supplied by the
digital-to-analog converter (DAC) internal to the ADuC7026. (Simplified Schematic: All Connections and Decoupling Not Shown)
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
09091-001
P1.4/SPM4/PLAI[4]/IRQ2
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
doubler can be used to produce approximately 10 V from the
USB voltage. An ADP3334 regulates the 10 V down to 5.5 V
to supply the AD8034 voltage gain circuit shown in Figure 1.
The USB voltage regulation circuit is shown Figure 2.
The circuit in Figure 1 shows how to use the ADuC7026
precision analog microcontroller to communicate with
the ADXRS450. This interface can be used, for example, to
communicate with a LabVIEW™ interface. The interface sets the
supply voltage to the ADXRS450 using the digital-to-analog
converter internal to the ADuC7026. Internal ADXRS450
settings can also be set using the LabVIEW interface, and the
angular rate output can be monitored.
COMMON VARIATIONS
The configuration is shown here with an adjustable supply
voltage, but it can also be used with a static supply voltage.
A static voltage can be supplied by the DAC0 output and
amplified by the AD8034, as shown in Figure 1. Alternatively,
an existing supply rail can power the ADXRS450 directly.
This circuit can also be used in a standalone configuration
in which the microcontroller is preprogrammed to perform
certain instructions based on the angular rate output.
Instead of a UART connection to the ADuC7026, a USB connection may be desired. To achieve this, a CP2102 USB-toUART converter can be connected to Pin 62 and Pin 61, UART
Tx and Rx, respectively. The addition of a USB input to the
circuit provides a convenient supply voltage. A simplified
connection diagram is shown in Figure 3.
Representation of supply voltage generation is omitted for
schematic clarity and because it depends on the desired voltage
supplies. Assuming a USB voltage, an ADP1713 (3.3 V option)
voltage regulator can be used to produce the 3.3 V supply
for the ADuC7026. An ADM660 switched capacitor voltage
10V
R5
0Ω, 1%
U2
ADM660ARZ
USB_V+
1
2
3
4
C4
0.1µF
C5
10µF
FC
V+
CAP+
OSC
GND
LV
CAP–
OUT
5.5V
C8
10µF
C9
10µF
2
3
6
5
10V
R3
470kΩ
1%
R2
430kΩ
1%
R4
75kΩ
1%
C2
470pF
4
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
SD
GND
FB
8
7
6
5
C6
10µF
09091-002
R1
470kΩ
1%
C10
0.1µF
7
U1
ADP3334ARMZ
1
C1
10µF
8
Figure 2. Voltage Regulation from a 5 V USB Supply to 5.5 V for an ADXRS450 Adjustable Supply Voltage
(Simplified Schematic: All Connections and Decoupling Not Shown)
USB_V+
U6
CP2102-GM
7
6
3
8
TP19
J1
VDD
GND
VBUS
C19
0.1µF
VBUS
5
D–
4
D+
ID
GND
REGIN
5
C3
10µF
C18
0.1µF
C17
0.1µF
D–
D+
9
CR1
2
1
28
27
26
25
24
23
SML-210MTT86
RST
R8
12
SUSPEND
1kΩ, 1%
11
SUSPEND
RI
DCD
DTR
DSR
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
2
SIN
SOUT
1
TO ADuC P1.0 (PIN 62)
TO ADuC P1.1 (PIN 61)
TP18
GND
SHIELD
R7
0Ω, 1%
AGND CONNECTS TO DGND AT THIS
LOCATION NEAR USB CONNECTOR
DGND
AGND
09091-003
6,7,8,9
Figure 3. CP2102 USB-to-UART Converter Enables Use of a USB Interface for Supply Voltage and Programming Interface
(Simplified Schematic: All Connections and Decoupling Not Shown)
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
LEARN MORE
This circuit is used in the inertial sensor evaluation board with
an ADXRS450 satellite (EVAL-ADXRS450Z-M). For
information on ADXRS450 operation and register functions,
see the ADXRS450 data sheet.
For information on programming the ADuC7026, see the
ADuC7026 data sheet.
Data Sheets and Evaluation Boards
ADXRS450 Data Sheet
ADXRS450 Evaluation Tools
ADuC7026 Data Sheet
ADuC7026 Evaluation Tools
ADM660 Data Sheet
ADP3334 Data Sheet
AD8034 Data Sheet
REVISION HISTORY
4/11—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Figure 1........................................................................... 1
5/10—Revision 0: Initial Version
(Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may
use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patents or other intellectual property by application or use of
the "Circuits from the Lab". Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, "Circuits from the Lab" are supplied "as is" and without warranties of any
kind, express, implied, or statutory including, but not limited to, any implied warranty of merchantability, noninfringement or fitness for a particular purpose and no responsibility is assumed
by Analog Devices for their use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from their use. Analog Devices reserves the right to change any "Circuits
from the Lab" at any time without notice, but is under no obligation to do so. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
©2010-2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
CN09091-0-4/11(A)
www.BDTIC.com/ADI