LED HIGH BAY
advertisement

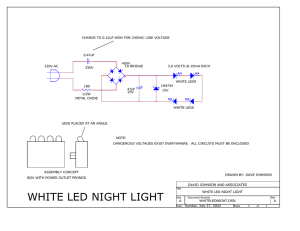
Commercial . Interior . Industrial . Emergency . Exterior ∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙ Tamlite LED Lighting Range •••••••••••••• L E D H I G H B A Y • High Power LED • High Luminous Efficiency Energy Saving Anti-Static Thermoplastic Paint Finish WHAT MAKES OUR LED HIGH BAYS UNIQUE? HEAT SINK Extruded Aluminum alloy heat sink: Large exposed contact area for maximum heat dissipation. LED’S High Power LEDs: High power LEDS produce a cool white light with high color rendering. POWER SUPPLY Constant current power supply regulates the output current against changes in line, load, ambient temperature, and time, and enables a power factor ≥90%. Scan for LED High Bay Spec. Sheet Commercial . Interior . Industrial . Emergency . Exterior ∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙ Tamlite LED Lighting Range •••••••••••••• Description Tamlite HID’s LED high bays offer rugged, long life construction with a minimal carbon footprint making them an ideal choice for energy rebates and most high bay lighting applications. The high bays have a die-cast aluminum housing and an extruded aluminum heat sink. Finish Anti-static thermoplastic spray paint for corrosion and oxidation resistance. Aluminum metal printed circuit boards are coated with an epoxy resin for protection against dust, condensation, and oxidation. Green Friendly Tamlite HID’s LED high bays are lead and mercury free. Their long performance life of up to 50,000 hours coupled with high system efficiency make this a fixture that is both maintenance and environmentally friendly. Lead.………............................. 100% Reduced Mercury…................................ 100% Reduced Energy Consumption ……...…... 62% Reduced Warranty 2 year warranty. Certification UL Listed for Dry Location LED HIGH BAY CATALOG # HBLED132W INPUT VOLTAGE 100-277 VAC FREQUENCY 50/60 Hz POWER CONSUMPTION 153W LED POWER CONSUMPTION 132W LED CURRENT 350mA COLOR TEMP. COOL WHITE LUMINOUS FLUX OPERATION TEMP. # OF LEDs 9652 lm -30°C to 50°C 126 Commercial . Interior . Industrial . Emergency . Exterior ∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙ Tamlite LED Lighting Range •••••••••••••• ABOUT LEDs LED Basics An LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a semi conductor that produces photons of light when energized by an electrical current. LEDs are made up of two semi-conductor layers, one positive and one negative, and is known as the P-N Junction. Where these two layers meet is called the “Depletion Region”. When current is applied to the LED electrons flow across the depletion region causing it to emit photons. (Figure A) Surface mounted high power LED’s are constructed of five main components, the diode or semiconductor (1), reflector cup (2), lens (3), heat sink slug (4), and the anode and cathode leads (5). The heat sink slug while integral to the LED is designed to protrude from the bottom to ensure positive contact with a larger heat sink designed to accommodate the total number of LED’s in the luminaire and conduct the heat away from the LED’s. (Figure B) LEDs are powered or driven by an electronic driver. The LED driver is used to convert the input AC line voltage to a lower DC voltage while producing a constant DC current on the output. The amount of current at the output is critical as it affects both the light output and the junction temperature of the LEDs. A constant current is also important as a fluctuating current will cause inconsistent light output. Photons Light Emitting Forward Plastic Lens (2) Semiconductor Chip (1) Depletion Region Electron Flow Figure B Thermal Management and Useful Life Heat Sink Slug (4) 70,000 60,000 Lifetime (Hours) The three main design elements critical to the performance and useful life of LED’s are junction temperature, drive current, and proper heat sinking. All three of these elements must be considered from the design stage through the installation of the luminaire to prevent adverse effects on system performance. When the junction temperature of an LED reaches its maximum, the result can be lower light output along with a color shift towards the higher end of the spectrum. A 30% to 50% decrease in its useful life can be realized for every 10ºC increase in temperature. For example, an LED being driven by 500mA of current operating in an ambient environment of 25°C (77°F) producing a junction temperature of 85°C (185°F) should realize a life expectancy of 60,000 hours. (See Fig. C) If the same LED was exposed to an ambient environment of 35°C (95°F) The result would be an increase in the junction temperature to 95°C (203°F) and the life expectancy would be reduced to 40,000 hours. Basically, as temperature increases in an LED system whether it is caused by increased drive currents or higher ambient temperatures, the result is decreased efficiency (less lumens per watt), a shortened useful life, or both. Cathode Lead (5) Reflector Cup (2) DC Power Supply Figure A 350mA 50,000 400mA 40,000 500mA 600mA 30,000 700mA 20,000 10,000 0 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 Junction Temperature (°C) Figure C Visit us @ www.tamliteusa.com Tamlite Lighting USA 660 NW Peacock Blvd, Port Saint Lucie, FL 34986 phone: 772.878.4944 fax: 772.879.2192 www.tamliteusa.com