Wieland-K55 CuNi3Si1Mg Rolled Product Datasheet
advertisement

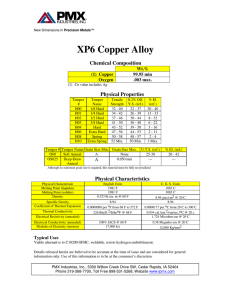
Wieland-K55® Rolled Products CuNi3Si1Mg C70250 Material Designation Chemical Composition (Reference) Typical Applications EN no EN standard Ni 3% UNS* C70250 Si 0.65 % Mg 0.15 % Cu balance · Components for the electrical industry · Stamped parts ·Connectors · Relay springs · Semiconductor components * Unified Numbering System (USA) Physical Properties* Electrical Conductivity MS/m %IACS 25 43 Thermal Conductivity W/(m·K) 190 Coefficient of Electrical Resistance** 10-3/K 1.8 Coefficient of Thermal Expansion** 10-6/K 17.6 Density 8.82 g/cm3 Modulus of Elasticity GPa Specific Heat 130 0.399 J/(g·K) Poisson’s Ratio 0.34 * Reference values at room temperature ** Between 0 and 300 °C Fabrication Properties Corrosion Resistance Capacity for Being Cold Worked good Machinability less suitable Capacity for Being Electroplated Wieland-K55® has good corrosion resistance in natural atmosphere. It is insensitive to stress corrosion cracking. good Capacity for Being Hot-Dip Tinned good Soft Soldering good Resistance Welding fair Gas Shielded Arc Welding good Laser Welding less suitable K55 Mechanical Properties R690 R760 TR02 Tensile Strength Rm MPa 620–760 620–740 34 650–780 690–800 760–840 608–725 Yield Strength Rp0.2 MPa ≥ 500 ≥ 550 Elongation A50mm % ≥ 10 ≥ 14 (180–220) (180–230)25 (200–240) Hardness HV (for information only) R620 Y550 37 El. Conductivity (MS/m) Temper R650 31 ≥ 585 ≥ 655 ≥ 720 550–650 28 ≥7 ≥5 ≥7 ≥6 (220–260) (210–250) (180–220) 22 19 R620 Y550 R650 R690 R760 TR02 Temper 37 6 34 5 31 28 25 22 19 R620 Y550 R650 R690 Temper K55 6 90° Bendability (Strip Thickness t ≤ 0.5 K55 mm) K55 R760 TR02 Rel. Bending Radius r/t El. Conductivity (MS/m) Electrical Conductivity 4 3 180° bending edge –I rolling direction bending edge II rolling direction 2 1 0 R620 Y550 R650 R690 Temper R760 TR02 Wieland-K55® CuNi3Si1Mg C70250 K55 220 220 210 210 200 200 190 190 180 170 160 Temper R620 400 °C 450 °C 500 °C 150 140 130 0 5 10 15 20 Time (min) 25 30 Vickers Hardness HV Vickers Hardness HV Resistance K55to Softening Vickers hardness after heat treatment (typical values) 180 170 160 Temper TR02 400 °C 450 °C 140 500 °C 130 0 5 10 15 20 Time (min) 150 25 30 K55 Thermal Stress Relaxation Stress remaining after thermal relaxation as a function of Larson-Miller parameter (F. R. Larson, J. Miller, Trans ASME74 (1952) 765–775) given by: P = (20 + log(t))*(T + 273)*0.001. Time t in hours, temperature T in °C. Example: P = 9 is equivalent to 1.000 h/118 °C. Measured on stress relief annealed specimens parallel to rolling direction. Total stress relaxation depends on the applied stress level. Furthermore, it is increased to some extent by cold deformation. 100 Residual Stress (%) 90 80 70 60 50 40 Temper R620, Y550, R650, R690 Temper R760, TR02 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 Larson-Miller parameter P 11.0 Fatigue Strength The fatigue strength is defined as the maximum bending stress amplitude which a material withstands for 107 load cycles under symmetrical alternate load without breaking. It is dependent on the temper tested and is about 1/3 of the tensile strength Rm. · Standard coils with outside diameters up to 1400 mm · Traverse-wound coils with drum weights up to 1.5 t · Multicoil up to 5 t Wieland-Werke AG Dimensions Available · Hot-dip tinned strip · Contour-milled strip · Sheet · Strip and sheet with protective coating www.wieland.com Graf-Arco-Str. 36, 89079 Ulm, Germany, Phone +49 731 944 2030, Fax +49 731 944 4257, info@wieland.de This printed matter is not subject to revision. No claims can be derived from it unless there is evidence of intent or gross negligence. The product characteristics are not guaranteed and do not replace our experts’ advice. · Strip thickness from 0.10 mm, thinner gauges on request · Strip width from 3 mm, however min. 10 x strip thickness 10/14 Bm (R+G) Types and Formats Available