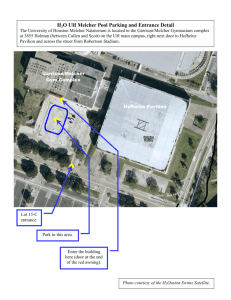
design report - University of Wisconsin
advertisement

DESIGN REPORT DIVISION OF FACILITES DEVELOPMENT 101 East Wilson Street, 7th Floor Post Office Box 7866 Madison, WI 53707-7866 Date: August 27, 2012 Project Number: 11 F3C Project Title: Dobson and Melcher Renovation University of Wisconsin - Platteville For The: University of Wisconsin System Project Manager: Beth Alderman 608-266-5886 Architect: Assemblage Architects Middleton, WI 53562 608-827-5047 Project Type: Remodeling 1. Project Description: This project will renovate Dobson Hall, a 1964 four story plus basement residence hall, (37,859 ASF /66,280 GSF) and Melcher Hall, a 1965 four story plus basement residence hall, (31,093 ASF/ 55,905 GSF). The project will shift the toilet-shower rooms in Dobson Hall to better align the building circulation and create open lounge space near the center of the floor. This design will take two resident rooms off-line in order to create ADA accessible shower space. Two lounges will then be converted into resident rooms so the bed count will not be reduces. In Dobson, the toilet-shower rooms will undergo a major renovation to the plumbing systems. The project will also replace both buildings’ mechanical systems with A/C in the basement of Dobson only. Electrical to be upgraded and the emergency power to support life safety will be provided by utilizing the existing generator at Porter Hall. Sprinkler systems are to be added to both buildings. Common spaces to be reconfigured to accommodate current program requirements, upgrade finishes throughout, and reconcile code and accessibility non-compliant conditions by replacing entrance doors and adding a new elevator in Dobson Hall; and adding a stair shaft in Melcher. The project will follow DFD sustainability standards. 2. Authorized Budget and Funding Source: The authorized budget amount is $12,179,000 (Program Revenue Supported Borrowing) The requested budget is $13,466,000 ($12,179,000 PRSB + $1,287,000 PRSB-Residual) 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Assemblage Architects Page 1 August 27, 2012 2 3. Space Summary: Dobson Hall Melcher Hall Existing ASF 41,800 34,100 Existing GSF 64,210 54,660 Added GSF 2,070 1,245 Proposed ASF 37,859 31,093 Proposed GSF 66,280 55,905 Building Efficiency 57% 55% 4. Schedule: Final Documents: Bid Opening: Start of Construction: Substantial Completion / Occupancy: November 2012 January 2013 April 2013 August 2013 5. Budget Summary: Per A/E Request & Enumeration Construction Costs: Hazardous Material Abatement: Total Construction Value Contingency: (7%) A/E Fee: Other Fees: DSF Mgmt: Total Project Cost: Constr. Cost / GSF Total Cost / GSF 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Assemblage Architects Per Program & Design $9,882,000 120,000 $10,982,000 $120,000 $9,982,000 $738,000 $800,000 $209,000 $430,000 $12,179,000 $11,102,000 $800,000 $879,000 $209,000 $476,000 $13,466,000.00 $81.98 100.03$ $91.82 $110.60 Page 2 August 27, 2012 DESIGN REPORT APPENDIX Date: August 27, 2012 Project Title: Dobson and Melcher Renovation For The: University of Wisconsin - Platteville University of Wisconsin System DIVISION OF STATE FACILITIES 101 East Wilson Street, 7th Floor Post Office Box 7866 Madison, WI 53707-7866 Project Number: 11 F3C Project Manager: Beth Alderman (608) 266-5886 Architect: Assemblage Architects Middleton, WI 53562 608 827 5047 Project Type: Remodeling Table of Contents 1. Special Design and Planning Issues A. Site Conditions……………………………………………… Page 3 B. Zoning………………………………………………………. Page 3 C. Utility Services……………………………………………… Page 3 D. Historic preservation……………………………………… Page 3 E. Environmental impact…………………………………….. Page 3 F. Other legal / regulator or unresolved issues……………. Page 3 G. Schedule Issues…………………………………………… Page 3 2. Space tabulation A. Dobson Hall……………………………………………….. Page 4 B. Melcher Hall.……………………………………………… Page 4 3. Design Concept /Basis of Design A. Overall / Architectural Design Concept…………………. B. Site Design………………………………………………… C. Architectural Systems……………………………………. D. Structural Systems……………………………………….. E. Fire Protection……………………………………………. F. Plumbing………………………………………………….. G. HVAC……………………………………………………… 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 5 Page 5 Page 5 Page 5 Page 6 Page 6 Page 9 Page 1 August 27, 2012 H. Electrical…………………………………………………… Page 15 I. Telecommunications……………………………………... Page 28 4. Energy Conservation Measures A. Sustainability Strategies…………………………………. B. DFD Sustainable Facilities Guidelines checklist……… C. Daylighting Criteria Form……………………………….. D. Building Energy Modeling………………………………. E. Renewable Energy Sources…………………………… F. Life Cycle Cost Analysis………………………………… G. Energy Conservation Measures Form………………… Page 30 Page 31 Page 43 Page 43 Page 43 Page 43 Page 48 5. Budget Detail……………………………………………………… Page 49 6. Equipment…………………………………………………………. Page 50 7. Drawings…………………………………………………………….. Page 51 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 2 August 27, 2012 1. Special Design and Planning Issues A. Site Conditions Melcher and Dobson Halls are adjacent building located in the central campus. The site offers convenient vehicular access to Dobson Hall thus making Dobson a viable candidate for a fully accessible Resident Hall within central campus. At Melcher Hall, modest re-grading at the main entrance will improve site surface drainage conditions. Topography The site is rolling and the existing sidewalk patterns will remain unchanged. B. Zoning: No zoning modification is intended. C. Utility Services New 8” water mains will replace existing connections. D. Historic preservation Not Applicable E. Environmental impact The UW Platteville has classified this as a Type 3 project requiring neither an Environmental Assessment nor an Environmental impact statement. F. Other legal / regulator or unresolved issues Two variance regarding ADA applicability will be sought from Department of Commerce. G. Schedule Issues Both building renovation will occur during the 87 days between the end of the academic year and the beginning of the following year. The following strategies are developed to accommodate the short construction schedule: • ACM Abatement will occur during winter break. • Basement selective demolition will occur during Spring break. • At the end of heating season the mechanical equipment in the basement will be demolished. • Elevator and stair shafts construction will begin in March 2013. • The projects are designed with significant casework components to allow for their advanced manufacturing. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 3 August 27, 2012 2. Space Tabulation The following space tabulation is a summary of usable and common areas. A. Dobson Hall Room type Floor level st No of Occupants Resident Rooms * 34 rooms 1 floor nd Resident Rooms * 44 rooms 2 floor rd Resident Rooms * 44 rooms 3 floor th Resident Rooms * 44 rooms 4 floor st Resident Director apartment 1 floor Custodial IT/electrical / temp Closets and rooms B-4 Lobby 1 floor Lobby Basement Meeting rooms Basement Gathering / common study Basement TV lounge Basement Multi-purpose Basement Storage Basement Kitchen Basement Laundry Basement Total Square Feet * resident room occupancy based on 2 students per room Assignable square feet Gross square feet (including addition) Efficiency Factor 68 88 88 88 4 18 15 71 63 81 146 6 7 Assignable square feet 5628 7278 7278 7278 1136 685 292 880 709 1062 945 1202 2184 682 294 326 37,859 37,859 66,280 57% B. Melcher Hall Room type Floor level No of Occupants Resident Rooms * 25 rooms 1st floor Resident Rooms * 34 rooms 2nd floor rd Resident Rooms * 34 rooms 3 floor th Resident Rooms * 34 rooms 4 floor st Resident Director apartment 1 floor Custodial IT/electrical / temp Closets B-4 Lobby 1 floor Lobby Basement Meeting rooms Basement Gathering / common study Basement TV lounge Basement Storage Basement Kitchen Basement Laundry Basement Total Square Feet * resident room occupancy based on 2 students per room Assignable square feet Gross square feet (including addition) Efficiency Factor 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects 50 68 68 68 4 14 14 43 90 57 29 8 Assignable square feet 4404 5917 5917 5917 1325 930 368 657 674 644 1342 848 1424 342 384 31,093 31,093 55,905 55% Page 4 August 27, 2012 3. Design Concept /Basis of Design A. Overall / Architectural Design Concept The project intent is to upgrade the two buildings infrastructure, accessibility and interior finishes, to improve the quality of student life. At Melcher Hall, in addition to the building’s system upgrades, the interior finishes will be updated, new stair will take will connect lounges on each floor and new curtain wall will allow greater daylight into the space. Approximately half of the basement will be renovated including a new laundry room, a small kitchen accommodating student activities, a gathering space. The existing common shower and toilet rooms on resident floors shall remain with minor modification on the first floor. At Dobson, in addition to the building’s system upgrades, the interior finishes will be updated, a new elevator will provide accessibility to the entire building thus creating a fully accessible residence’s hall in the central campus that will satisfy the accessibility of four residence halls in the area. The basement will be reconfigured to create a range of small and large spaces to support the resident’s life living and learning experiences. Dobson Hall’s aging bathrooms will also be completely reconfigured to increase the quantities and improve the quality and accessibility of the spaces. Both building’s resident director apartments will be renovated to include new kitchen, bathroom and dedicated exterior entrance to improve the apartments living quality. B. Site Design The buildings utilize existing sites. Modifications will occur at Dobson’s new entrance and elevator addition including the paved surfaces. Melcher will have site modification to address site water drainage issues. C. Architectural Systems: Both building’s exterior envelopes are in good shape and new windows have been installed recently. The exterior work is limited to the following: • • • • • The entrances will be replaces with aluminum curtain wall entrance systems. A new central stair will be added to Melcher Hall to improve egress path and convenient circulation. A new elevator will connect all floors of the Dobson Hall providing the required accessible path. New curtain wall system will improve the central lounge in Melcher Hall. Interior construction shall remain CMU at resident rooms and hallways for durability. New partitions shall be either CMU or metal stud and drywall. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 5 August 27, 2012 D. Structural Systems The existing cast in place concrete system of floor slabs, beams and columns to remain. Building additions will be masonry load bearing walls on concrete foundation system. E. Fire Protection Applicable Codes, Guidelines, and Standards The fire suppression systems will be designed in accordance with the following codes, guidelines and standards: • NFPA 13, Installation of Sprinkler Systems, latest edition • State of Wisconsin, DOA, Division of Facilities Development Technical Design Guidelines and Master Specifications The fire suppression systems will consist of: 1. 2. 3. 4. Complete wet pipe automatic sprinkler system Each floor will be a separate sprinkler zone. Quick response sprinklers will be installed throughout the building. Semi-recessed pendant sprinklers will be furnished in offices and similar spaces with ceilings. 5. Intermediate temperature rated sprinklers will be installed at the top of the elevator hoistway, and in Mechanical and Electrical rooms 6. Resident Rooms - concealed horizontal sidewall sprinklers. 7. Exposed upright, pendant or horizontal sidewall sprinklers will be furnished in all other rooms and spaces without ceilings. a. Wire sprinkler guards will be furnished in areas open to residents. 8. Flexible sprinkler connectors are allowed in areas with ceilings. 9. The piping for the wet pipe sprinkler system will be black steel. a. Unscheduled specialty steel piping is not allowed. b. CPVC piping will be allowed in concealed spaces. 10. One wall-mounted two-way fire department inlet connection in location subject to Fire Department approval. F. Plumbing Applicable Codes, Guidelines, and Standards The plumbing piping systems will be designed in accordance with the following codes, guidelines and standards: • SPS 381-387, Wisconsin Plumbing Code, latest edition • State of Wisconsin, Division of Facilities Development Technical Design Guidelines and Master Specifications. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 6 August 27, 2012 Domestic Water Distribution 1. A water meter with strainer, meter test connection, and full size bypass for the domestic water system. 2. Domestic hot and cold water will be provided to all plumbing fixtures and any other devices and equipment that require a domestic water supply. 3. Maximum pressure of 80 psi. 4. Minimum available pressure at the most hydraulically remote fixture of 35 psi. 5. The domestic hot and cold water systems will be Type L copper tube with wrought copper fittings and soldered joints. Solder will be lead-free, 95-5 type solder. a. Copper mechanical grooved fittings and couplings on roll grooved pipe may be used in lieu of soldered fittings. 6. Domestic water piping 1 ¼”and smaller may be CPVC, copper tube size. 7. Isolation valves at all riser connections, branch piping connections to fixture groups, and at each plumbing fixture. 8. The water system piping will be insulated with fiberglass pipe insulation. 9. Hot water system temperature will be maintained by re-circulation of the hot water with an in-line circulating pump(s). 10. Cold water will be distributed to: a. water closets b. urinals c. lavatories d. sinks e. electric water coolers f. hose bibs g. wall hydrants 11. Softened cold water shall be furnished to domestic water heating equipment. Sanitary Drain Waste & Vent 1. A sanitary drain waste and vent system will be provided for all plumbing fixtures, floor drains, indirect waste receptors, and equipment that require drainage. 2. Plumbing fixtures and devices will be drained by gravity through conventional drain, waste and vent stacks and building drain below the lowest floor level. 3. Every trap and trapped fixture shall be vented. 4. Below ground sanitary waste and vent piping will be cast iron pipe or PVCDWV Schedule 40 with solvent welded joints. 5. Above ground sanitary waste and vent piping will be cast-iron pipe or PVC, Schedule 40. Storm and Clearwater Waste & Vent 1. Clearwater waste from air handling units will be conveyed by gravity through a separate drain and vent piping system and will connect to the storm building drain. 2. Clearwater waste and vent piping will be cast iron pipe or type PVC-DWV Schedule 40 with solvent welded joints. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 7 August 27, 2012 Plumbing Fixtures 1. Water Closets: a. Wall hung vitreous china with manually operated dual flush valve, 1.1/1.6 gallons per flush (gpf) in all resident bathrooms and public/staff toilet rooms. 2. Urinals: a. Unisex or Family Toilet room – Stall type urinal with manually operated flush valve, 0.5 gpf 3. Lavatories: a. Wall hung china 4. Lavatory faucets: a. Faucets shall be manually operated lever handles. Flow shall be restricted to 0.5 gpm. 5. Sinks: a. 18 gauge under-mount stainless steel single compartment sinks with manually operated faucets with double lever handles. Flow will be restricted to 1.6 gpm maximum. b. Interior grease interceptors will be provided to serve basement kitchen sinks. 6. Electric Water Coolers: a. Two station electric water coolers with bottle filling stations and inlet water filter. 7. Shower Valve: a. Pressure balancing shower valve with fixed shower head for nonADA showers and fixed shower head and hand shower with 24” glide bar and 72” long hose at all ADA showers. b. Shower heads shall be flow restricted to 2.0 gpm 8. Bath Tubs: a. Modular acrylic tub/shower units. b. Pressure balancing shower valve with fixed shower head for nonADA showers and fixed shower head and hand shower with 24” glide bar and 72” long hose at all ADA showers. c. Shower heads shall be flow restricted to 2.0 gpm 9. Floor Drains: a. One floor drain per bathroom. b. Two floor drains per common bath area. 10. Mop Basins: a. 32” x 32” terrazzo mop service basins with 6” high rim. Faucet with hose connection vacuum breaker and lever handles. One fixture per floor. 11. Laundry: a. Plumbing connections including cold/hot water supplies and waste standpipe receptors shall be provided for automatic clothes washers. 12. Self-draining frost resistant wall hydrants with ¾” hose connections will be provided along the building perimeter in the same locations as the existing. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 8 August 27, 2012 Plumbing Equipment and Specialties 1. New duplex water softeners will be provided to soften hot water. 2. Campus steam will be used for domestic water heating. Water heaters shall have new double walled heat exchanger to replace existing single wall heat exchanger. A hot water storage tank with electric heating elements for use during annual steam system shut-down at 50% of normal load will be furnished. 3. Hot water return circulating pumps will provide positive circulation within the domestic hot water piping system. 4. Reduced pressure principle backflow preventers will be furnished in the make-up water lines to all mechanical equipment not furnished with an integral air gap on the water inlet to the equipment. 5. A clearwater sump pump will be installed in a sump basin at the bottom of the elevator hoistway. G. HVAC Applicable Codes, Guidelines, and Standards Design and construction codes and standards are listed below. The codes and standards listed are minimum requirements. Nothing is to prevent the design team from exceeding the applicable requirements. ASHRAE 62.1 Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor air Quality IBC 2009 International Building Code–as adopted by the State of Wisconsin IECC 2009 International Energy Conservation Code–as adopted by the State of Wisconsin IMC 2009 International Mechanical Code–as adopted by the State of Wisconsin UL Underwriters Laboratories Division of Facilities Development Master HVAC Specifications Division of Facilities Development HVAC Systems Standards & Design Guidelines University of Wisconsin-Platteville Design Standards Summary of Mechanical System In general, the Mechanical system goals for this project are environmental comfort and quality, energy conservation, and sustainability. All proposed HVAC systems will be designed in accordance with DFD Standards. Design Criteria 1. Outdoor Design Conditions a. Summer: 87 F db / 75 F wb b. Winter: -15 F 2. Indoor Design Conditions a. Summer: 76 F db b. Winter: 68 F db 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 9 August 27, 2012 3. Relative Humidity a. Summer: 50% +- 10% b. Winter: No humidification 4. Heated Only Spaces a. The following spaces will be heated only: b. All Resident Rooms c. Janitor Rooms d. Toilet Rooms e. Mechanical and Electrical Rooms f. Storage Rooms g. Staircases h. Vestibules 5. Air Conditioned Spaces a. Telecommunication rooms that get remodeled 1. Use a DX split system for each room b. Dobson basement c. Apartment Unit on 1st floor of Dobson 1. Use a through-wall unit(s) d. Apartment Unit on 1st floor of Melcher 1. Use a through-wall unit(s) e. Dobson and Melcher resident rooms will not be air conditioned. 6. No provisions are being made for future expansion of these buildings or expansion of the mechanical systems. Chilled Water Systems No chilled water systems will be used. Steam and Condensate Systems 1. High pressure steam from the campus power plant will be utilized for building heat. The existing steam and condensate service will remain. The pressure reducing stations in the mechanical rooms of Dobson and Melcher will be replaced, the steam pressure will distribute at a nominal 10 PSIG for use in the building for domestic water heating and building hot water heating. All steam piping will be contained within the MER. 2. Condensate will be collected into a single condensate receiver located in the basement mechanical room. The condensate receiver will be equipped with duplex pumps to pump condensate back to the central plant. 3. Condensate flow back to the plant will be metered as it leaves the building. 4. The high pressure steam piping will be sized for a maximum velocity of 12,000 fpm and a maximum pressure drop of 2 psi per 100 feet of piping. 5. The low pressure steam piping will be sized for a maximum velocity of 8,000 fpm and a maximum pressure drop of 0.5 psi per 100 feet of piping. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 10 August 27, 2012 Hot Water Heating Systems 1. Steam-to-hot water shell and tube heat exchangers will use low pressure steam to generate building heating water. 2. The hot water will be distributed with a variable volume pumping system. Two circulating pumps (one being 100% standby) will distribute hot water to air handling unit coils, reheat coils, unit ventilators, convectors, finned tube radiation, and cabinet unit heaters. Hot water temperature will be reset based on outside air temperature. The hot water heating pumps will not be on the emergency power system. 3. The hot water heating system will utilize a pot feeder and bag filter piped in a bypass arrangement around pumps. 4. The hot water piping will be sized for a maximum velocity of 8 fps and a maximum pressure drop of 3 feet w.c. per 100 feet of pipe. 5. The horizontal mains in the Basement, the hot water equipment in the basement (cabinet heaters, unit ventilators, convectors, finned tube), the zone pumps and the steam-to-hot water heat exchangers will all be removed and replaced with new equipment. 6. The convectors in each resident room, the cabinet unit heaters in the stairs, the convector/unit ventilators/finned tube in First through Fourth floor will be removed and replaced with new. 7. Existing hot water piping and insulation to be completely replaced in Dobson, including risers. 8. Existing hot water risers up through 1-4 floors for Melcher to remain. Patching of insulation will be required on risers, where asbestos abatement occurs. Ventilation Design Criteria 1. Ventilation air for the resident rooms will be provided by operable windows. 2. Ductwork will be designed for proper mixing of outdoor air and return air so that stratification does not occur before the air handling unit heating coils. 3. The outdoor and relief air distribution systems will be sized to utilize a full economizer (free cooling) mode of operation when outdoor air conditions permit. 4. Outside air plenums with drains in the bottom will be provided in an effort to prevent snow being entrained in the air handling unit on indoor units. 5. Outside air louvers will be sized at a maximum velocity of 500 fpm of the net free area. Units having a high percentage of outside air will be designed with lower velocities. 6. Minimum outside air requirements will meet or exceed the requirements of the Wisconsin Administrative Code, Chapter 64 and the ventilation rates of the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) Standard 62.1 - 2007. 7. Verification of the minimum outside air quantities in variable volume systems will be accomplished through the use of airflow measuring stations located in the outside air intake ductwork. 8. Air flow measuring stations will also be provided in the supply and return air systems of VAV systems to maintain the building at a slight positive pressure at all times. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 11 August 27, 2012 Central Air Handling Systems 1. Melcher indoor air handling unit will be a modular packaged unit installed in the mechanical room. The HVAC equipment in the mechanical room will be designed to provide full access for filter replacement, coil replacement, fan shaft removal and any other equipment maintenance and replacement procedures. 2. The unit will contain a hot water coil section, access sections, filter section, supply fan. 3. Dobson air handling unit will be roof mounted, with energy recovery and DX cooling with a condensing unit of approximately 40 tons. 4. The unit will contain a DX coil section, filter section, supply fan, energy recovery wheel, exhaust fan and hot water heating coil section. 5. The supply ductwork will run on the roof of Dobson to each of the three wings. The supply duct will serve to makeup air to the core toilet rooms and basement multipurpose rooms. The return and exhaust ducts will rise through the core of the building to the roof ERV unit. 6. Air handling units will be provided with 2” pre filters and 65% bag filters. 7. The following summarizes the anticipated air handling systems: AHU Tag AHU-D1 Service Dobson Roof System Type Variable Volume with reheat coils Cooling Yes AHU-M1 Melcher Basement Single Zone Heating Only No Energy Recovery 1. The use of energy recovery will be on the roofs of Dobson and Melcher Halls. One recovery unit is anticipated to serve as make-up air to AHU-D1 on Dobson for the core toilet room exhaust and basement. Two energy recovery units are anticipated on the roof of Melcher to serve each of the two core toilet room exhausts. Ventilation air will be supplied from the roof down through the core of the buildings on Melcher. 2. Exhaust from core toilet rooms will be used with a heat wheel type recovery unit. 3. The following summarizes the anticipated Energy Recovery Units: ERV Tag ERV-M1 ERV-M2 ERV-D1 Service Melcher Make-up Floors 1-4 Melcher Make-up Floors 1-4 Dobson Makeup to AHU-D1 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects System Type Heat Wheel Heat Wheel Heat Wheel Page 12 August 27, 2012 Air Distribution 1. The Dobson air distribution system will be as indicated in the air handling description. Dobson basement is single zone variable volume on the west and east wings and a multiple zoned variable air volume system with variable volume air terminal units with hot water reheat coils on the south wing. The hallway wings of Dobson will be served by constant volume boxes with hot water reheat coils. 2. The proposed air distribution systems in the east basement of Melcher are existing to remain unit ventilators with new DDC controls. 3. Unit ventilators at the core of Melcher on floors 2-4 will be replaced with new equipment and new controls. 4. The supply, return, and exhaust air systems will be distributed using a fully ducted system constructed of sheet metal per SMACNA standards. 5. Duct Insulation a. Supply air ductwork systems will be externally insulated. No duct lining will be used in the supply air stream, except for the first 5’ downstream of VAV boxes. Concealed ductwork will have flexible fiberglass insulation. Exposed ductwork will be insulated with rigid fiberglass insulation. Exposed ductwork serving the conditioned space may be installed without insulation. b. Fiberglass insulation will be pinned in place on sides and bottom when the ductwork exceeds 24” wide. c. The return and exhaust air ductwork system will be internally lined were necessary for acoustics only. The duct liner will be mat-faced type 1” thick. d. All transfer ducts located in sensitive areas will be lined for acoustics. 6. Grilles and diffusers will typically be selected with noise criterion rating of NC 25 or less. 7. The ductwork will typically be sized as follows: a. Mains (within masonry chases) - Max velocity of 1800 fpm and pressure drop of 0.10 inch w.c. per 100 feet of duct b. Mains & branches - Max velocity of 1500 fpm and pressure drop of 0.10 inch w.c. per 100 feet of duct c. Runouts - Max velocity of 800 fpm and a pressure drop of 0.08 inch w.c. per 100 feet of duct Building Exhaust 1. Roof mounted exhaust fans with isolation dampers will be the primary style used, where energy recovery is not implemented. 2. The Laundry Room dryer make-up air will be brought in through a make-up air system with a filter mixing box, pumped heating coil and supply fan. The make-up air system will be controlled to maintain a slight negative pressure in the Laundry Room in relation to the adjacent spaces. 3. The Laundry Room dryer exhaust will be a manifolded exhaust system with a dryer exhaust booster fan. The dryers will be electric and be required to be high static pressure models. The Laundry Room will also be provided with general exhaust connected to the building central exhaust system. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 13 August 27, 2012 Terminal Heating Devices 1. The resident rooms will all be provided with new hot water convectors, each having individual temperature control. 2. Finned tube radiation will be provided in all spaces in the basement having an exterior exposure for added comfort and to provide unoccupied heating of the building for shutdown of central air handlers when unoccupied. 3. Convectors or wall fin will be provided in all remaining rooms having exterior exposure. 4. Each thermostatic zone will take into consideration exposure, occupancy schedule, and space use. 5. Cabinet unit heaters will be installed in entry vestibules and at doors leading to the outdoors. Cabinet unit heaters will be hot water type with wall-mounted thermostat and be recessed wall or ceiling type whenever possible. Temperature Controls 1. This building will be integrated into the existing campus building automation system. 2. The resident room convectors will be individually controlled by communicating thermostats. Thermostats will be located at the corridor side of the room, nearest the closets. 3. Direct digital controls with electric actuation will be used to control the air handling units, booster coils, VAV boxes, and wall fin. 4. All cabinet unit heaters and unit heaters are to have electronic DDC control. 5. All control valves and dampers are to have electric actuation. 6. Air handling units will be provided with economizer controls. 7. A minimum of 8 hours of temperature control training will be specified. Testing, Adjusting and Balancing 1. The building will be tested and balanced in accordance with AABC or NEBB Standards. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 14 August 27, 2012 H. Electrical Dobson Hall Distribution – Normal Power 1. Medium Voltage Power Distribution a. The incoming electrical service is provided from the campus owned 12,470 volt primary power distribution system. A 15kV – Type MV-90, #4/0 feeder is routed via underground duct bank from pad mount switchgear SG-9 along Greenwood Ave into the Dobson Hall basement Transformer Room 38. Currently the west end of campus along Glenview Ave. is feed from a single circuit. The UW Platteville master plan outlines the future addition of sectionalizing switches with a second circuit to create a loop feed to this end of campus. Work associated with the master plan and campus medium voltage distribution is not part of this project. Modifications to the 15kV feeder serving Dobson Hall are not anticipated. b. The existing 150kVA unit substation is not of sufficient size to accommodate the increased electrical demand and will be replaced. The new unit substation, located within the existing Transformer Room 38, will consist of three sections: one 15kV fused interrupter switch section, one 225kVA - 12,470 to 208y/120 volt dry-type transformer section and one 800A-3P secondary main circuit breaker with digital metering section. The main breaker will be 100% rated, insulated case, solid state electronic type with adjustable trip settings. The existing 12,470 volt feeder will be terminated on the new equipment. c. Removal of the existing unit substation and installation of new equipment will create a sustained power outage. Temporary provisions will need to be arranged which include a 100A-208y/120V, 3 Phase feeder from Porter Hall MDP. d. Transformer Room 38 has an existing perimeter ground bus which will remain. The bussing will be modified to accommodate a new service door into the transformer room. e. Historical Peak Demand – 104kW February 2012 2. Low Voltage Power Distribution a. A main-lug main distribution panel, MDP, will be dead front construction and wall mounted within the existing Electrical Room 36. Low voltage distribution panels will have copper bus and shall utilize thermal magnetic, molded case circuit breakers for feeders up to 200 amps. Feeders 200 amps and larger shall utilize plug-on molded case, electronic trip type with adjustable settings. b. Feeders shall be copper or aluminum, provided the aluminum feeders are compliant with DFD specifications. All feeders will be installed in conduit. c. Two normal feeders will be extended from MDP to the normal side of the emergency transfer switches: • Emergency Loads – NEC 700 • Legally Required Standby NEC 701 & Optional Standby Loads NEC 702 d. Branch circuit panelboards shall be of dead front construction, copper bussing and shall utilize bolt-on molded case circuit breakers. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 15 August 27, 2012 Panelboards shall have space for 42, 54 or 84 single pole branch breakers. Panelboards will be main-lug type unless UW Platteville specifically requests main breakers for panelboards not located within the same room as their feeder breakers. If such a request is made, the addition of a main molded case switch device will be recommended in lieu of a main circuit breaker. e. Per DFD guidelines, branch circuits serving residence hall rooms shall be protected by an arc-fault circuit interrupter type breaker. f. Where existing panelboards are removed in masonry walls, the outer tub will remain as a splice/pull box for connection to existing branch circuits and associated raceways. A stainless steel cover plate will be fastened to the existing tub with tamper proof screws. g. Surge protection device will be installed on the load side of MDP and Surge arrestors on the primary side of the 12,470 volt transformer. h. Raceways for feeders and branch circuits shall be metallic rigid metal conduit, intermediate metal conduit or electrical metallic tubing. Minimum conduit size shall be ½” i. Raceways installed in or below concrete will be PVC. Minimum conduit size shall be 1”. 3. Motor Starters a. Manual motor starters shall be provided for motors ½ horsepower at 120volts. Run-Stop control relays will be coordinated with Div 23. b. Combination full voltage, non-reversing, magnetic type starter and circuit breaker disconnect switches shall be used for all single phase and three phase motors ½ horsepower and larger where variable frequency drive starters are not used. Overloads will be solid state type. c. Variable frequency drive starters shall be provided as part of mechanical equipment or furnished by Division 23. 4. Distribution System Modifications a. Basement: • Panelboards E, M, N and L will be replaced. • New Panelboard E will be branch circuit fusible type to aid in selective coordination of life safety distribution system. • A new panelboard “BB” will be added to supply east wing, west wing, kitchen and toilet room core areas. • A new load center type panelboard will be added to the Telecom closet to supply all closet related loads. b. First Floor: • Panelboards K, J, H & F will be demolished. • A new panelboard with shared feeder from MDP will be provided to supply resident rooms, toilet core and common areas. • A new load center type panelboard with dedicated feeder will be added to the resident director suite. c. Second, Third & Fourth Floors: • Panelboards A, B & D will be demolished. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 16 August 27, 2012 • A new panelboard with shared feeder from MDP will be provided to supply resident rooms, toilet core and common areas. 5. Short Circuit, Coordination Study and Arc Flash Assessment a. The specification will be written that require the electrical contractor to provide the report for approval by the engineer. Distribution – Emergency Power 1. Generator a. The existing 60kW generator near Porter Hall will supply emergency power. The existing genset does not have provisions for a separate feeder to Dobson. A new exterior tap cabinet will be wall mounted near the generator. The 100A feeder from the generator will be routed into the tap cabinet and tapped to supply Porter, Dobson and a future Morrow Hall. b. An underground 100A feeder will be routed from the genset location to Dobson Hall basement. Said feeder will be tapped within Electric Room 36 with fusible overcurrent protection and routed into NEC 700 and NEC 701/702 automatic transfer switches. c. In addition to the feeder routing, a 1” conduit will be extended from Dobson ATS to genset for start/stop signal wiring. 2. Transfer Equipment a. Two automatic transfer switches. ATS/E for Code required emergency loads (NEC 700) and ATS/X for legally required/optional standby loads (NEC 701 & NEC 702). b. Individual feeders from each ATS will be extended to dedicated distribution panelboards. All generator power will be distributed from Electrical Room 36. No additional panelboards will be located throughout the building. c. With exception of the generator, all emergency electrical system equipment will be located in the same room as the normal power distribution equipment. d. The existing 3-pole transfer switch within Porter Hall will be replaced with a new 4-pole ATS. Switching of the neutral conductor is required to allow isolation between the normal power systems of Dobson and Porter. The removed ATS will be turned over to UW Platteville. e. A grounding system electrode (ground rod) will be installed at the existing generator. The grounding electrode conductor will be bonded to the neutral conductor with system bonding jumper to create a separately derived system. 3. Generator Loads a. List of preliminary NEC 700 emergency loads connected to ATS/E: • Code required egress and exit lighting • Elevator car lighting • Fire alarm system • Access Control at egress doors 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 17 August 27, 2012 b. List of preliminary NEC 701 Legally Required Standby and NEC 702 Optional Standby connected to ATS/X • Passenger elevator – Traction type, 15HP or less. • Elevator machine room ventilation • Elevator pit sump pump. Lighting And Lighting Controls 1. Interior Lighting a. All lighting shall comply with the State of Wisconsin design guidelines and UW Platteville campus standards. b. All illumination levels will conform to the State of Wisconsin design guidelines and the Illuminating Engineering Society’s recommendations. Lighting levels indicated are average, maintained foot-candles. c. Illumination Levels shall be as follows: • Offices, Main Desk – 30 FC with multi-level control to 10 FC • Conference, Multi-Purpose & Meeting Rooms – 30 FC with multilevel control to 10 FC • Lounge – 10 to 20 FC • Kitchens – 50 FC • Restrooms – 20 FC • Main Lobby – 20 to 30 FC • General Circulation areas & Corridors – 10 FC • Electrical, Mechanical & Telecomm Rooms – 30 FC • Laundry – 30 FC • Storage – 15 FC d. Interior lighting, in general, will utilize compact fluorescent, LED and long life linear T8 fluorescent lamps, 3100 lumens per lamp and 4100K color temperature. Color temperature to be confirmed with campus staff. e. Renovation to existing lighting within the resident rooms is not part of this project. The wall mounted fluorescent luminaires will remain along with their associated controls. The decision to not replace the luminaires is based upon cost savings. Monies are being deferred to the Toilet Room renovation. 2. Exterior Lighting a. Building mounted luminaires will be added to the west entry. b. Existing exterior luminaires will be evaluated for replacement and connected to the emergency generator. 3. Lighting Controls a. Lighting in offices, multi-occupant rooms, restrooms, corridors, laundry, storage and similar spaces will be controlled by occupancy sensors in conjunction with manual wall switches. b. Lighting in mechanical, electrical and telecomm rooms will be control with a wall box timer. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 18 August 27, 2012 c. Lighting within daylight areas will have separate manual control in conjunction with indoor photo sensors to reduce electric light use when sufficient natural light is available. d. Emergency power, UL924 relay devices will be provided in restrooms to allow for switching of emergency egress lighting with normal lighting controls. e. At least one fixture in the elevator lobby will remain on at all times to provide 10 FC at the elevator threshold. f. Exterior lighting circuits will be routed through a mechanically latching contactor with provisions for control from UW Platteville campus DDC system. g. Renovation to existing lighting controls within the resident rooms is not part of this project. 4. Wiring Devices 1. General Purpose Receptacles a. Receptacles shall be 20 amp heavy-duty specification grade. b. All receptacles installed in restrooms, building exterior and near sinks shall be GFCI type. c. General purpose receptacle circuits shall have an average of 6 and a maximum of 10 duplex receptacles on a 120V, 20A circuit. d. Receptacles serving electronic equipment such as computers shall have no more than 4 duplex receptacles per 120V, 20A circuit. e. One additional 120V, 20A branch circuit will be provided to each resident room. New branch circuit wiring will be routed down corridor and connect to an existing, flush mounted, ceiling junction box located in the resident room closet. A junction box extension ring will be installed on the existing flush device to allow surface conduit entry from corridor. The four existing receptacle locations within the resident room will have their branch circuit conductors reconfigured such that each half of the resident room is on a dedicated circuit; two receptacle locations per circuit. f. One additional duplex receptacle for air conditioning will be added to the window wall. The new device will be circuited to one of the resident room circuits, not a dedicated circuit. The device will be surface mounted with the used of nonmetallic wireway (Wiremold or similar). g. Replacement to existing receptacles within the resident rooms is not part of this project. 5. Fire Alarm System 1. Control Panels a. The fire alarm system is an existing EST3 multiplexed addressable fire alarm system and no changes to the main control panel are anticipated. 2. Notification and Initiation Devices a. Manual pull stations will be provided at each floor exit and spaced such that travel to any station is less than 200 feet. b. Smoke detectors shall be located in corridors, electrical rooms, storage rooms and other locations required by DFD Design Guidelines. Corridor spacing will be 30 feet on-center 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 19 August 27, 2012 c. Duct smoke detectors will be installed at each air handler and furnished with remote test stations. d. Heat detectors shall be located in mechanical rooms and as required by DFD Design Guidelines. e. Elevator machine rooms, elevator lobbies and elevator shafts shall have smoke detectors installed. Elevator machine rooms and elevator shafts shall also have heat detectors installed. f. Required interface modules will be provided to monitor fire protection system, elevator recall and similar systems. g. Audible and Visual notification devices will be installed in public spaces as required by code. h. Self-contained, non-addressable 120V smoke alarms are existing within resident rooms and their replacement is not part of this project. i. Audible notification devices are existing within resident rooms and their replacement is not part of this project. 6. AV Rough In 1. Conduit and Back Boxes a. Standard electrical boxes and raceway will be used to rough in for AV cabling. Any special boxes will be provided by the AV contractor/installer. Empty conduit will be provided with pull string. b. AV equipment, cabling, terminations and design are not part of the division 26 scope of work. 7. Building Automation System Interface 1. Electric meters installed in electrical distribution equipment shall be provided with Communications ports to allow monitoring from the BAS data bus. 2. Exterior lighting control contactors shall interface to the BAS so that exterior building and site lighting is controlled along with all other campus lighting. 8. Design Criteria 1. Applicable Codes, Guidelines, and Standards a. Design and construction codes and standards are listed below. b. The codes and standards listed are minimum requirements. Nothing is to prevent the architect, engineer, or consultant from exceeding the applicable requirements. In the case of laboratory related research buildings, the recommendations of the guidelines below and the standards and requirements suggested by the design team will often address issues not sufficiently covered in local building codes. c. In all cases the most recent editions of referenced standards apply. IEEE IESNA NECA NEMA UL NFPA 70 NFPA 72 Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Illuminating Engineering Society of North America National Electrical Contractors Association National Electrical Manufactures Association Underwriters Laboratories 2011 National Electric Code National Fire Alarm code 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 20 August 27, 2012 NFPA 101 Life Safety Code NFPA 110 Standard for Emergency and Standby Power Systems Wisconsin Enrolled Commercial Building Code DFD Master Specifications DFD Electrical Systems Standards & Design Guidelines DFD Policy and Procedures Manuals for A/Es DFD Day Lighting Standards for State Facilities University of Wisconsin-Platteville Design Standards 2. Basic Design criteria a. Load Calculation Criteria: Functional Area Lighting Office Receptacles HVAC Load Density (VA/Sq. Ft) 1.0 1.5 3.0 b. Secondary Design Voltages: Motors larger than ½ HP General Lighting Receptacles & motors less than 1/2 HP 208V, 3 phase, 3 wire + ground 120V, 1 phase, 2 wire + ground 120V, 1 phase, 2 wire + ground c. Equipment Sizing Criteria (Preliminary estimate): Branch Circuit Load Calculations: Lighting Actual installed VA Receptacles 180VA per outlet Special Outlets Actual installed VA of equipment Motors 125% of motor VA Demand Factors: Lighting Receptacles Motors Fixed Equipment 125% of installed VA 100% of first 10Kva installed plus 50% of balance 125% of VA of largest motor plus 100% of VA of all other motors 100% of total VA installed Minimum Bus Sizes: 280Y/120V Panels 100 Amps Diversity Factor: A diversity factor shall be used per the 2003 Wisconsin Electrical Code (Comm. 16.2392), in establishing power service, feeders, and equipment capacities. Spare Capacity: 25% spare capacity to accommodate function changes over the life of the building shall be included in the design of the power distribution system. Power distribution equipment shall be sized to reserve 20% space for physical expansion. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 21 August 27, 2012 9. Scope Exclusions a. The following list represents specification and design of building components which are not part of Henneman Engineering’s scope of work. • Lightning protection • Building clock system • AV systems • Area of rescue assistance Melcher Hall Distribution – Normal Power 1. Electrical Service a. The incoming 208y/120 volt, 3 phase, 4 wire electrical service is provided from adjacent Porter Hall. A 600A-3P circuit breaker is installed within Porter Hall’s main distribution panel. Modifications to the underground service feeder or the feeder breaker are not anticipated. b. The 600A-3P Melcher Hall feeder breaker and 1200A-3P main breaker installed within the Porter Hall MDP should be evaluated for coordination. While coordination is not required by code, it is good design practice to reduce the ability for a fault in Melcher to open the 1200A main prior to opening the 600A feeder breaker. c. Historical Peak Demand – 71kW November 2011 2. Low Voltage Power Distribution a. A new main-breaker, main distribution panel, MDP, will be dead front construction and wall mounted within the existing Electrical Room 29. Low voltage distribution panels will have copper bus and shall utilize thermal magnetic, molded case circuit breakers for feeders up to 200 amps. Feeders 200 amps and larger shall utilize plug-on molded case, electronic trip type with adjustable settings. b. Feeders shall be copper or aluminum, provided the aluminum feeders are compliant with DFD specifications. All feeders will be installed in conduit. c. Branch circuit panelboards shall be of dead front construction, copper bussing and shall utilize bolt-on molded case circuit breakers. Panelboards shall have space for 42, 54 or 84 single pole branch breakers. Panelboards will be main-lug type unless UW Platteville specifically requests main breakers for panelboards not located within the same room as their feeder breakers. If such a request is made, the addition of a main molded case switch device will be recommended in lieu of a main circuit breaker. d. Where existing panelboards are removed in masonry walls, the outer tub will remain as a splice/pull box for connection to existing branch circuits and associated raceways. A stainless steel cover plate will be fastened to the existing tub with tamper proof screws. e. Per DFD guidelines, branch circuits serving residence hall rooms shall be protected by an arc-fault circuit interrupter type breaker. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 22 August 27, 2012 3. Motor Starters a. Manual motor starters shall be provided for motors ½ horsepower at 120volts. b. Combination full voltage, non-reversing, magnetic type starter and circuit breaker disconnect switches shall be used for all single phase and three phase motors ½ horsepower and larger where variable frequency drive starters are not used. Solid-state overloads will be specified. c. Variable frequency drive starters shall be provided as part of mechanical equipment or furnished by Division 23. 4. Distribution System Modifications a. Basement: • Panelboards EA, G & F will be replaced with new panelboards in the existing location. • New Panelboard EA will be branch circuit fusible type to aid in selective coordination of life safety distribution system. • A new panelboard L will be added to supply the laundry room loads. • A new panelboard M will be added to supply mechanical room loads. b. First Floor: • Panelboards C & D will be demolished with tubs to remain as pull/splice boxes. • A new panelboard will be added in the east recycling room to supply branch circuits to east wing resident rooms. Panelboard “#A” will be provided with sub-feed lugs and share a common feeder from MDP. • A new panelboard will be added in the west recycling room to supply branch circuits to west wing resident rooms. Panelboard “#B” will be provided with sub-feed lugs and share a common feeder from MDP. c. d. Second, Third & Fourth Floors: • Panelboards A & B will be demolished with tubs to remain as pull/splice boxes. • A new panelboard will be added in the east recycling room to supply branch circuits to east wing resident rooms. Panelboard “#A” will be provided with sub-feed lugs and share a common feeder from MDP. • A new panelboard will be added in the west recycling room to supply branch circuits to west wing resident rooms. Panelboard “#B” will be provided with sub-feed lugs and share a common feeder from MDP. Short Circuit, Coordination Study and Arc Flash Assessment • The specification will be written that require the electrical contractor to provide the report for approval by the engineer. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 23 August 27, 2012 Distribution – Emergency Power 1. Service a. 208y/120V, 3 phase, 4 wire emergency power is provided from panelboard E in Porter Hall. A 70A-3P breaker is installed within Porter Hall’s panelboard E. Modifications to the underground service feeder or the feeder breaker is not anticipated. b. The intent of panelboard E (Porter) and EA (Melcher) is to provide generator power to emergency loads, NEC 700. At present, both emergency and optional standby loads are connected to the panelboards. Any non-emergency loads in Melcher Hall will be removed from panelboard EA. No provisions are being made to supply generator power to optional standby loads and therefore those circuits which are removed from panelboard EA will be re-circuited to the nearest normal power branch circuit panelboard. c. It is unlikely that the 20A-1P branch breaker installed in panelboard EA will coordinate with the upstream 50A-3P MCB in panelboard EA, the 70A3P feeder breaker in panelboard E and the 100A-3P circuit breaker installed within the Porter Hall Generator. The generator breaker type requires further investigation and fusible panelboards may be explored to achieve coordination. There appears to be a condition where a branch circuit fault in Melcher could open the generator MCB and de-energize emergency power to both Porter, Melcher, Dobson and future Morrow Halls. d. Panelboard EA serving emergency loads will remain installed within the same room as the normal power distribution equipment. 2. Generator Loads a. List of preliminary NEC 700 emergency loads connected to Panelboard EA: • Code required egress and exit lighting • Fire alarm system • Access Control at egress doors Lighting And Lighting Controls 1. Interior Lighting a. All lighting shall comply with the State of Wisconsin design guidelines and UW Platteville campus standards. b. All illumination levels will conform to the State of Wisconsin design guidelines and the Illuminating Engineering Society’s recommendations. Lighting levels indicated are average, maintained foot-candles. c. Illumination Levels shall be as follows: • Offices, Main Desk – 30 FC with multi-level control to 10 FC • Conference, Multi-Purpose & Meeting Rooms – 30 FC with multi-level control to 10 FC • Lounge – 10 to 20 FC • Kitchens – 50 FC • Restrooms – 20 FC • Main Lobby – 20 to 30 FC 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 24 August 27, 2012 • • • • General Circulation areas & Corridors – 10 FC Electrical, Mechanical & Telecomm Rooms – 30 FC Laundry – 30 FC Storage – 15 FC e. Interior lighting, in general, will utilize compact fluorescent, LED and long life linear T8 fluorescent lamps, 3100 lumens per lamp and 4100K color temperature. Color temperature to be confirmed with campus staff. f. Renovation to existing lighting within the resident rooms is not part of this project. The wall mounted fluorescent luminaires will remain along with their associated controls. The decision to not replace the luminaires is based upon cost savings. Monies are being deferred to the Dobson Hall Toilet Room renovation. 2. Exterior Lighting a. Existing exterior luminaires will be evaluated for replacement and connected to the emergency generator. 3. Lighting Controls a. Lighting in offices, multi-occupant rooms, restrooms, corridors, laundry, storage and similar spaces will be controlled by occupancy sensors in conjunction with manual wall switches. b. Lighting in mechanical, electrical and telecomm rooms will be control with a wall box timer. c. Lighting within daylight areas will have separate manual control in conjunction with indoor photo sensors to reduce electric light use when sufficient natural light is available. d. Emergency power, UL924 relay devices will be provided in restrooms to allow for switching of emergency egress lighting with normal lighting controls. e. Exterior lighting circuits will be routed through a mechanically latching contactor with provisions for control from UW Platteville campus DDC system. f. Renovation to existing lighting controls within the resident rooms is not part of this project. Wiring Devices 1. General Purpose Receptacles a. Receptacles shall be 20 amp heavy-duty specification grade. b. All receptacles installed in restrooms, building exterior and near sinks shall be GFCI type. c. General purpose receptacle circuits shall have an average of 6 and a maximum of 10 duplex receptacles on a 120V, 20A circuit. d. Receptacles serving electronic equipment such as computers shall have no more than 4 duplex receptacles per 120V, 20A circuit. e. One additional 120V, 20A branch circuit will be provided to each resident room. New branch circuit wiring will be routed down corridor and connect to an existing, flush mounted, ceiling junction box located in the resident room closet. A junction box extension ring will be installed on the existing 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 25 August 27, 2012 f. flush device to allow surface conduit entry from corridor. The four existing receptacle locations within the resident room will have their branch circuit conductors reconfigured such that each half of the resident room is on a dedicated circuit; two receptacle locations per circuit. Replacement to existing receptacles within the resident rooms is not part of this project. Fire Alarm System 1. Control Panels a. The fire alarm system is an existing GE EST multiplexed addressable fire alarm system and no changes to the main control panel are anticipated. 2. Notification and Initiation Devices a. Manual pull stations will be provided at each floor exit and spaced such that travel to any station is less than 200 feet. b. Smoke detectors shall be located in corridors, electrical rooms, storage rooms and other locations required by DFD Design Guidelines. Corridor spacing will be 30 feet on-center c. Duct smoke detectors will be installed at each air handler and furnished with remote test stations. d. Heat detectors shall be located in mechanical rooms and as required by DFD Design Guidelines. e. Required interface modules will be provided to monitor fire protection system, elevator recall and similar systems. f. Audible and Visual notification devices will be installed in public spaces as required by code. g. Self-contained, non-addressable 120V smoke alarms are existing within resident rooms and their replacement is not part of this project. h. Audible notification devices are existing within resident rooms and their replacement is not part of this project. AV Rough In 1. Conduit and Back Boxes a. Standard electrical boxes and raceway will be used to rough in for AV cabling. Any special boxes will be provided by the AV contractor/installer. Empty conduit will be provided with pull string. b. AV equipment, cabling, terminations and design are not part of the division 26 scope of work. Building Automation System Interface 1. Electric meters installed in electrical distribution equipment shall be provided with Communications ports to allow monitoring from the BAS data bus. 2. Exterior lighting control contactors shall interface to the BAS so that exterior building and site lighting is controlled along with all other campus lighting. Design Criteria 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 26 August 27, 2012 1. Applicable Codes, Guidelines, and Standards a. Design and construction codes and standards are listed below. b. The codes and standards listed are minimum requirements. Nothing is to prevent the architect, engineer, or consultant from exceeding the applicable requirements. In the case of laboratory related research buildings, the recommendations of the guidelines below and the standards and requirements suggested by the design team will often address issues not sufficiently covered in local building codes. c. In all cases the most recent editions of referenced standards apply. IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers IESNA Illuminating Engineering Society of North America NECA National Electrical Contractors Association NEMA National Electrical Manufactures Association UL Underwriters Laboratories NFPA 70 2011 National Electric Code NFPA 72 National Fire Alarm code NFPA 101 Life Safety Code NFPA 110 Standard for Emergency and Standby Power Systems Wisconsin Enrolled Commercial Building Code DFD Master Specifications DFD Electrical Systems Standards & Design Guidelines DFD Policy and Procedures Manuals for A/Es DFD Day Lighting Standards for State Facilities University of Wisconsin-Platteville Design Standards 2. Basic Design criteria a. Load Calculation Criteria: Functional Area Lighting Office Receptacles HVAC Load Density (VA/Sq. Ft) 1.0 1.5 3.0 b. Secondary Design Voltages: Motors larger than ½ HP General Lighting Receptacles & motors less than 1/2 HP 208V, 3 phase, 3 wire + ground 120V, 1 phase, 2 wire + ground 120V, 1 phase, 2 wire + ground c. Equipment Sizing Criteria (Preliminary estimate): Branch Circuit Load Calculations: Lighting Actual installed VA Receptacles 180VA per outlet Special Outlets Actual installed VA of equipment Motors 125% of motor VA Demand Factors: Lighting Receptacles Motors 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects 125% of installed VA 100% of first 10Kva installed plus 50% of balance 125% of VA of largest motor plus 100% of VA of all other motors Page 27 August 27, 2012 Fixed Equipment 100% of total VA installed Minimum Bus Sizes: 280Y/120V Panels 100 Amps Diversity Factor: A diversity factor shall be used per the 2003 Wisconsin Electrical Code (Comm. 16.2392), in establishing power service, feeders, and equipment capacities. d. Spare Capacity: 25% spare capacity to accommodate function changes over the life of the building shall be included in the design of the power distribution system. Power distribution equipment shall be sized to reserve 20% space for physical expansion. Scope Exclusions 1. The following list represents specification and design of building components which are not part of Henneman Engineering’s scope of work. • Lightning protection • Building clock system • AV systems • Area of rescue assistance I. Telecommunications 1. Campus Backbone Cable a. Fiber and copper outdoor rated backbone cable exists and shall remain in place. Conduits and cable routing shall be determined as the design phase’s progress. New cabling will be routed from where the cables enter each building to the New TR locations. 2. Telecommunications Rooms (TRs) a. Telecom Rooms are existing and will be expanded. The space needs are less than desirable and not adequate for the intended use and purpose of the buildings. New racks will be added for new terminated jacks. b. The existing telecom grounding system will be updated to conform to current standards and best practices. c. TRs within both buildings should have ¾" fire-retardant plywood on all walls to accommodate miscellaneous mounting requirements for current and future flexibility. d. There are currently no cooling units provided for the existing TRs and the installation of one in each room is anticipated to be added within the scope of this project. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 28 August 27, 2012 e. Doors are typically secured with key access, off public corridors. Additional power circuits may be required on walls for wall mounted equipment and convenience. f. The MTR may also be considered the building entrance facility (BEF). g. Systems typically located within TRs include cable and electronics for: voice, data, security CCTV, access control, fire alarm, audio-visual, cable TV, cable connections to other floors, cable connections to outside campus or telecommunications services, connections to roof or antennae, and other systems as determined by User Agency or local departments. Overhead cable runways shall be connected to top of all data racks and securely fastened to at least two walls for stability. Provide a minimum of six 20 Amp, 120 volt electrical circuits in this room. 3. Telephone System a. Telephone system hardware, electronics, and handsets are to be provided by the User Agency. Voice cabling, pathways (conduit, back boxes, surface mounted raceways and cable tray) outlets, faceplates, termination blocks, backboards, termination and testing are included as part of this project, these outlets are minimal – approximately 15 total – they will be placed within meeting rooms and lounges not within each resident room. 4. Data System a. Data system electronics, (including but not limited to switches, routers, servers, distributed and/or rack mounted uninterruptible power supplies and other electronic equipment) are provided by the User Agency, unless noted otherwise. Data (horizontal copper) cabling, pathways (conduit, back boxes, surface mounted raceway and cable tray), outlets, faceplates, patch panels, equipment racks, terminations, and testing are included as part of this project. 5. Cable TV System (CATV) a. CATV system electronics (such as players, signal processors, and amplifiers) are existing to remain. Amplifiers are also existing to remain. CATV cabling, pathways, backboards, terminations will be new and be included as part of this project. The head end equipment will need to be physically moved to the new walls within the new room. 6. Security Access Control System a. The User Agency has retained responsibility to provide access control systems. Back box, conduit, raceway and power locations shall be coordinated for card readers and other security devices as required by the User Agency at minimal building entrance locations as will be indicated on the plans. 7. Security Closed Circuit TV Systems (CCTV) a. The User Agency has retained responsibility to provide CCTV systems for building use. Locations shall be coordinated with the Owner. Back box, conduit, raceway and power shall be provided for cameras and other 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 29 August 27, 2012 devices as required by the User Agency and the locations will be indicated on the plans. 8. Overhead Paging System a. Overhead paging is not a part of this project. 9. General Requirements: a. The cabling infrastructures are existing to be removed and currently a Category 5E solution for data and a Category 3 for voice. Cable for all new systems is to be routed in new pathway, within surface mounted raceway and in j-hooks above the new hallway ceilings. Each resident room will have a minimum of one data outlet on each side of the room, location to be determined during later design phases. Each resident room will have a minimum of one CATV coaxial outlet on each side of the room, again location to be determined during later design phases. All of these data and CATV jacks will need to be tested as part of this project. Provide data jacks in hallway ceilings for wireless access points. b. For voice backbone cable requirements and all other requirements not discussed in this narrative consult the DOA Telecommunications Guidelines for Structured Building Wiring Systems. Station jacks are to be terminated with either TIA 568A or 568B pin configurations. Both are acceptable to DSF. Consult with User Agency and DSF prior to final design to determine which pin out is required on this campus. c. Provide grounding and bonding system for all telecommunications systems and equipment, bonded to one central location at the main electrical service for the building. Provide telecommunications grounding bus bars in every TR. 4. Energy Conservation Measures A. Sustainability Strategies The sustainable design principal executed is reuse of an existing building. These renovations will double the expected usable life thus reducing the need for construction a new residence hall. Interior materials will include low-VOC and urea-formaldehyde free products will be specified. B. DFD Sustainable Facilities Guidelines checklist 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 30 August 27, 2012 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 31 August 27, 2012 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 32 August 27, 2012 Sustainable Site Requirements SS W1 Construction Site Erosion & Sedimentation Control Intent Minimize erosion during construction to reduce negative impacts on water and air quality. Requirements Design a sediment and erosion control plan, specific to the site that conforms to the requirements of NR 216 or COMM 61.115, NR 151 and any local construction site erosion control ordinances. The plan shall meet the following objectives: _ Prevent loss of soil during construction by stormwater runoff and/or wind erosion, including protecting topsoil by stockpiling for reuse. _ Prevent sedimentation of storm sewer or receiving streams. _ Prevent polluting the air with dust and particulate matter. The plan will be designed and constructed in accordance with the Wisconsin DNR Storm Water Management Technical Standards for Construction Site Erosion & Sediment Control at http://dnr.wi.gov/org/water/wm/nps/stormwater/techstds.htm#Construction Rev.02/ Strategy: Project utilizes existing building on established sites. There will be minor disturbance at areas of the building additions. Erosion and sediment control will be provided. SS C1 Site Selection Intent Avoid development on inappropriate site and reduce the environmental impact of the location of a building on a site. Requirements Avoid developing buildings, roads or parking area on portions of site that meet any one of the following criteria: Prime farmland, land whose elevation is lower than 5 feet above the elevation of the 100 year flood. Land which is specifically identified as habitat for any species on the threatened or endangered lists, within 100 feet of any water including wetlands, land which prior to acquisition for the project was public parkland. Strategy: Project utilizes existing buildings on established sites. SS C2 Development Density & Community Connectivity Intent Channel development to urban areas with existing infrastructure, protect greenfields and preserve habitat and natural resources. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 33 August 27, 2012 Requirements OPTION 1 — DEVELOPMENT DENSITY Construct or renovate building on a previously developed site AND in a community with a minimum density of 60,000 square feet per acre net (Note: density calculation must include the area of the project being built and is based on a typical two-story downtown development). OR OPTION 2 — COMMUNITY CONNECTIVITY Construct or renovate building on a previously developed site AND within 1/2 mile of a residential zone or neighborhood with an average density of 10 units per acre net AND within ½ mile of at least 10 Basic Services AND with pedestrian access between the building and the services. Basic Services include, but are not limited to: 1) Bank; 2) Place of Worship; 3) Convenience Grocery; 4) Day Care; 5) Cleaners; 6) Fire Station; 7) Beauty; 8) Hardware; 9) Laundry; 10) Library; 11) Medical/Dental; 12) Senior Care Facility; 13) Park; 14) Pharmacy; 15) Post Office; 16) Restaurant; 17) School; 18) Supermarket; 19) Theater; 20) Community Center; 21) Fitness Center; 22) Museum. Proximity is determined by drawing a 1/2 mile radius around the main building entrance on a site map and counting the services within that radius. Strategy: Project utilizes existing building on established sites. SS C4.2 Alternative Transportation: Bicycle Storage & Changing Rooms Intent Reduce pollution and land development impacts from automobile use. Requirements For commercial or institutional buildings, provide secure and covered bicycle storage with convenient changing/shower facilities (within 200 yards of the building) for 5% or more of regular building occupants. For residential buildings, provide covered storage facilities for securing bicycles for 15% or more of building occupants. Strategy: Existing bicycle storage is provided adjacent to the buildings and will be maintained or relocated within site. SS C4.3 Alternative Transportation: Low Emitting & Fuel Efficient Vehicles Intent Reduce pollution and land development impacts from automobile use. Requirements Provide preferred parking for low-emitting and fuel-efficient vehicles for 5% of the total vehicle parking capacity of the site. Low-emitting and fuel-efficient vehicles are defined as vehicles that are either classified as Zero Emission Vehicles (ZEV) by the California Air Resources Board or have achieved a minimum green score of 40 on the American Council for an Energy Efficient Economy (ACEEE) annual vehicle rating guide. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 34 August 27, 2012 “Preferred parking” refers to the parking spots that are closest to the main entrance of the project (exclusive of spaces designated for handicapped) or parking passes provided at a discounted price. Strategy: UW Platteville can include signage for preferential parking stalls. Project scope does not have any work in parking lots. SS C5.2 Reduced Site Disturbance: Development Footprint Intent Conserve existing natural areas and restore damaged areas to provide habitat and promote biodiversity. Requirements Reduce the development footprint (defined as entire building footprint, access roads and parking) to exceed the local zoning’s open space requirement for the site by 25%. For areas with no local zoning requirements (e.g., some university campuses and military bases), designate open space area adjacent to the building that is equal to the development footprint. Maximize development using vertical rather than horizontal strategies. Strategy: Project utilizes existing building on established site. Construction limits, contractor entrances, dumpster locations will be noted on the bid documents. Water Efficiency Requirements WE C1.2 Water Efficient Landscaping: No Potable Use or No Irrigation Intent Limit or eliminate the use of potable water for landscape irrigation. Requirements Use only captured rain or recycled site water to eliminate all potable water use for site irrigation (except for initial watering to establish plants), OR do not install permanent landscape irrigation systems. Maximize use native plantings that do not require additional irrigation in dry spells Strategy: No irrigation Energy and Atmosphere Requirements EA P1 Commissioning Intent Implement commissioning practices into all procedures and documentation used in the planning, design, construction, closeout and operations of state facilities. Provide for verification through the commissioning process that building systems are designed, installed, and perform according to DFD’s project requirements, basis of design, and construction documents. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 35 August 27, 2012 Requirements Implement the fundamental best practice commissioning procedures as outlined in the DFD Policy & Procedure Manual for Architects/Engineers and Consultants Strategy: Level one commissioning as part of project EA P2 Minimum Energy Performance Intent Establish the minimum level of energy efficiency for the base building and systems. Requirements Design the building to comply with ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-2004 (without amendments) or the local energy code, whichever is more stringent. Follow the requirements of the DFD Energy Design Guidelines and Lighting Design Guidelines available at DFD’s Master Specifications and Design Guidelines Strategy: Will comply with the state of WI energy code. EA P3 CFC and HCFC Reduction in HVAC&R Equipment Application These requirements apply where at least 3 commonly available manufacturers can provide equipment that complies with these requirements. The Engineer is expected to research products for specific project equipment and capacity needs to determine which manufacturer’s equipment can comply. If only 2 or less manufacturer’s equipment complies then the requirements do not apply. Intent Reduce ozone depletion and support early compliance with the Montreal Protocol while minimizing direct contributions to global warming. Requirements OPTION 1 Do not use refrigerants. OR OPTION 2 Select refrigerants and HVAC&R that minimize or eliminate the emission of compounds that contribute to ozone depletion and global warming. The base building HVAC&R equipment shall comply with the following formula, which sets a maximum threshold for the combined contributions to ozone depletion and global warming potential: LCGWP + LCODP x 105 ≤ 100 Where: LCODP = [ODPr x (Lr x Life +Mr) x Rc]/Life LCGWP = [GWPr x (Lr x Life +Mr) x Rc]/Life LCODP: Lifecycle Ozone Depletion Potential (lbCFC11/Ton-Year) LCGWP: Lifecycle Direct Global Warming Potential (lbCO2/Ton-Year) GWPr: Global Warming Potential of Refrigerant (0 to 12,000 lbCO2/lbr) ODPr: Ozone Depletion Potential of Refrigerant (0 to 0.2 lbCFC11/lbr) 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 36 August 27, 2012 Lr: Refrigerant Leakage Rate (0.5% to 2.0%; default of 2% unless otherwise demonstrated) Mr: End-of-life Refrigerant Loss (2% to 10%; default of 10% unless otherwise demonstrated) Rc: Refrigerant Charge (0.5 to 5.0 lbs of refrigerant per ton of cooling capacity) Life: Equipment Life (10 years; default based on equipment type, unless otherwise demonstrated) For multiple types of equipment, a weighted average of all base building level HVAC&R equipment shall be applied using the following formula: [ Σ (LCGWP + LCODP x 105) x Qunit ] / Qtotal ≤ 100 Where: Qunit = Cooling capacity of an individual HVAC or refrigeration unit (Tons) Qtotal = Total cooling capacity of all HVAC or refrigeration Small HVAC units (defined as containing less than 0.5 lbs of refrigerant), and other equipment such as standard refrigerators, small water coolers, and any other cooling equipment that contains less than 0.5 lbs of refrigerant, are not considered part of the “base building” system and are not subject to the requirements of this credit. AND Do not install fire suppression systems that contain ozone-depleting substances (CFCs, HCFCs or Halons). Strategy: Cooling equipment will be specified to use R-410 A or equivalent refrigerant. There will only be selective cooling in Dobson and no cooling in Melcher. All Fire protection shall be water based. EA C1 For Projects >$2million Optimize Energy Performance Intent Achieve increasing levels of energy performance above the prerequisite standard to reduce environmental impacts associated with excessive energy use. Requirements Reduce design energy cost compared to the energy cost budget for energy systems regulated by ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-2004 (without amendments), as demonstrated by a whole building simulation using the Energy Cost Budget Method described in Section 11 of the Standard. New Bldgs. Existing Bldgs. 30% 20% Regulated energy systems include HVAC (heating, cooling, fans and pumps), service hot water and interior lighting. Non-regulated systems include plugloads, exterior lighting, garage ventilation and elevators (vertical transportation). Two methods may be used to separate energy consumption for regulated systems. The energy consumption for each fuel may be prorated according to the fraction of energy used by regulated and non-regulated energy. Alternatively, separate meters (accounting) may be created in the energy simulation program for regulated and non-regulated energy uses. If an analysis has been made comparing the proposed design to local energy standards and a defensible equivalency (at minimum) to ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-2004 has been established, then the comparison against the local code may be used in lieu of the ASHRAE Standard. Strategy: determining current requirements. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 37 August 27, 2012 EA C5 Measurement and Verification Intent Provide for the ongoing accountability and optimization of building energy and water consumption performance over time. Requirements Meters shall meet the requirements of sections 23 05 15, 23 09 14, or 26 27 13 of the State's Master Specifications. Install continuous metering equipment connected to a data gathering system such as a building automation system for the following end-uses: Total building electrical energy consumption, Total building steam or hot water energy consumption, Total building chilled water consumption, Total building domestic water consumption, Total building natural gas consumption, Sub-metering or monitoring similar to the following is encouraged for buildings where staff resources are employed to actively manage energy consuming systems: _ Lighting systems and controls _ Appropriate motor loads _ Chiller energy use _ Cooling loads _ Air and water economizer analysis _ Air distribution static pressures and ventilation air volumes _ Building-related process energy systems and equipment _ Domestic water not returned to sanitary Develop a Measurement and Verification plan, for all buildings, that incorporates the monitoring information from the above end-uses and is consistent with Option B, C or D of the 2001 International Performance Measurement & Verification Protocol (IPMVP) Volume I: Concepts and Options for Determining Energy and Water Savings. Strategy: The project will meter steam and electricity as they enter the building, additional sub metering not in the project scope. Total building energy consumption, total building steam energy consumption will be measured and the meters will be integrated into the campus wide building automation system. Materials and Resources Requirements MR P1 Storage & Collection of Recyclables Intent Facilitate the reduction of waste generated by building occupants that is hauled to and disposed of in landfills. Requirements Provide an easily accessible area that serves the entire building and is dedicated to the separation, collection and storage of materials for recycling including (at a minimum) paper, corrugated cardboard, glass, compostable food wastes, plastics and metals. Strategy: Existing recycling rooms are located with both buildings and recycling service is in place. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 38 August 27, 2012 MR C4.1 Recycled Content: 10-20% (post-consumer + 1/2 post-industrial) Intent Increase demand for building products that incorporate recycled content materials, therefore reducing the impacts resulting from extraction and processing of new virgin materials. Requirements Use materials with recycled content such that the sum of post-consumer recycled content plus one-half of the post-industrial content constitutes at least 10-20% of the total value of the materials in the project. The value of the recycled content portion of a material or furnishing shall be determined by dividing the weight of recycled content in the item by the total weight of all material in the item, then multiplying the resulting percentage by the total value of the item. Mechanical and electrical components shall not be included in this calculation. Recycled content materials shall be defined in accordance with the Federal Trade Commission document, Guides for the Use of Environmental Marketing Claims, 16 CFR 260.7 (e), available at www.ftc.gov/bcp/grnrule/guides980427.htm. Strategy: Effort will be made to specify interior finishes to contain higher recycled material content MR C5.1 Regional Materials: 20% manufactured regionally Intent Increase demand for building materials and products that are extracted and manufactured within the region, thereby supporting the regional economy and reducing the environmental impacts resulting from transportation. Requirements Use a minimum of 20% of building materials and products that are manufactured* regionally within a radius of 500 miles. * Manufacturing refers to the final assembly of components into the building product that is furnished and installed by the tradesmen. For example, if the hardware comes from Dallas, Texas, the lumber from Vancouver, British Columbia, and the joist is assembled in Kent, Washington; then the location of the final assembly is Kent, Washington. Strategy: Effort will be made to specify local/regional materials MR C6 Renewable Materials Intent Reduce the use and depletion of finite raw materials and long-cycle renewable materials by replacing them with renewable materials. Requirements Use renewable building materials and products (made from plants that are typically harvested within a ten-year cycle or shorter) for 5% of the total value of all building materials and products used in the project. Submittals _ Reference in Design Report or written documentation. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 39 August 27, 2012 _ Provide a letter, signed by the architect or responsible party, declaring that the requirements have been met. Include calculations demonstrating that the project incorporates the required percentage of renewable products. Show their cost and percentage of renewable components, and the total cost of all materials for the project. Strategy: Effort will be made to specify renewable materials but do to the nature of the renovation scope, do not anticipate reaching the 5% threshold. MR C7 Certified Wood Intent Encourage environmentally responsible forest management and use of local forest products Requirements 70% of wood-based materials and products, must be obtained from forests certified in accordance with Wisconsin State, County or Managed Forest Law certification program and certain national certification programs listed below, for wood building components including, but not limited to, structural framing and general dimensional framing, flooring, finishes, furnishings, and non-rented temporary construction applications such as bracing, concrete form work and pedestrian barriers. WI MFL Tree Farm Group Record #007 Certificate #NSF-ISR 1Y544-T1 WI County Forest Certificate #NSF-SFIS-1Y943-S1 WI County Forest Certificate #SCS-FM/COC-083G WI State Forest Certificate #SCS-FM/COC-0007N WI State Forest Certificate #NSF-SFIS-1Y941-S1 American Tree Farm System (ATFS) Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) Sustainable Forest Initiative (SFI) Strategy: Doors and other wood materials will be specified to contain certified wood Indoor Environmental Quality Requirements EQ P1 Minimum IAQ Performance Intent Establish minimum indoor air quality (IAQ) performance to prevent the development of indoor air quality problems in buildings, thus contributing to the comfort and well-being of the occupants. Requirements Meet the minimum requirements of Sections 4 through 7 of ASHRAE 62.1-2004, Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality, and approved Addenda using the Ventilation Rate Procedure. Submittals _ Reference in Design Report or written documentation. _ Provide a letter, signed by the mechanical engineer or responsible party, declaring that the project is fully compliant with ASHRAE 62.1-2004 and all published Addenda and describing the procedure employed in the IAQ analysis (Ventilation Rate Procedure). Strategy: will pursue and anticipate meeting requirements / intent of ASHRAE. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 40 August 27, 2012 Required EQ C4.1 Low-Emitting Materials: Adhesives & Sealants Intent Reduce the quantity of indoor air contaminants that are odorous, potentially irritating and/or harmful to the comfort and well-being of installers and occupants. Requirements The VOC content of adhesives and sealants used must be less than the current VOC content limits of South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD) Rule #1168, AND all sealants used as fillers must meet or exceed the requirements of the Bay Area Air Quality Management District Regulation 8, Rule 51. Strategy: Specify Low-VOC materials in construction documents. Ensure that VOC limits are clearly stated in each section where adhesives and sealants are addressed. Required EQ C4.2 Low-Emitting Materials: Paints and Coatings Intent Reduce the quantity of indoor air contaminants that are odorous, potentially irritating and/or harmful to the comfort and well-being of installers and occupants. Requirements VOC emissions from paints and coatings must not exceed the VOC and chemical component limits of Green Seal’s Standard GS-11 requirements. Strategy: Specify Low-VOC paints and coatings in construction documents. Ensure that VOC limits are clearly stated in each section where paints are addressed. Required EQ C4.3 Low-Emitting Materials: Carpet Intent Reduce the quantity of indoor air contaminants that are odorous, potentially irritating and/or harmful to the comfort and well-being of installers and occupants. Requirements Carpet systems must meet or exceed the requirements of the Carpet and Rug Institute’s Green Label Indoor Air Quality Test Program. Strategy: Specify Low-VOC carpet products and systems in construction documents. Ensure that VOC limits are clearly stated where carpet systems are addressed. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 41 August 27, 2012 EQ C4.4 Low-Emitting Materials: Composite Wood Intent Reduce the quantity of indoor air contaminants that are odorous, potentially irritating and/or harmful to the comfort and well-being of installers and occupants. Requirements Composite wood and agrifiber products must contain no added urea-formaldehyde resins. Strategy: Specify wood and agrifiber products, including doors, that contain no added urea-formaldehyde resins. EQ C5 Indoor Chemical & Pollutant Source Control Intent Avoid exposure of building occupants to potentially hazardous chemicals that adversely impact air quality. Requirements Design to minimize pollutant cross-contamination of regularly occupied areas: _ Employ permanent entryway systems (grills, grates, etc.) to capture dirt, particulates, etc. from entering the building at all high volume entryways. _ Where chemical use occurs (including housekeeping areas and copying/printing rooms), provide segregated areas with deck to deck partitions with separate outside exhaust at a rate of at least 0.50 cubic feet per minute per square foot, no air re-circulation and maintaining a negative pressure of at least 7 PA (0.03 inches of water gauge). _ Provide drains plumbed for appropriate disposal of liquid waste in spaces where water and chemical concentrate mixing occurs. Strategy: Design separate exhaust and plumbing systems for custodial rooms. Install permanent entrance grills at main entryway to prevent occupant borne contaminants from entering the building. EQ C8.1 Daylight and Views Intent Provide for the building occupants a connection between indoor spaces and the outdoors through the introduction of daylight and views into the regularly occupied areas of the building. Requirements Comply with DFD’s "Daylighting Standards for State Facilities". Find a link to those Standards at http://www.doa.state.wi.us/pagesubtext_detail.asp?linksubcatid=252&linkcatid=125&linkid= Strategy: The project scope utilizes existing building envelope including windows within resident rooms and in basements. The common areas will incorporate additional curtain wall systems at entrances, lobbies and student lounges. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 42 August 27, 2012 C. Daylighting Criteria Form Not applicable, existing building envelope and windows. D. Building Energy Modeling Not applicable as existing building. E. Renewable Energy Sources Solar domestic water heating was investigated but demonstrated cost effective for this project. F. Life Cycle Cost Analysis Summary 1. The use of solar domestic water heating was analyzed for potential use on this project using the DSF discounted energy payback form. The analysis found that this option has a discounted payback exceeding 50 years. Given the payback exceeded 15 years and the life of the proposed system, this option has not been implemented. 2. The use of energy recovery wheels for the toilet exhaust systems for both Melcher and Dobson halls was evaluated using the DSF discounted energy payback form. This analysis resulted in a discounted payback of 9.5 years for Melcher Hall and 14.3 years for Dobson Hall. Since the paybacks were less than 15 years, the design team was directed to implement the energy recovery wheels. 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 43 August 27, 2012 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 44 August 27, 2012 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 45 August 27, 2012 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 46 August 27, 2012 G. Energy Conservation Measures Form PROJECT: UW PLATTEVILLE, RESIDENCE HALLS RENOVATION – PHASE I PROJECT NO.: 11F3C LOCATION: PLATTEVILLE, W ISCONSIN DATE: 8-27-2012 BUILDING SYSTEM ENERGY CONSERVATION MEASURES (ECM’S) DISCOUNTED ENERGY PAYBACK CALC. YES 1. ENVELOPE NO YEARS 1.1 1.2 2. PLUMBING 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 2.1 3. HVAC 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 3.1 Integration of occupancy sensors and VAV boxes 4. ELECTRICAL 3.2 Reset of static pressure control based upon demand 3.3 Energy recovery wheels for toilet exhaust 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 4.1 Occupancy sensors for automatic shutoff 5. OTHER 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 5.1 No No No No 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 47 August 27, 2012 5. Budget Detail Construction Per program Per design Reduced or revised program to budget Construction General construction Plumbing Fire Protection HVAC Electrical Telecommunications $4,702,000 $250,000 $450,000 $2,400,000 $1,800,000 $280,000 $5,587,485 $618,309 $373,118 $2,636,219 $1,449,828 $275,041 $885,485 $368,309 -76,882 $236,219 -$350,172 -$4,959 Construction subtotal Construction testing Hazardous Material Abatement Construction subtotal Construction contingency (7%) Construction total $9,882,000 0 $120,000 $9,982,000 $738,000 $10,720,000 $10,926,264 $20,000 $120,000 $11,066,264 $800,000 $11,866,264 $1,044,264 $10,000 0 $1,124,465 $62,000 $1,186,465 Design & Supervision DFD management fee A/E Fees Commissioning and/or LEED Other fees A/E reimbursable Geotechnical Investigation Site Survey Plan Review Fees Design and Supervision subtotal $430,000 $800,000 0 $209,000 0 0 0 0 $1,439,000 $476,000 $879,000 0 $209,000 0 $5,000 $5,000 $10,000 $1,584,000 $46,000 $79,000 Equipment Movable equipment Special equipment Communications equipment Equipment Subtotal N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A Land purchase Percent for art Total estimated project cost N/A 0 $12,179,000 N/A 0 $13,446,000 0 0 $5000 $5000 $10,000 $145,000 Work by Agency 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects $1,287,000 Page 48 August 27, 2012 6. Equipment Not applicable 7. Drawings A. Dobson Hall Basement Plan B. Dobson Hall First Floor Plan C. Dobson Hall Second Floor Plan D. Dobson Hall Third Floor Plan E. Dobson Hall Fourth Floor Plan F. Dobson Hall Roof Floor Plan G. Melcher Hall Basement Plan H. Melcher Hall First Floor Plan I. Melcher Hall Second Floor Plan J. Melcher Hall Third Floor Plan K. Melcher Hall Fourth Floor Plan L. Melcher Hall Roof Floor Plan 11 F 3 C UW Platteville Melcher and Dobson Halls Renovation Design Report Appendix Assemblage Architects Page 49 August 27, 2012