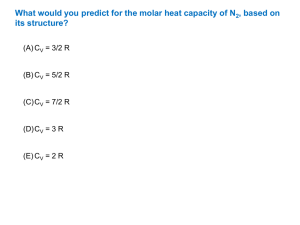Gas constant - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
advertisement

Gas constant - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia 1 of 2 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_constant Gas constant From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia The gas constant (also known as the universal or ideal gas constant, usually denoted by Values of R symbol R) is a physical constant used in equations of state to relate various groups of state 8.314472 functions to one another. It is another name for the Boltzmann constant, but when used in the ideal gas law it is usually expressed in the more convenient units of energy per kelvin per 0.0820574587 mole rather than simply energy per kelvin per particle. 8.20574587 x 10-5 The ideal gas constant occurs in the simplest equation of state, the ideal gas law, as follows: 8.314472 Units J · K-1 · mol-1 L · atm · K-1 · mol-1 m³ · atm · K-1 · mol-1 cm3 · MPa · K-1 · mol-1 8.314472 L · kPa · K-1 · mol-1 8.314472 m3 · Pa · K-1 · mol-1 62.3637 L · mmHg · K-1 · mol-1 62.3637 L · Torr · K-1 · mol-1 83.14472 L · mbar · K-1 · mol-1 1.987 cal · K-1 · mol-1 6.132439833 lbf · ft · K-1 · g · mol-1 R appears in the Nernst equation as well as in the Lorentz-Lorenz formula. 10.7316 ft³ · psi · °R-1 · lb-mol-1 Its value is: 8.63 x 10-5 eV · K-1 · atom-1 0.7302 ft3·atm·°R-1·lb-mole-1 where P is the pressure of an ideal gas T is its temperature is its molar volume This can also be written as: where V is the volume the gas occupies n is the moles of gas -1 -1 R = 8.314472(15) J · K · mol The two digits between the parentheses denote the uncertainty (standard deviation) in the last two digits of the value. Contents 1 Boltzmann constant 2 Specific gas constant 3 US Standard Atmosphere 4 See also 5 References 6 External links Boltzmann constant The Boltzmann constant kB (often abbreviated k) may be used in place of the other forms of the ideal gas constant by working in pure particle count rather than number of moles of gas; this simply requires carrying a factor of Avogadro's number. Writing: One can then express the ideal gas law in direct terms of Boltzmann's constant: with N = nNA is the actual number of molecules Specific gas constant 6/22/2007 11:13 AM Gas constant - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia 2 of 2 The specific gas constant of a gas or a mixture of gases ( gas/mixture. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_constant ) is given by the universal gas constant, divided by the molar mass ( M ) of the It is common to represent the specific gas constant by the symbol R. In such cases the context and/or units of R should make it clear as to which gas constant is being referred to. For example, the equation for the speed of sound, is usually written in terms of the specific gas constant. The specific gas constant of air is US Standard Atmosphere The US Standard Atmosphere, 1976 (USSA1976) defines the Universal Gas Constant (R) as:[1][2] The USSA1976 does recognize, however, that this value is not consistent with the cited values for the Avogadro constant and the Boltzmann constant.[2] Still, the USSA1976 uses this value of R for all the calculations of the standard atmosphere. This disparity is not a significant departure from accuracy. When using the ISO value of R, the calculated pressure increases by only 0.62 pascals at 11,000 meters (the equivalent of a difference of only 0.174 meters – or 6.8 inches) and an increase of 0.292 pascals at 20,000 meters (the equivalent of a difference of only 0.338 meters – or 13.2 inches). See also Boltzmann constant References 1. ^ Standard Atmospheres (http://www.sworld.com.au/steven/space/atmosphere/) . Retrieved on 2007-01-07. 2. ^ a b U.S. Standard Atmosphere (http://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19770009539_1977009539.pdf) , 1976, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1976 (Linked file is 17 MiB). External links Gas Constant CODATA Value (http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?r|search_for=gas+constant) at NIST Boltzmann Constant CODATA Value (http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?k|search_for=boltzmann) at NIST Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_constant" Categories: Gases | Physical constants This page was last modified 10:35, 30 May 2007. All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License. (See Copyrights for details.) Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a US-registered 501(c)(3) tax-deductible nonprofit charity. 6/22/2007 11:13 AM