Electrical Engineering
advertisement
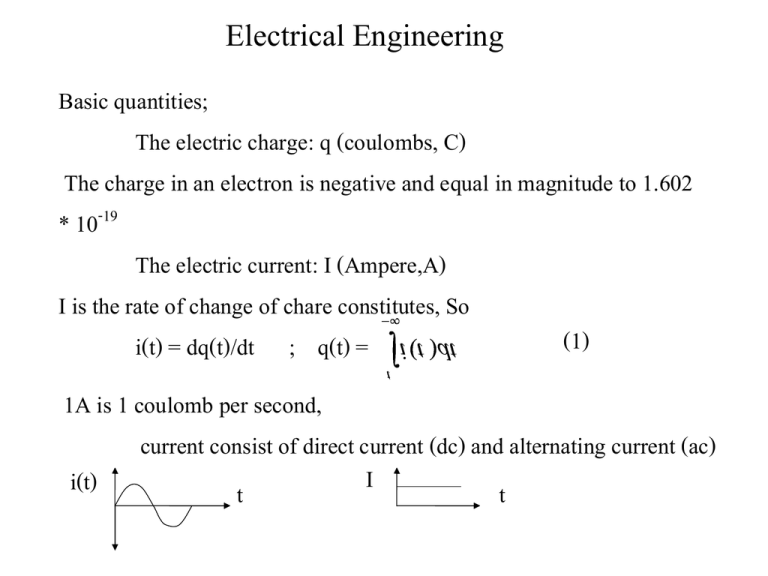
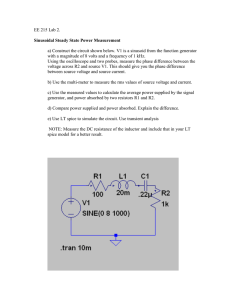
Electrical Engineering Basic quantities; The electric charge: q (coulombs, C) The charge in an electron is negative and equal in magnitude to 1.602 * 10 -19 The electric current: I (Ampere,A) I is the rate of change of chare constitutes, So (1) i(t) = dq(t)/dt ; q(t) = 1A is 1 coulomb per second, current consist of direct current (dc) and alternating current (ac) I i(t) t t Electrical Engineering Voltage or potential or electromotive force: we use to define the difference in energy level of a unit charge of the two point. Work or energy, w(t) or W, is measure in joules; 1 joule is 1 newton meter (N.m) 1 Volt is 1 joule per coulomb or = 1 Newton meter per coulomb D1.3 Five joules of energy are absorbed by 1C of charge when we moved from point B to point A in 1s. Find the voltage between points A and B A B V AB = 5 j/1C = 5 V We have defined voltage in J/C as the energy required to move a positive charge of 1 C through an element , then v = dw / dq (2) Multiplying this quantity by the current in the element yields vi = (dw/dq)(dq/dt) = dw/dt = p (3) we define the change in energy from t1 to t2 can be found by integrating t w = ò t 2 1 pdt = t 2 ò t v · idt 1 E 1.1 Determine the amount of power absorbed or supplied by the elements in fig. E 1.1 2A V 1 =12 v P= - 48 w V 1 = 4 v 4 A P=8w p 1 = ( 100 / 6 ) t p 2 = 100 + ( 0 - 100 ) t P=100 w = int p 1 dt + int . p 2 dt p1 0 p2 6 t 12 Circuit element - an active element is capable of generating energy those are batteries, generators, and transistor models. a passive element cannot generate energy. They are resistor, capacitor, and inductors. Independent Sources: An independent voltage source is a two-terminal element that maintains a specified voltage between its terminals regardless of the current through it. A A A v(t) i(t) V B B B Dependent Sources dependent sources generate a voltage or current that is determine by a voltage or current at a specified location in the circuit. v o v = mv o vo i = gv o io v = r * i o io i = b * i o Four different types of dependent sources E1.4 Determine the power supplied by the dependent sources in figure below Io=2A 10Vs V s = 4v I s = 4A 1 4I s 10v 1 Hint: 80w, 160w Example 1.7 Let us compute the power that is absorbed or supplied by the elements in the network in figure below I x =4A 1*Ix 2A 12v 1 2A 2 p15 24v 3 28v