GaN LED S
advertisement
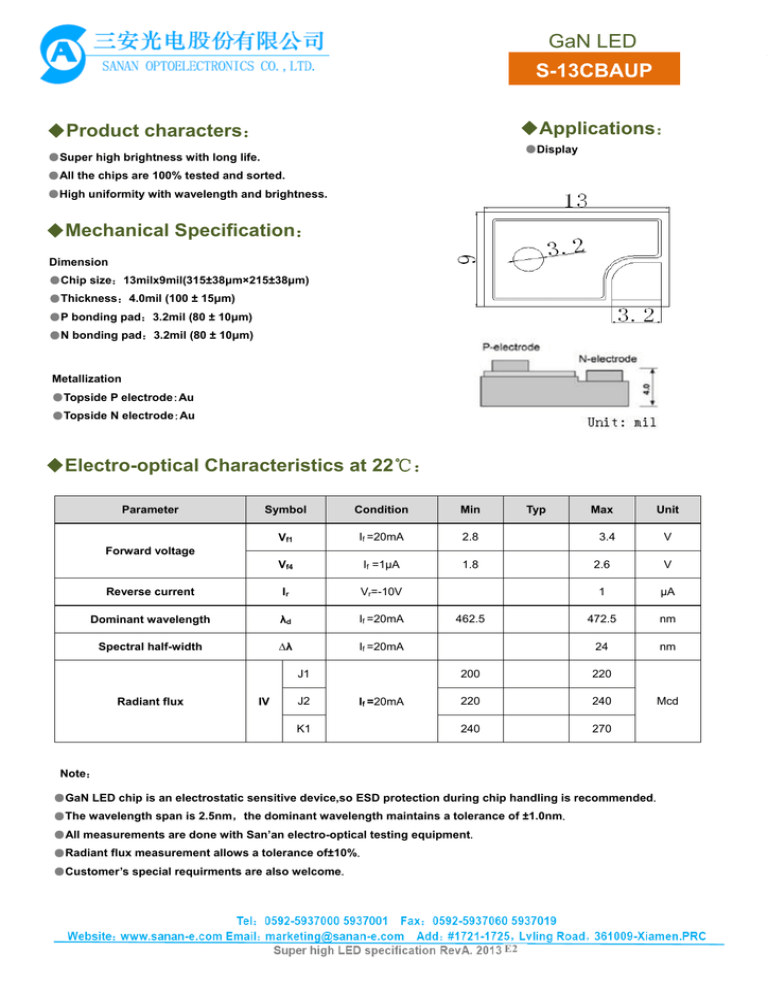
GaN LED S-13CBAUP ◆Applications: ◆Product characters: ●Display ●Super high brightness with long life. ●All the chips are 100% tested and sorted. ●High uniformity with wavelength and brightness. ◆Mechanical Specification: Dimension ●Chip size:13milx9mil(315±38μm×215±38μm) ●Thickness:4.0mil (100 ± 15μm) ●P bonding pad:3.2mil (80 ± 10μm) ●N bonding pad:3.2mil (80 ± 10μm) Metallization ●Topside P electrode:Au ●Topside N electrode:Au ◆Electro-optical Characteristics at 22℃: Parameter Symbol Condition Min Vf1 If =20mA 2.8 Vf4 If =1μA 1.8 Reverse current Ir Vr=-10V Dominant wavelength λd If =20mA Spectral half-width ∆λ If =20mA Typ Max Unit 3.4 V Forward voltage J1 Radiant flux IV J2 If =20mA K1 462.5 2.6 V 1 μA 472.5 nm 24 nm 200 220 220 240 240 270 Mcd Note: ●GaN LED chip is an electrostatic sensitive device,so ESD protection during chip handling is recommended. ●The wavelength span is 2.5nm,the dominant wavelength maintains a tolerance of ±1.0nm. ●All measurements are done with San’an electro-optical testing equipment. ●Radiant flux measurement allows a tolerance of±10%. ●Customer’s special requirments are also welcome. E2 GaN LED S S-13CBAUP ◆ ◆Absolu ute Maxiimum Ra atings: Parameter Symbol Condition Rating Unit Forw ward DC currrent If Tc = 22℃ ≤30 mA Junction temperature Tj ---- ≤115 ˚C chip -40~+85 ˚C chip--on-tape/storrage 0~40 ˚C chip-on--tape/transpo ortation -20~+65 ˚C ---- 280(<10s) ˚C Stora age temperatture Temperatu ure during pa ackaging Tstg ---- Note: N ● ●Maximum ra atings are pa ackage depen ndent. The above a maximum ratings were w determined using a Printed Circ cuit B Board(PCB) w without an en ncapsulant. Stresses S in excess e of the e absolute ma aximum ratin ngs such as forward f curre ent and junction te emperature may m cause da amage to the LED. ● ●The LED is not n designed d to be driven n in reverse bias, we suggest it should be operated under forwarrd current. ◆ ◆Charact teristic Curves: C : Fig.1-Re elative Luminous Intensity y vs. Forward d Current Fig.3--Relative Inte ensity (@20m mA) vs. Ambie ent Fig.2-Forrward Current vs. Forward d Voltage Fig.4- Forrward Voltage e (@20mA) vs s. Ambient Temperrature Te emperature Fig.5 5- Dominant Wavelength W (@ @20mA) vs. Fig.6F Maximum Driving F Forward DC Current C vs. Am mbient Ambien nt Temperaturre ature ( Deratin ng based on Tj max=115℃ ℃) Tempera E2