Lecture slides with notes
advertisement

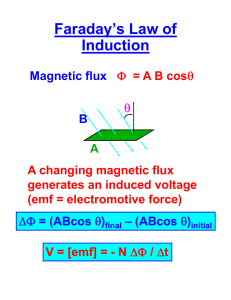
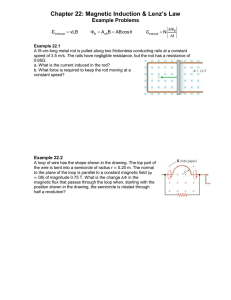
Physics ys cs 132: 3 Lecture ectu e 22 Elements of Physics II A Agenda d for f T Today d Lenz’ Law Emf opposes change in flux Faraday’s Law Induced EMF in a conducting loop Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 1 Lenz’s Law Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 2 Lenz’s Law Why? Does lenz lenz's s law apply to the moment of the change in flux or will the induced B field be the "permanent" field after the change. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 3 Lenz’s Law Reasoning Strategy 1. Find the direction of the magnetic flux that penetrates the coil. 2. Determine whether the magnetic flux that penetrates the coil is increasing or decreasing. Increasing: induced b-field opposes magnetic flux Decreasing: induced b-field aligned with magnetic flux 3. Use RHR-2 to determine the direction of the induced current. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 4 Clicker Question 1: The magnetic field f points out off the page and is increasing. (a) The induced current will flow counterclockwise. (b) The induced current will flow clockwise. (c) There will be no induced current. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 5 Clicker Question 1: Correct: “The The loop creates an induced magnetic field opposite of the actual magnetic field to keep the magnetic flux constant. Since the induced field points into the page, the current will flow clockwise because of the right hand rule rule.” “The change in flux is increasing out of the page, so by the righthand rule a clock-wise current is needed to induce a magnetic field pointing into the page.” “When the magnetic field is increasing the induced field of the induced current is pointing in the opposite direction of the magnetic field. I used the curly right hand rule : thumb points in direction of induced magnetic field and fingers curl in direction of induced current current. “ “Science” Incorrect: “The external magnetic g field p points out, the induced field must always counteract this field and point in.” Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 6 Clicker Question 2: The magnetic field f points out off the page and is decreasing. (a) The induced current will flow counterclockwise. (b) The induced current will flow clockwise. (c) There will be no induced current. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 7 Clicker Question 3: The two loops off wire in the figure f are stacked one above the other. Does the upper loop have a clockwise current (from above), a counterclockwise current, or no current at the following times? Before the switch is closed. (a) The current will flow counterclockwise. (b) The current will flow clockwise clockwise. (c) There will be no current. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 8 Clicker Question 4: The two loops off wire in the figure f are stacked one above the other. Does the upper loop have a clockwise current (from above), a counterclockwise current, or no current at the following times? Immediately after the switch is closed. (a) The current will flow counterclockwise. (b) The current will flow clockwise clockwise. (c) There will be no current. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 9 Clicker Question 5: The two loops off wire in the figure f are stacked one above the other. Does the upper loop have a clockwise current (from above), a counterclockwise current, or no current at the following times? Long after the switch is closed. (a) The current will flow counterclockwise. (b) The current will flow clockwise clockwise. (c) There will be no current. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 10 Clicker Question 6: The two loops off wire in the figure f are stacked one above the other. Does the upper loop have a clockwise current (from above), a counterclockwise current, or no current at the following times? Immediately after the switch is reopened. (a) The current will flow counterclockwise. (b) The current will flow clockwise clockwise. (c) There will be no current. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 11 Example: The bar magnet is pushed toward the center of a wire loop. Which is true? A. There is a clockwise induced current in the loop. B. There is a counterclockwise induced current in the loop. C. There is no induced current in the loop. p Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 12 Clicker Question 7: A ccircular cu a co conducting duc g loop oop is s be being g moved o ed up upward ad (toward a current-carrying wire) at a constant speed. What will be the direction of the induced current? (a) No current will be induced (no flux change). (b) Current will be induced clockwise. (c) Current will be induced counter counter-clockwise. clockwise Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 13 Clicker Question 8: If a coil is rotated as shown, in a magnetic field pointing p g to the left,, in what direction is the induced current? a) clockwise b) counterclockwise c) no induced current Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 14 Faraday’s Law An emf is induced in a conducting loop if the magnetic flux through the loop changes changes. The magnitude of the emf is: The direction of the emf is such as to drive an induced current in the direction given by Lenz’s law. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 15 Using Faraday’s Law If we slide a conducting wire along a U-shaped conducting rail, we can complete a circuit and drive an electric current. We can find the induced emf and current by using F d ’ llaw and Faraday’s d Oh Ohm’s ’ law: Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 16 Example: A 4 ccm × 3 ccm rectangular ec a gu a loop oop is s made ade o of a wire e with resistance of 3.5 Ohm. The loop is placed in a region of uniform magnetic field, B = 5 T. The direction of B is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and points into the page as shown. The magnetic field starts to increase at a uniform rate of 0.1 T/sec. What is the magnitude of the induced current in the loop? (a) I = 0 A (b) I = 3.4 3 4 × 10-55 A (c) I = 1.2 × 10-4 A (d) I = 0.02 A (e) I = 4.8 48A Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 17 Example: A 4 cm × 3 cm rectangular loop is made of a wire with resistance off 3.5 3 5 Ohm. Oh The Th loop l iis placed l d iin a region i off uniform if magnetic ti field, B = 5 T. The direction of B is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and points into the page as shown. The magnetic field starts t t to t increase i att a uniform if rate t off 0.1 0 1 T/sec. T/ What Wh t is i the th magnitude of the induced current in the loop? Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 18 Clicker Question 9: A 4 ccm × 3 ccm rectangular ec a gu a loop oop is s made ade o of a wire e with resistance of 25 Ohm/m. The loop is placed in a region of uniform magnetic field, B = 5 T. The direction of B is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and points into the page as shown. The magnetic field starts to increase at a uniform rate of 0.1 T/sec. What is the direction of the induced current? (a) counterclockwise (b) clockwise (c) There is no induced current. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 19 Example: A solenoid with cross sectional area A = 4 × 10-4 m2 is 0 0.120 120 m long and has 2500 turns turns. The magnetic field at the center of the solenoid is 5 × 10-3 T pointing into the page. A square wire loop 1.5 cm on each side is fixed inside the solenoid as shown shown. The current in the solenoid is uniformly decreased to zero over 10 seconds. What is the magnitude of the induced emf in the square loop? (a) 1.125 × 10-7 V (b) 1.259 × 10-7 V (c) 2.124 × 10-7 V (d) 2.486 × 10-6 V ((e)) 1.124 × 10-6 V Direction? CW Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 20 Example: A solenoid with cross sectional area A = 4 × 10-4 m2 is 0.120 m l long and dh has 2500 tturns. The Th magnetic ti field fi ld att th the center t off th the solenoid is 5 × 10-3 T pointing into the page. A square wire loop 1.5 cm on each side is fixed inside the solenoid as shown. The currentt in i the th solenoid l id iis uniformly if l d decreased d tto zero over 10 seconds. What is the magnitude of the induced emf in the square loop? Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 21 Applications of Faraday’s Faraday s Law – Electric Guitar A vibrating string induces an emf in a coil Ap permanent magnet g inside the coil magnetizes a portion of the string nearest the coil As the string vibrates at some frequency, its magnetized segment produces a changing flux through the pickup coil The changing flux produces an induced emf that is fed to p an amplifier Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 22 Applications of Faraday’s Faraday s Law – Microphone Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 23 Applications of Faraday’s Faraday s Law – Apnea Monitor The coil of wire attached to the chest carries an alternating current An induced emf produced by the varying field passes through g ap pick up p coil When breathing stops, the pattern of induced voltages g stabilizes and external monitors sound an alert Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 24