Period 9 Outline: Power
advertisement

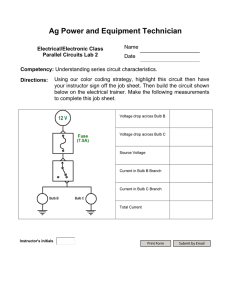
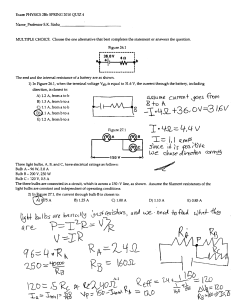
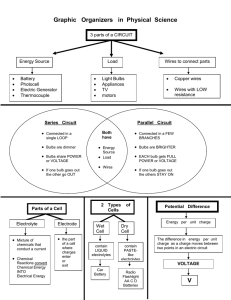
Name _________________________ Section ___________________ 8/8/12 1103 Period 17: Electric Circuits Activity 17.1: What Is the Result of Adding Resistors in Series? 1) Bulbs in series: Use single bulb trays to determine the effect of adding resistors in series. a) Connect a single bulb tray to a 3-battery tray. Note the brightness of the bulb. b) Now connect a second single bulb tray in series with the first bulb. What happens to the brightness of the bulb? ___________________________________________ c) What will happen if you connect a third single bulb tray in series with the first two bulb trays? Prediction: _________________ Answer: ____________________ d) How does the amount of current flowing through the circuit change as more bulbs are added in series? Why? 2) Total series resistance: Next we examine the total resistance of the circuit when resistors are added in series. DISCONNECT THE BATTERIES FROM THE CIRCUIT. Use a digital multimeter to measure the resistances and record the values in the table. Resistors Resistance (in ohms) All 3 bulbs connected together First single bulb tray Second single bulb tray Third single bulb tray a) How does the total resistance of the circuit compare to the resistances of the single bulb trays? b) Group Discussion Question: If the sum of the resistances of the 3 single bulb trays does not equal the resistance of the circuit when all three bulb trays are connected together, why is this so? 103 8/8/12 Activity 17.2: What is the Result of Adding Resistors in Parallel? 3) Bulbs in parallel: Use a 4-bulb try to determine the effect of adding resistors in parallel. a) Connect a 4-bulb tray to a 3-battery tray with connecting wires. Are the bulbs in the tray wired together in series or in parallel? _______________________ Explain how to tell whether bulbs are connected in series or parallel by examining the circuit and by turning individual bulbs off and on. b) Disconnect the battery tray from the 4-bulb tray. Unscrew all but one of the bulbs. Measure the resistance across the entire bulb tray with a digital multimeter. ____________ c) Screw in a second bulb and measure the resistance across the tray. _______________ d) Predict what will happen when the third bulb is screwed in. ________________________ Check your prediction by measuring the resistance. ___________________ e) What happens to the total resistance of a circuit when resistors are added in parallel? Explain why resistors in parallel have this effect. f) A circuit consists of one 4 ohm resistor connected in parallel to a 6 ohm resistor. Calculate the total resistance of the circuit, assuming that these resistors are the only sources of resistance in the circuit. Activity 17.3: What is the Resistance of Humans? 4) Human resistance: Before using the analog multimeter to measure resistance, reset the meter by connecting the two meter leads together and setting the meter scale to zero. Note: the zero setting is at the far right side of the dial. a) Measure the resistance between the hands of each person at your table by firmly gripping a meter lead in each hand. Your resistance will vary depending on how tightly you grip the meter leads and how dry your hands are. Before taking your measurement, dry your hands by rubbing them together. ___________ __________ ___________ ___________ __________ ___________ b) Using hollow metal rods, connect 3 or more people into a series circuit. (Each person holds a rod in one hand and grasps the end of the rod held by the next person.) Measure the resistance of your series circuit with the analog multimeter. ___________________ c) How does the resistance of the circuit compare to the sum of the resistances of the individuals? Series circuit resistance: ________ Sum of individual resistances: _______ 104 Name _________________________ Section ___________________ 8/8/12 d) Using two rods, connect 3 or more people into a parallel circuit. (Each person puts one hand on each of the rods.) Measure the resistance of this parallel circuit. ___________________ e) Would you expect that adding more people (resistors) in parallel would increase or decrease the total resistance of the circuit? Check your prediction. f) Is the total resistance of the parallel circuit less than, equal to, or greater than the resistance of an individual person’s resistance? Activity 17.4: What is an Electric Circuit? 5) Circuit in a flashlight: Examine a flashlight to find the path that the current takes. a) Draw a diagram of the flashlight. Use colored pencils to draw the path the current follows. b) If a flashlight does not work, it must have an open circuit. List problems that could cause an open circuit in a flashlight. 105 Activity 17.5: What Voltage and Current Occurs in Combination Circuits? 8/8/12 6) Voltage across two bulbs in series: Close the switch on the circuit board and unscrew bulb #3, leaving bulb #1 and bulb #2 connected in a series circuit. Close the switch and observe the brightness of the bulbs. a) Measure the total voltage boost of the batteries with a digital multimeter. ________ b) Measure the voltage drop across bulb #1. Record the voltage in the box beside the bulb in the diagram. Repeat for bulb #2. c) Why is the sum of the voltage drops less than the total voltage boost? 7) Current through two bulbs in series: Open the switch and connect one multimeter lead to either side of the switch opening. Change the settings on the meter to measure DC current. a) Measure the current flowing through the circuit. ______________________ b) How much of this current do you think flows through bulb #1? __________________ c) How much flows through bulb #2? ________________________ d) Based on your measurements of voltage and current, how do the resistances of bulbs #1 and #2 compare? Are their resistances approximately equal? ______ 1 e) Explain how you decided that the resistances of bulbs #1 and #2 are or are not approximately equal. 3 106 Bulb #1 voltage _____________ 2 Bulb #2 voltage _____________ 8/8/12 Name _________________________ Section ___________________ 8) Voltage across two bulbs in parallel connected in series to one bulb: Close the switch on the circuit board and in screw in bulb 3. Observe the brightness of all three bulbs. a) Measure the total voltage boost of the batteries with a digital multimeter. ________ b) Measure the voltage drop across bulb #1. Record the voltage in the box beside the bulb in the diagram. Repeat for bulbs #2 and #3. c) Why is the total voltage drop equal to the voltages across bulb #1 plus bulb #2 or the voltages across bulb #1 plus bulb #3? Why is the total voltage drop not equal to the sum of the voltages across bulb #1 plus bulb #2 plus bulb #3? d) Does Vboost = Vdrop apply to all of the bulbs in a circuit, or to only the bulbs in each separate circuit path? 9) Current through two bulbs in parallel connected in series to one bulb: Open the switch and connect one multimeter lead to either side of the switch opening. Change the settings on the meter to measure DC current. a) Are the three bulbs equally bright? If not, which one is the brightest? _____________ b) Measure the current flowing through the circuit. ______________________ c) How does this amount of current compare to the current you measured when only two bulbs were lit? __________________ 1 d) How much of this current flows through bulb #1? __________________ 3 e) If the bulbs are identical, how much current flows through bulb #2? __________ Bulb #1 voltage _____________ 2 Bulb #2 voltage _____________ Bulb #3 voltage _____________ f) How much current flows through bulb #3? ___________ g) Group Discussion Question: Why does more current flow through the circuit when bulb #3 is lit? Explain how adding resistors in parallel changes the resistance of a circuit. 107 8/8/12 108 Name _________________________ Section ___________________ 8/8/12 Period 17 Exercises: Electric Circuits Write answers to the questions below. Show your mathematical steps and the units of the quantities. This sheet with your answers should be turned in at the beginning of Period 18. 1. Relating current and resistance: The circuits below have identical resistors and batteries. Rank the circuits in order From the circuit in which the largest amount of current would flow from the battery to the circuit in which the smallest amount of current would flow from the battery. a) b) c) d) Ranking: ___________ 2. Combining resistors in parallel: A circuit consists of three resistors with resistances of 5.0 ohms and 2.5 ohms and 2.0 ohms. What is the total circuit resistance when these three resistors are connected in parallel? ___________ 3. Analyzing parallel and series circuits: Two identical bulbs #1 and #2 are connected in series to a battery. Identical bulb #3 is added in parallel to bulb #1 as shown in the diagram. #1 #3 #2 a) When bulb #3 is added in parallel to bulb #1, what happens to the brightness of bulb #1? Why does this happen? b) When bulb #3 is added, what happens to the brightness of bulb #2? Why does this happen? 109 8/8/12 110