Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) FETs: Outline
advertisement
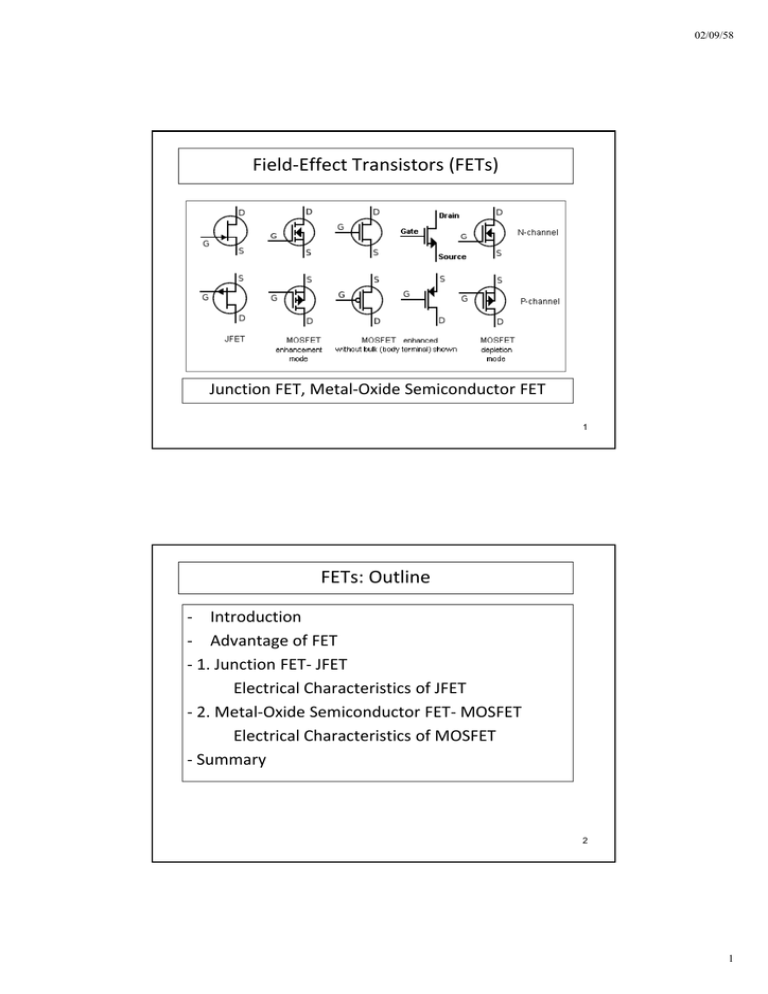
02/09/58 Field‐Effect Transistors (FETs) Junction FET, Metal‐Oxide Semiconductor FET 1 FETs: Outline ‐ Introduction ‐ Advantage of FET ‐ 1. Junction FET‐ JFET Electrical Characteristics of JFET ‐ 2. Metal‐Oxide Semiconductor FET‐ MOSFET Electrical Characteristics of MOSFET ‐ Summary S 2 1 02/09/58 Introduction ‐ BJTs are current‐controlled devices ‐ FETs are voltage‐controlled devices 3 Advantages of FET ‐ Field‐ Effect Transistors or FETs are majority –carrier devices ‐> high speed ‐ 2 main groups of FETs are; >> Junction FETs or JFETs >> Metal‐Oxide Semiconductor FETs or MOSFET 4 2 02/09/58 1. Junction FET: Types ‐ 2 types of JFET: n channel & p channel ‐ Three terminals of FET : Drain (D), Gate (G), & Source (S) 5 Symbols of JFETs ‐ The arrow on the gate points "in" for n channel & "out" for p channel. 6 3 02/09/58 Construction of n‐channel JFETs ‐Water analogy provides a picture for the JFET control at the gate terminal. Gate controls flow from source to drain. 7 JFET in the VGS = 0 V and VDS > 0 V Varying reverse‐bias potentials across the p‐n junction of an n‐channel JFET 8 4 02/09/58 Pinch‐off (VGS = 0 V, VDS = VP) VDS is increased to a level such that the two depletion regions would “touch” (Pinch‐off Voltage; VP ) 9 Current source equivalent for VGS = 0 V, VDS > VP IDSS is the maximum drain current for a JFET and is defined by the conditions VGS = 0 V and VDS > |VP| 10 5 02/09/58 JFET; VGS < 0 V 11 V‐I Characteristic of JFET - n-Channel JFET characteristics with IDSS = 8 mA and VP = -4 V - 3 regions of operation : ohmic, saturation or constant current and cut off 12 6 02/09/58 Voltage Controlled Resistor ‐The region to the left of the pinch‐off locus is referred to as the ohmic or voltage‐controlled resistance region ‐ Can be employed as a variable resistor (used in automatic gain control or AGC) 13 P‐Channel JFET ‐ Same construction with n‐channel JFET except reversal of p‐type and n‐type 14 7 02/09/58 Summary of JFET Max. current Switch off Voltage Controlled Current Source 15 JFET Transfer Characteristics ‐ BJTs have linear relation but JFETs have nonlinear one ‐> Shockley’s equation 16 8 02/09/58 Transfer Curve of JFET ‐ Obtaining the transfer curve from the drain characteristics 17 JFET Forward Transconductance ‐ Or Transfer conductance gm ‐ Depend on DC operating point 18 9 02/09/58 JFET: Operating region ‐ Operating region for linear amplifier 19 Comparison between BJT and JFET 20 10 02/09/58 2. MOSFETs The most popular FETs 21 MOSFETs : SMD package Most hand-held electronic equipment employ SMD enhancement MOSFETs. 22 11 02/09/58 2.1 Enhancement MOSFET: Symbols 23 Enhancement‐Type MOSFET: Construction 24 12 02/09/58 Enhancement‐type MOSFET: Channel Formation 25 E‐type MOSFET : Pinch‐Off ‐There is a pinch‐off near the Drain terminal. h l 26 13 02/09/58 E‐type MOSFET : Drain Characteristic There are minimum gate‐source voltages called Threshold Voltage, VT 27 E‐type MOSFET : Transfer Characteristic 28 14 02/09/58 E‐type MOSFET: If VGS > VT 29 P‐channel enhancement MOSFET 30 15 02/09/58 Complementary MOSFET : CMOS ‐ This is a very useful device as an Inverter Gate. ‐ Power consumption is very low. 31 2.2 Depletion‐Type MOSFET: Symbols 32 16 02/09/58 Depletion‐Type MOSFET: construction 33 D‐type MOSFET: Diffuse Channel D‐type MOSFET can conduct the current at VGS = 0 V 34 17 02/09/58 Drain & Transfer Characteristic of Depletion-type MOSFET D-type MOSFETs have partly JFET and partly E-type MOSFET transfer characteristic 35 Summary of FET Important Characteristics JFET D‐type MOSFET E‐type MOSFET 36 18 02/09/58 FET : Summary ‐ 3‐terminal Devices : Drain, Gate & Source Majority‐Carrier Carrier Devices Devices ‐ Majority ‐ 2 types : n‐channel & p‐channel ‐ 3 regions : Ohmic, Saturation & Cut off ‐ The most popular FET is enhancement‐type MOSFET. 37 19