A Highly Integrated 2.2V RF Frequency Converter with
advertisement
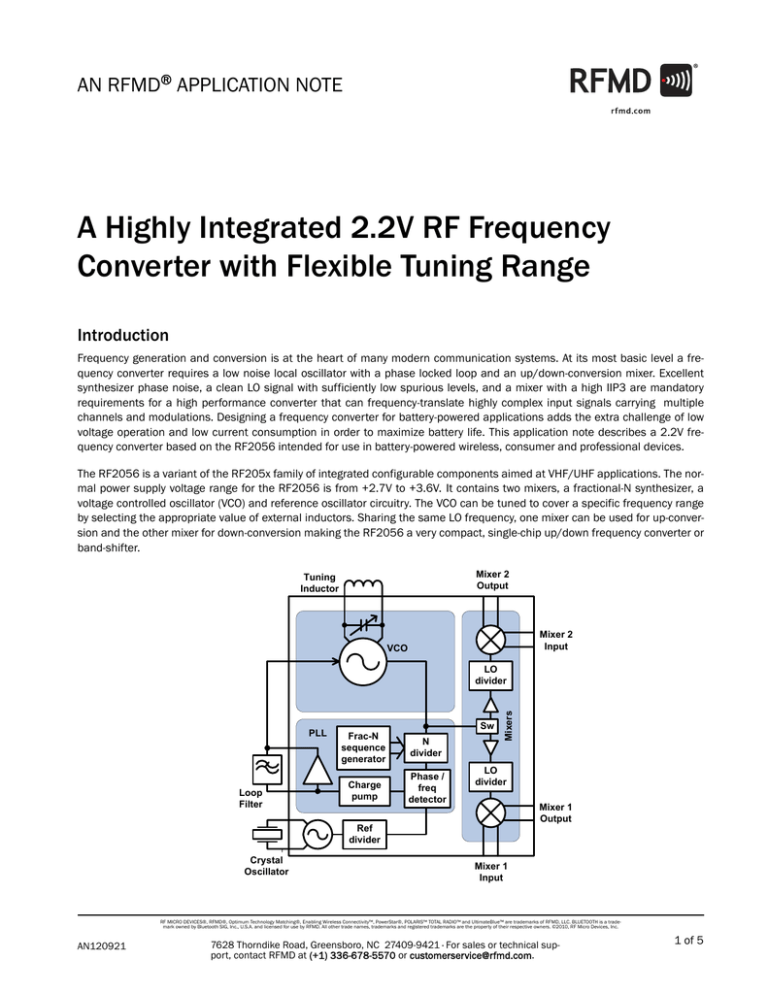
AN RFMD® APPLICATION NOTE A Highly Integrated 2.2V RF Frequency Converter with Flexible Tuning Range Introduction Frequency generation and conversion is at the heart of many modern communication systems. At its most basic level a frequency converter requires a low noise local oscillator with a phase locked loop and an up/down-conversion mixer. Excellent synthesizer phase noise, a clean LO signal with sufficiently low spurious levels, and a mixer with a high IIP3 are mandatory requirements for a high performance converter that can frequency-translate highly complex input signals carrying multiple channels and modulations. Designing a frequency converter for battery-powered applications adds the extra challenge of low voltage operation and low current consumption in order to maximize battery life. This application note describes a 2.2V frequency converter based on the RF2056 intended for use in battery-powered wireless, consumer and professional devices. The RF2056 is a variant of the RF205x family of integrated configurable components aimed at VHF/UHF applications. The normal power supply voltage range for the RF2056 is from +2.7V to +3.6V. It contains two mixers, a fractional-N synthesizer, a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) and reference oscillator circuitry. The VCO can be tuned to cover a specific frequency range by selecting the appropriate value of external inductors. Sharing the same LO frequency, one mixer can be used for up-conversion and the other mixer for down-conversion making the RF2056 a very compact, single-chip up/down frequency converter or band-shifter. Mixer 2 Output Tuning Inductor Mixer 2 Input VCO PLL Loop Filter Sw Frac-N sequence generator N divider Charge pump Phase / freq detector Mixers LO divider LO divider Mixer 1 Output Ref divider Crystal Oscillator Mixer 1 Input RF MICRO DEVICES®, RFMD®, Optimum Technology Matching®, Enabling Wireless Connectivity™, PowerStar®, POLARIS™ TOTAL RADIO™ and UltimateBlue™ are trademarks of RFMD, LLC. BLUETOOTH is a trademark owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc., U.S.A. and licensed for use by RFMD. All other trade names, trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. ©2010, RF Micro Devices, Inc. AN120921 7628 Thorndike Road, Greensboro, NC 27409-9421 · For sales or technical support, contact RFMD at (+1) 336-678-5570 or customerservice@rfmd.com. 1 of 5 A Highly Integrated 2.2V RF Frequency Converter with Flexible Tuning Range The RF2056 will work well to above 1GHz at supply voltages down to +2.2V. Dropping the operating voltage extends the battery life and reduces the current draw in the chip with only marginal degradation in performance. Using an external inductor the VCO can be tuned to run at the LO frequency of choice without using on-chip LO dividers thus further minimizing the current consumption. The mixer bias can also be set to give low current operation, at the expense of linearity. Operating at +2.2V the total power consumption of the synthesizer and one mixer will be typically 105mWatts, making the RF2056 ideal for low power applications. RF2056 Set Up The measurements in this report were made with the following frequency plan, selected to demonstrate the performance at typical RF, IF and LO frequencies: RF in 900MHz IF out 70MHz LO 970MHz Most of the measurements concentrate on the performance at the lowest mixer current setting, MIX_IDD = 1. A standard RF2056 evaluation board was used, reference page 37 of the RF2056 datasheet, with some small modifications as highlighted below. Logic Levels The UM232R USB to serial adaptor is normally set for 3V3 logic. The limit on the RF2056 for the logic high voltage is Vdd + 0.3V, so the logic high level needs to be reduced to track the power supply voltage. This is easily done by removing the link on header J1 of the UM232R adaptor. The VIO pin for the UM232R, pin 4 on J5 of the RF2056 board, is then connected to the digital supply, pin 14 on J5. ENBL Series Resistor To ensure that the ENBL high voltage does not reduce below the logic threshold of 1.5V, the series resistor R21 was changed from 100KΩ to 22KΩ. VCO Inductors Two 3.3nH inductors (L3 and L4) were used in the differential VCO resonator circuit. This sets the VCO3 frequency range of around 850MHz to 1200MHz, with the required frequency of 970MHz coming out near centre in the CT_CAL range. The damping resistor R20 was removed as it is not required for this VCO frequency range. Refer to page 12 of the RF2056 datasheet for guidance on selecting inductor values. AC Coupling The AC coupling capacitors on the RF inputs (C23, C24, C29, and C30) were reduced from 1nF to 100pF in order to improve performance at the RF frequency of 900MHz. The following section presents results for the RF2056 synthesizer and mixers when run at reduced supply voltage, and over the full operating temperature range. The following results were measured on mixer path 1 of the RF2056 evaluation board, from SMA connector J4 to J3. The results include PCB trace and balun losses. AN120921 7628 Thorndike Road, Greensboro, NC 27409-9421 · For sales or technical support, contact RFMD at (+1) 336-678-5570 or customerservice@rfmd.com. 2 of 5 A Highly Integrated 2.2V RF Frequency Converter with Flexible Tuning Range Typical Results Total Supply Current versus Mixer Current Setting Total Supply Current versus Temperature One Mixer Enabled, LO = 970MHz One Mixer Enabled, MIX_IDD = 1, LO = 970MHz 75.0 51.0 50.0 65.0 60.0 MIX_IDD = 1 55.0 MIX_IDD = 2 MIX_IDD = 3 50.0 Supply Current (mA) Supply Current (mA) 70.0 49.0 48.0 47.0 -40C 46.0 +25C MIX_IDD = 4 45.0 +85C MIX_IDD = 5 45.0 40.0 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 44.0 3.2 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 Power Supply (Volts) Power Supply (Volts) Mixer Conversion Gain versus Current Setting Mixer Conversion Gain versus Temperature +25 Degrees C MIX_IDD = 1 -2.0 -2.0 -40C +25C -3.0 +85C Conversion Gain (dB) Conversion Gain (dB) -3.0 -4.0 -5.0 MIX_IDD = 1 MIX_IDD = 2 -4.0 -5.0 -6.0 MIX_IDD = 3 -6.0 -7.0 MIX_IDD = 4 MIX_IDD = 5 -8.0 -7.0 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 2.0 3.2 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.0 3.2 Power Supply (Volts) Power Supply (Volts) Mixer Input IP3 versus Current Setting Mixer Input IP3 versus Temperature +25 Degrees C MIX_IDD = 1 30.0 16.0 14.0 Input IP3 (dBm) Input IP3 (dBm) 25.0 20.0 15.0 MIX_IDD = 1 10.0 12.0 10.0 -40C 8.0 +25C +85C 6.0 MIX_IDD = 2 4.0 MIX_IDD = 3 5.0 MIX_IDD = 4 2.0 MIX_IDD = 5 0.0 0.0 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 Power Supply (Volts) AN120921 2.8 3.0 3.2 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 Power Supply (Volts) 7628 Thorndike Road, Greensboro, NC 27409-9421 · For sales or technical support, contact RFMD at (+1) 336-678-5570 or customerservice@rfmd.com. 3 of 5 A Highly Integrated 2.2V RF Frequency Converter with Flexible Tuning Range Typical Results (continued) Mixer Noise Figure versus Current Setting Mixer Noise Figure versus Temperature MIX_IDD = 1 14.0 12.0 12.0 10.0 Noise Figure (dB) Noise Figure (dB) +25 Degrees C 10.0 8.0 MIX_IDD = 1 MIX_IDD = 2 6.0 MIX_IDD = 3 MIX_IDD = 4 4.0 8.0 -40C +25C 6.0 +85C 4.0 MIX_IDD = 5 2.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 2.0 2.2 2.4 Power Supply (Volts) 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.0 3.2 Power Supply (Volts) Mixer LO Leakage versus Current Setting Mixer LO Leakage versus Temperature LO = 970MHz, +25 Degrees C LO = 970MHz, MIX_IDD = 1 0.0 0.0 -40C -10.0 MIX_IDD = 1 -10.0 +25C +8C LO Leakage (dBm) LO Leakage (dBm) MIX_IDD = 2 MIX_IDD = 3 -20.0 MIX_IDD = 4 MIX_IDD = 5 -30.0 -40.0 -20.0 -30.0 -40.0 -50.0 -50.0 -60.0 -70.0 -60.0 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 2.0 3.2 2.2 RMS Integrated Phase Noise at 970MHz 2.6 2.8 Synthesizer Phase Noise vs Temperature Integration Bandwidth 1KHz to 40MHz +2.2V Supply, 970MHz LO, 26MHz Crystal -60.0 0.7 -40C -70.0 0.6 +25C -80.0 +8C Phase Noise (dBc/Hz) RMS Integrated Phase Noise (Degrees) 2.4 Power Supply (Volts) Power Supply (Volts) 0.5 0.4 0.3 -40C 0.2 +25C -90.0 -100.0 -110.0 -120.0 -130.0 -140.0 +85C -150.0 0.1 -160.0 1.0 0.0 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 10.0 100.0 1000.0 10000.0 100000.0 Offset Frequency (KHz) Power Supply (Volts) AN120921 7628 Thorndike Road, Greensboro, NC 27409-9421 · For sales or technical support, contact RFMD at (+1) 336-678-5570 or customerservice@rfmd.com. 4 of 5 A Highly Integrated 2.2V RF Frequency Converter with Flexible Tuning Range Conclusions The RF2056 can be operated with power supply voltages down to +2.2V, with little impact on performance. The mixer gain and linearity fall slightly, the input IP3 reduced by 1 to 2dB at +2.2V compared to +3.0V. The synthesizer and VCO phase noise are unaffected. It is not recommended to operate at below +2.1V, as the performance starts to drop significantly. Operating with the synthesizer and one mixer enabled at +2.2V consumes a total power of typically just 105mWatts. This represents a 30% reduction on the power consumption at the nominal +3.0V supply. With two mixers enabled (Full Duplex mode) the total power consumption at +2.2V will be around 130mWatts. Summary of typical results at +2.2V (MIX_IDD = 1) Total supply current, one mixer enabled 47mA Total supply current, two mixers enabled 58mA Mixer conversion gain (incl balun loss) -5dB Mixer input IP3 +11dBm Mixer Noise Figure 9dB Synthesizer Integrated PN (1K to 40M) <0.5 RMS AN120921 7628 Thorndike Road, Greensboro, NC 27409-9421 · For sales or technical support, contact RFMD at (+1) 336-678-5570 or customerservice@rfmd.com. 5 of 5