Rev_Circuits KEY
advertisement

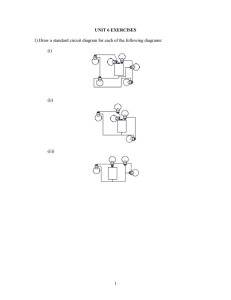
KEY Name: ________________________ 614 Block: ____ Date: ____/____/____ Review: Electric Current and Circuits (614) (KEY) 1. Describe the primary energy transformation takes place with a battery when it is in a circuit. (name at least 2 forms of energy in your explanation) A battery converts CHEMICAL energy into ELECTRICAL energy. 2. A light bulb changes electrical energy into what type(s) of energy? A light bulb changes electrical energy into LIGHT (and HEAT ) energy. 3. Do batteries provide direct current or alternating current? DIRECT CURRENT 4. Do wall outlets provide direct current or alternating current? ALTERNATING CURRENT 5. Draw the schematic symbol used for a battery: 6. Draw the schematic symbol used for a light bulb: 7. Draw the schematic symbol used for a resistor: Standard(s): 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 TA: _____________ Independence Level: __________% Assistance, coaching, prompting: __________________________________________________ 8. Switches: a. Draw the schematic symbol used for a switch. b. What are switches used for and how do they work? Switches are used to turn things on and off. When they are in the off position, the circuit is OPEN and current cannot flow. 9. What does the following symbol represent? What is it used for? A This is a picture of an AMMETER. It is used to measure CURRENT. 10. Series Circuits: a. Draw a circuit diagram (using the symbols learned in class) that shows 2 light bulbs in series. b. If one of the bulbs breaks, what happens to the other bulb? Why does this happen? If one bulb breaks, the other bulb DOES NOT light. This is because there is a BROKEN path. 11. Parallel Circuits: a. Draw a circuit diagram (using the symbols learned in class) that shows 2 light bulbs in parallel. b. If one of the bulbs breaks, what happens to the other bulb? Why does this happen? If one bulb breaks, the other bulb DOES light. This is because there is still an UNBROKEN path. 12. Look at the following diagram. How many amperes of current will flow through the ammeter? SHOW YOUR WORK IN THE SPACE BELOW. 6V Knowns: 2Ω Formula & Calculations: V=6V A A I=? R=2Ω I = 3 Amperes 13. Look at the following diagram. How many amperes of current will flow through the ammeter? SHOW YOUR WORK IN THE SPACE BELOW. 4.5 Ω Formula & Calculations: V = 12 V I=? A A 12 V Knowns: R = 4.5 Ω I = 2.7 Amperes 14. Look at the following diagram. What is the value of the resistor? SHOW YOUR WORK IN THE SPACE BELOW. Formula & Calculations: Knowns: V=9V 9V R=? I = 2.5 A A A 2.5 A R=? R = 3.6 Ohms 15. Look at the following diagram. What is the value of the resistor? SHOW YOUR WORK IN THE SPACE BELOW. Formula & Calculations: 100 V Knowns: R=? V = 100 V I=4A A A 4A R=? R = 25 Ohms 16. What voltage battery should be used so that 0.4 Amperes of current flow through an item with a resistance of 50 ohms? SHOW YOUR WORK! Knowns: Formula & Calculations: V= ? I = 0.4 A R = 50 ohms V = 20 Volts 17. Suppose a light bulb with a resistance of 3 ohms is attached to a 9 volt battery. How much current flows through the light bulb? SHOW YOUR WORK! Knowns: Formula & Calculations: V=9V I=? R = 3 ohms I = 3 Amperes 18. 10 Amps of current flow through an appliance. If the voltage is 120 Volts, what is the power rating of the appliance? SHOW YOUR WORK! Knowns: Formula & Calculations: V = 120 V I = 10 A P = 1200 Watts P=? Key Term Review: Match each term in Column B with its definition in Column A. Write the correct letter in the space provided. Each term is used once and only once. Column A D _______ 1. atomic particle with a negative electric charge I _______ 2. material through which electric charges do not flow easily J _______ 3. flow of electric charges through a conductor Column B a. proton b. alternating current c. parallel circuit d. electron L _______ 4. switch that opens a circuit if too much current is flowing e. electric circuit _______ 5. circuit in which electric current follows only one path F f. series circuit N _______ 6. material through which electric charges flow easily A _______ 7. atomic particle with a positive electric charge _______ 8. current in which electrons change direction at a regular B rate C _______ 9. circuit in which electric current can follow more than one path R _______ 10. the rate at which work is done. O _______ 11. unit used to measure resistance K _______ 12. energy available to move electric charges through a wire E _______ 13. path that an electric current follows P _______ 14. the units used for power G _______ 15. opposition to the flow of electric current M _______ 16. unit used to measure electric current Q _______ 17. the units used for energy H _______ 18. unit used to measure voltage g. resistance h. volt i. insulator j. electric current k. voltage l. circuit breaker m. ampere n. conductor o. ohm p. Watt q. Joule r. power OLD MCAS QUESTIONS: A ______1. An electric circuit is shown below. The accompanying table shows the current measured at different levels of resistance. Resistance (Ω) 0.10 0.50 2.5 10.0 Current (A) 15.0 3.0 0.60 0.15 Based on the data shown in the table, what is the voltage drop across the variable resistor? A. 1.5 V B. 6 V C. 9 V D. 12 V A ______2. Mr. Jenkins constructed a circuit consisting of a variable source, wires, and a resistor. In order to triple the amount of current, how should he change the voltage of the source? A. make the voltage three times larger B. make the voltage one-third as great C. make the voltage nine times larger D. make the voltage one-ninth as great D ______3. What is the voltage in a circuit with a current of 3 Amps and a total resistance of 12 Ω? A. 0.25 V B. 4 V C. 15 V D. 36 V B ______4. The circuit diagram below shows three resistors, an ammeter, and a battery. How much current flows through the ammeter? A. 1.0 A B. 6.0 A C. 13.0 A D. 24.0 C ______5. Students in a physics lab are studying the circuit shown in the diagram below. Which of the following options will double the current through the ammeter? A. replacing the battery with a 5 V battery B. adding a 30 Ω resistor in parallel with R C. replacing the resistor with a 30 Ω resistor D. adding a second 60 Ω resistor in series with R B ______6. A 72 W navigation unit on a commercial aircraft has a 24 V power supply and uses 3 A of electric current. What is the electrical resistance of the navigation unit? A. 4 Ω B. 8 Ω C. 13 Ω D. 22 Ω D ______7. The diagram below shows an incomplete circuit due to a break in the wire at point X. A student is testing materials to see if they conduct electricity. The student places each item shown at position X, making sure the object is in contact with the loose end of each wire. Which item will electricity flow through, causing the bulb to light? C ______8. When a light bulb is turned on, energy changes from one form to another. Which of the following best describes this change? A. sound energy to light energy B. nuclear energy to light energy C. electrical energy to light energy D. magnetic energy to light energy A ______9. Marta has a radio in her room. It requires electricity in order to play. Which of the following is necessary in order for electricity to move from the source to the radio? A. a circuit B. a magnet C. a light bulb D. an insulator D ______10. The figures below show a light bulb connected to a battery in two different ways. When the switch in Figure 1 is closed the bulb will light. A plastic ring is inserted in the circuit as shown in Figure 2. What will happen when the switch is closed in Figure 2? A. The bulb will light just as it did in Figure 1. B. The bulb will be brighter than it was in Figure 1. C. The bulb will light, but will be less bright than it was in Figure 1. D. The bulb will not light at all. MCAS Open Response Questions: Please answer each of the following questions in the boxes below the questions. Label all parts. 1. Look at the objects shown below. Some of these objects are conductors of electricity and some are insulators. a. List all the objects that are conductors. b. List all the objects that are insulators. c. Describe the difference between a conductor of electricity and an insulator of electricity. A. The following items are conductors: -PAPER CLIP -COPPER TUBING -CLOTHES HANGER (ASSUMING IT IS METAL) B. The following items are insulators: -RUBBER BAND -GLASS TUBE C. The difference between a conductor of electricity and an insulator of electricity is that the CONDUCTOR allows charges to flow through it easily while the INSULATOR does not. This is because the electrons in the conductor are LOOSELY bound. Written Response Answer the following questions in complete sentences in the box below the question. 2. Kamaria is hanging a string of decorative lights. When she plugs the lights in, she notices that one light in the string is burned out. The rest of the lights are still lit. Are the lights wired in a series circuit or in a parallel circuit? How do you know? The lights are wired in a PARALLEL circuit. I know this because in a SERIES circuit all of the lights go out when one light goes out. This is because in a SERIES circuit the current has ONLY ONE path to follow, and if a bulb is broken, there is a break in the circuit and CURRENT STOPS EVERYWHERE. In a parallel circuit, when a bulb is broken, there are still other unbroken paths, so the lights still light. 3. What are the forms of energy involved in a simple circuit? There are four major forms of energy involved. Write two to three sentences discussing the energy transformations that take place. CHEMICAL potential energy is stored in the battery. The battery converts the CHEMICAL potential energy to ELECTRICAL energy. The electrons flowing through the wires have KINETIC energy. When the electrons flow through the light bulb, the bulb converts the ELECTRICAL energy into HEAT and LIGHT energy.