ET 304b Laboratory 5 Superposition Theorem With Ac and Dc
advertisement

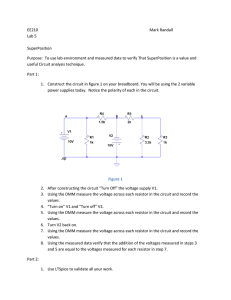
ET 304b Laboratory 5 SuperpositionTheorem With Ac and Dc Sources Objective: Use the Superposition theoremto find the total responseto sinusoidalac and dc inputs. Use an oscilloscopeto measureac waveswith a dc offset. Measurecompositesignals with digital multimetersand determinethe rms valuesof the ac and dc components. Theoretical Background The superpositiontheoremis a techniquefor solving electric circuits that have more than one source. Nodal and meshanalysisalso can find solutionsfor complex networksthat include multiple sources,but requirethe solutionof an entire set of voltagesor currents. Another limitationof thesemethodsis that the sourcesmust all be of the samecurrenttype: ac or dc. The superposition theoremdoesnot havethis limitation,which makesit a valuabletechniquein electroniccircuit design. The superposition theoremonly appliesto linearcircuitsand linearcircuit responses. A circuit must containlinearelementsto be linear. A linearcircuit elementhasa proportional outputfor a given input. Componentsthat follow Ohm'slaw are all linear elements.All componentscoveredin the lecturequalify as linearelements,includingdependentsourcesthat havea linearrelationshipbetweentheir outputandthe controllingparameter.Linear responses arethe currentthroughany branchand the voltagedrop acrossany component.Powercan not be found directlyby superposition becauseit is a non-linearfunctionof currentor voltageand the componentvalue. Superposition is implemented by first identifyingthe circuitresponse of interest.This is the voltageor currentfor which we will solvethe circuit. Unlike the other networktechniquesit will not be necessary to solvefor othervariablesto find this response.The procedurefor using superposition is: l.) de-activeall independentsourcesexceptone. Replacede-activatedvoltagesources by shortcircuitsand de-activated currentsourcesby opencircuits. 2.) Calculatethe desiredresponseof the circuit for the remainingsource. 3.) RepeatstepsI and2 until responses are found for all sourcesin the circuit. 4.) Add the individualresponsefrom eachsourcesto get the total responseto all the circuit sources. Superposition is especiallyusefulin finding the responseof a circuit to combinedac and dc inputs. This is typicalin electroniccircuits. Electroniccircuitsuseactivecomponentssuchas transistorsand integratedcircuitsto amplify ac signals. A dc voltageis necessary for the activecomponentsto operate.The output is generallya compositesignalthat hasboth a dc and ac component.[n practiceit is not possible to de-activatethe dc sourceand measurethe ac responsebecausethe dc bias is necessaryfor circuit operation.It is possibleto measurethe dc outputonly with the ac input de-activated. The oscilloscopecan effectivelymeasurecompositeac and dc signals. It is also possible to measurethe ac componentseparately usingthe oscilloscope.To isolatethe ac signalfrom the dc level,the verticalcouplingswitch mustbe in the properposition.The verticalcouplingswitch is locatedbelow the verticalinputsand hasthreepositions.ac, gnd, dc. The gnd position groundsthe input. The scopechannelis referencedto zerowith the input in this position. The S p r i n g2 0 0 2 exp504b.doc other two positionsdeterminehow the input signalcouplesto the scopesvertical input amplifier. Figure I showsthat with the switch in the ac positionthe input connectsto the vertical amplifier through a capacitor,C6. input Vert.Amp. To vertial deflection circuits FigureL VerticalCouplingSwitchCircuit. The capacitorblocksthe dc componentof the input signalwhile passingthe ac signal. Ac couplingmakesmeasurement of low level ac voltagespossibleeven if a significantdc componentis present. Moving the switchto the ac positionwill block the dc componentand centerthe ac wave aboutthe groundpositionon the display. The ac portioncan now be amplifiedif necessaryby decreasing the V/div scalingof the scopechannel.Placing the couplingswitch in the dc position displaysboth the dc levelsand the superimposed ac level. Ac couplingwill centerany waveformthat hasa dc component,evenpulses. The pulse in Figure2-a goesfrom 0 to +V when dc coupledto the scope.Ac couplingcentersthis wave aboutthe groundreference,as shownin Figure2-b This is not the correctdisplayof the wave sinceit only goespositive. a. ) b.) Figure 2. Effects of Ac ScopeCoupling on positivc Voltage pulses. Digital multimeterscan alsomeasurecompositesignals,but meterconstructionand the type of waveformare a consideration.True rms digital multimetersdisplaythe rms values,or effectivevalue,of the total ac and dc componentsof the signal. The rms uulu" of time vaiying wavesdependson the shapeof the signal. True rms metersaccuratelyrespondto any waveform and displaythe correctrms value. Averagerespondingmultimeterdesignsassumesinusoidalac inputsand calibratethe outputto readcorrectly.Measuringa non-sinusoidal ac wave with an averagerespondingmultimeterproduceserroneousresults. Before measuringac waveswith a DMM, determinewhetherthe instrumentis a true rms or averagerespondingdevice. Also determinethe frequencyresponselimit of the instrument. Instrumentinstructionmanualsusuallycontainthis information. Spring2002 exp504b.doc Procedure Before starting the lab, install 10x probes to both channelsof the scopeand compensatethem. Obtain frequency responseinformation about the DMM used for making the following measurements.Also determine if the DMM is true rms or average responding. 1.) Constructthe circuit in Figure3. Use the sourcetransformationtheoremto find an equivalentac voltage sourcefor the given currentsource. V,r 12Vdc C lrr 0.02uF 2.5mApeak f=5.0kHz Figurc 3. Lab Circuit l. 2.) 3.) 4 .) s.) 6.) De-activatethe 12 Vdc sourceand replaceit with a shortcircuit accordingto the superposition theorem. Measurethe resultingvoltageacrossthe capacitor,V" usingthe scopewith dc couplingand recordthe resultin Table 1. Make the samemeasurement usinga DMM and recordthe resultin Table 1 Find the rms value of the scope measurement by usingthe formulatV,n,,:0.707Vp"ur. De-activatethe equivalentac voltagesourceand replaceit with a short circuit. Activate the dc sourceand measurethe dc voltageappearingacrossthe capacitorwith a oscilloscopeand DMM. Keep the scopein the dc couplingmode. Recordthese measurements in Table l. Activateboth voltagesourcesin the circuit. With the scopein the dc couplingmode, measurethe voltageacrossthe capacitor.Sketchthe traceon the grids provided. Determinethe dc level by measuringthe verticaloffsetfrom ground. Switchthe scopeinput to ac couplingand observethe waveformof V". Sketchthe trace on the grids provided. Measurethe peakvalueof the wave and convertit to rms by using the formula in step2. Solvethe circuit in Figure! usingthe superposition theorem.Find the rms value of the ac responseand the dc level. Enterthesevaluesin Table l. Calculatethepercentageerror betweenthe theoreticalvaluesand the measuredvaluesof the scopeand the DMM measurements usingthe following formula: Spring2002 exp504b.do c Discussion Points Whatis the procedurefor findingvoltagesandcurrentsusingsuperposition? How doesthe verticalcouplingeffectthe displayof the measured voltage?Whattypeof couplingshouldbe dc signalswith the scope?Low levelacwith highleveldc? Ac voltagesonly? usedto measure Do thetheoreticalvaluesmatchthe measured valueswithin component tolerances?Whattypeof DMM is usedfor the experiment: responding? truermsor average Spring2002 exp504b.doc Table l. Circuit I Measurements for Circuit 1' Table2. Enor Percentages o/oErrorDMM o/oErrorScoPq Vc (ac rms) Vc (dc) Circuit2 Rc: Table 3. Circuit 2 Measurements Enor Circuit2' Table4. Percentage o/nF.rror DMM o/oErrorScoPe Vn (ac rms) Vn (dc) exp504b. doc Spring2002 ChannelI Volts/div Itr r ttl ChannelI Volts/div tttl r ll Channel2 Volts/div lt r tl tttl rtl -l tl rrtL Channel2 Volts/div Time/div l ttl rltl tttl II' ttl lll ttl tl tl Time/div Spring2002 exp504b.doc ttll tl rtl ttlt ttl ttl ChannelI Volts/div I ChannelI Voltsidiv Spring2002 ttl ttl Jll ttl ll ttl tttT l ttL I tll ti l tl l ttl l Time/div Channel2 Volts/div ttl til l tf ttL I ttl I ttl Channel2Volts/div ttl l tl ttl Time/div exp504b.doc