Examples of Metals
advertisement

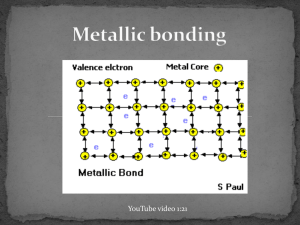
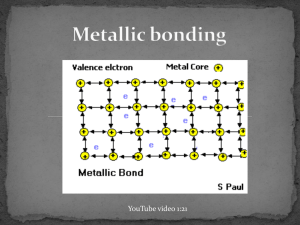
December 03, 2013 Examples of Metals http://www.ndt-ed.org/EducationResources/CommunityCollege/Materials/Introduction/metals.htm http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Native_gold_nuggets.jpg December 03, 2013 Metallic Bonds • In metal atoms, valence electrons are not held tightly to any nuclei • They can move easily from one atom to another and are called delocalized electrons *Metallic bond: Metal nuclei are attracted to delocalized electrons http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nuvola_di_elettroni.svg December 03, 2013 Metallic Bonds • Metals achieve octet by sharing the electrons in its outer shell with multiple other atoms • For example, in Sodium (Na), the 3s orbitals of each sodium atom overlaps the 3s orbitals of 8 other atoms http://www.chemguide.co.uk/atoms/bonding/metallic.html December 03, 2013 Metallic Bonds • Electron sea model: All metal atoms in a metallic solid contribute their valence electrons to form a "sea" of electrons December 03, 2013 Properties of metals: 1. 2. 3. High melting point and boiling point Malleable and ductile Good conductors of heat and electricity December 03, 2013 Melting and Boiling Point • Metallic bonds are strong • Metallic solids have moderately high melting point: > Can vary: Hg (Mercury) is a liquid at room temperature > Most metals are solids at room temperature • Metallic solids have high boiling point December 03, 2013 Malleable and Ductile Malleable: Can hammer into flat sheets Ductile: Can be pulled into a thin wire The electrons are mobile (remember sea of electrons!) so you can push/pull the atoms out of position without breaking the bonds. https://www.uwgb.edu/dutchs/EarthSC202Notes/minerals.htm December 03, 2013 Good conductors of heat and electricity Conducting electricity: remember, you need charged particles that can move. • The delocalized electrons are free to move when an electric current is applied. Conducting heat: delocalized electrons can move heat faster https://www.uwgb.edu/dutchs/EarthSC202Notes/minerals.htm December 03, 2013 Metallic bond strength • Metallic bonds are relatively strong: nuclei of metals are attracted to delocalized electrons • Bond strength depends on the number of delocalized electrons. > More delocalized electrons = stronger bond > transition metals have many delocalized electrons (valence electrons + d sublevel electrons): Very strong bonds, high melting point Which metal would you expect to have a higher boiling point: Na or Mg? Na: 884ºC Mg: 1090ºC December 03, 2013 In the lab, how could you determine if a solid has an ionic bond or a metallic bond?