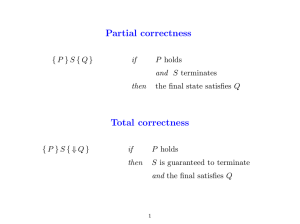
Addendum No. 5 Attachment H - Eastern Municipal Water District
advertisement

SPECIFICATION NO.1197S Addendum No.5 Attachment H TVRWRF Electrical Coordination Studies Page 1 of 2 Specification No. 1197S Addendum No. 5 ATTACHMENT H TABLE OF CONTENTS TVRWRF Electrical Coordination Studies: TVRWRF Power System Analysis Report (dated 9/30/2015 by PES ) Page 2 of 2 Specification No. 1197S Addendum No. 5 September 30,2015 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS REPORT Client: Eastern Municipal Water District 2270 Trumble Road Perris, CA 92572 Sntdy Perþrmed for Location: Temecula Valley R\ryRF Photovoltaic System Installation PES Reference: 48638-1s This leport was prepared by: The results of this study relate only to those items covered in this report and not to the condition or acceptance of any other related equipment. This report shall not be reproduced, except in full, without the written approval of PES. 2703 Saturn Street, Brea,CA,9282l Telephone (714) 524-9100 Facsimile (714) 528-8782 www.pespower.com September 30, 2015 PES No.4863B-15 EMWD/Aro Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Dianne Kilwein, P,E. Civil Engineer Eastern Municipal Water District 2270 Trumble Road Perris, CA92572 Subject: Eastern Municipal Water District Temecula Valley RWRF Photovoltaic System Power System Analysis Dear Ms. Kilwein, Power Engineering Sewices, Inc. (PES) performed a Power System Analysis, inclucling Short Circuit and Protective Device Coordination Studies, and an Arc Flash Hazard Assessment for the Eastern Municipal Water District Photovoltaic System at Temecula Valley RWRF as requested and in accordance with the PES proposal. This analysis includecl all of the electrical equipment operating at 480V and 2401120V, including new switchboards, new step-up/step-down transformers, and new panelboards. Data for the analysis were collected from construction drawings and manufacturer's submittals and shop drawings. The results of the Power System Analysis relate only to those items covered in this report. This report shall not be reproducecl, except in full, without the written approval of PES. If you have any questions concerning this report, please clo not hesitate to contact our office. Cordially, 2703 Saturn Street, Brea,CA,9282l Telephone (714) 524-9100 Facsirnile (714) 528-8182 'ù/ww.pespower.com September 30,2015 PES No.48638-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Report Certification Page No Eol2¿185 I hereby certify that this engineering document was prepared by me or under rny direct personal supervision and that I am a duly licensed Professional Engineer under the laws of the State of California. 3a Douglas E. Effenberger, P.E. License Number: E-0 I 2485 License Expiration: September 30, 2017 2703 Saturn Street, Brea, CA 92821 Telephone (714) 524-9100 Facsimile (714) 528-8782 www.pespower.com %E September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Contents Page EXECUTIVE SUMMARY .................................................................................................................... 1 1.0 GENERAL.................................................................................................................................... 4 1.1 Purpose ................................................................................................................................... 4 1.2 Scope ...................................................................................................................................... 4 1.3 Analytical Software ................................................................................................................ 4 1.4 Study Notes and Assumptions ................................................................................................ 5 2.0 SHORT CIRCUIT STUDY ........................................................................................................ 6 2.1 General ................................................................................................................................... 6 2.2 Short Circuit Model Simplifications ...................................................................................... 7 2.3 Short Circuit Study Results .................................................................................................... 7 3.0 PROTECTIVE DEVICE COORDINATION STUDY ............................................................ 8 3.1 General ................................................................................................................................... 8 3.2 Calibration and Testing of Protective Devices ....................................................................... 8 3.3 Recommended Protective Device Settings............................................................................. 8 4.0 ARC FLASH HAZARD STUDY ............................................................................................. 11 4.1 General ................................................................................................................................. 11 4.2 SKM Arc Flash Module Calculation Assumptions .............................................................. 12 4.3 SKM Arc Flash Module Study Options ............................................................................... 13 4.4 Arc Flash Hazard Study Results ........................................................................................... 14 5.0 PROJECT RECOMMENDATIONS ....................................................................................... 16 APPENDIX A APPENDIX B APPENDIX C APPENDIX D APPENDIX E APPENDIX F APPENDIX G SHORT CIRCUIT INPUT DATA & CALCULATION RESULTS, 30 pages SELECTED TIME-CURRENT CURVES, 13 pages ARC FLASH CALCULATIONS, 7 pages UTILITY SHORT CIRCUIT DUTY, 2 pages GLOSSARY, 3 pages INVERTER TECHNICAL DATA, WITH SHORT CIRCUIT CONTRIBUTION, 1 page SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS DEVELOPED FOR STUDIES, 4 pages Table of Contents, Page 1 of 1 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Background The Power System Analysis included Short Circuit, Protective Device Coordination, and Arc Flash Hazard studies of electrical equipment at Eastern Municipal Water District Temecula Valley RWRF. This study includes new equipment to be installed as part of a facility photovoltaic installation. The Short Circuit study investigated the ability of equipment to interrupt and withstand a short circuit occurrence. The Protective Device Coordination study determined the selective operation of protective devices to assure the device closest to a fault or overload operates in order to minimize the number of apparatus that are affected. The Arc Flash Hazard assessment calculated the amount of energy that would be released in the event of an arcing short circuit at each equipment location. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) was then specified based on the available arc energy and other factors such as the operating voltage of the equipment. PPE must be utilized by personnel performing work on electrical equipment, unless the equipment has been de-energized and confirmed to be safe by lock-out and tag-out testing procedures. Data Gathering Data for the analysis were collected from construction drawings, manufacturer’s submittals and shop drawings. The data gathered included electrical plan and single-line drawings, equipment details, and protective device ratings. Available fault current at the utility services was provided by Southern California Edison. Short Circuit Study A short circuit study was performed in order to determine the maximum available short circuit current at each equipment component included in this study. The calculated values of short circuit current were compared to the equipment short circuit ratings. Equipment must have a withstand or interrupting rating that exceeds the calculated value of short circuit current in order to safely withstand the occurrence of a short circuit. If a device is subjected to short circuit currents greater in magnitude than its ratings, equipment damage and injury to personnel are likely. The short circuit study showed that all system components studied were suitably rated for the available short circuit current. All devices in the system had a withstand or interrupting rating that exceeded the worst-case calculated short circuit current, in compliance with California Electrical Code 110.9. Page 1 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Protective Device Coordination Study The goal of the Protective Device Coordination study is to provide proper coordination and time separation between the operation of protective devices. Proper coordination among protective devices will minimize the amount of equipment that would be affected by a short circuit or overload event. In the event of a short circuit or overload, the protective device closest to the short circuit should operate when devices are properly coordinated. In the event that the closest device does not clear the short circuit the next upstream device should then operate. Recommended protective device settings for adjustable devices are provided in Section 3 of this report. The recommended protective device settings will provide coordination between upstream and downstream circuit breakers, as well as minimize Arc Flash incident energy values. Arc Flash Hazard Study The Arc Flash Hazard study determines the incident energy and flash hazard boundary resulting from an arcing short circuit. Warning labels for the equipment were produced as part of this study that identify Arc Flash hazards, including approach boundaries, shock hazard boundaries, and required PPE to be worn by personnel working on the equipment while it is energized. The following equipment had calculated incident energies above 8.0 cal/cm2. Incident energies above 8.0 cal/cm2 require personnel to wear arc flash hazard suits with an arc rating that matches or exceeds the incident energy calculated and printed on the arc flash warning label. Reduction of the incident energy values at the following equipment is not readily feasible due to either relatively low available fault current, or lack of adjustable settings on protective devices such as thermal-magnetic circuit breakers and fuses. However, additional barriers and guards can be installed on equipment to provide enhanced protection against accidental contact with energized equipment parts. Refer to Section 4.4 for more details. Equipment ACDS-1 PNL-1 PNL-2 TR-1 Secondary TR-2 Primary (480V) Incident Energy Value 23 34 21 35 15 For all equipment, personnel must use PPE with an arc rating that meets or exceeds the incident energy printed on the arc flash warning label. Note that the arc flash incident energies are valid only when the recommended circuit breaker settings in Section 3.3 are applied. Page 2 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Validity Statement This Power System Study and Arc Flash Hazard assessment is accurate as of the date of this report for the equipment installed as shown on the attached one-line drawings. Changes to the electrical system circuits, including system impedance, short-circuit duty, voltage, or fault clearing times, will invalidate this study and require re-evaluation, calculation, and installation of new warning labels. This study should be updated on a regular basis and at intervals no greater than allowed by applicable Codes and standards. Page 3 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 1.0 GENERAL 1.1 Purpose The purpose of this power system study was to identify and establish the arc flash hazards at the Eastern Municipal Water District Temecula Valley RWRF new photovoltaic system electrical equipment. Arc flash hazards were identified and calculated. Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements applying to each component within the scope of work for this study were determined. Warning labels were provided that comply with 2014 CEC and 2015 NFPA 70E requirements in effect as of this report date for arc flash hazards. 1.2 Scope The scope of the Arc Flash study is limited to: • Temecula Valley RWRF new electrical equipment for the new photovoltaic system. • 480V switchboards, 12kV-480V transformers, 480V panelboards, and 480V inverters. • Determination of short circuit fault currents available at the electrical components within the scope of the study. • Comparison of the calculated short circuit current values to the short circuit current ratings of the equipment within the scope of the study. • Providing recommended settings for protective devices. • Determination of Arc Flash incident energy available at the electrical components within the scope of the study. • Listing required arc rating of personal protective equipment (PPE) in accordance with NFPA 70E to be worn by personnel while working on energized equipment. The scope of the Arc Flash study does not include: • Building and site electrical equipment and systems not listed above. • Evaluation of the competency of design of the electrical distribution system. • Evaluation of the adequacy of design of the electrical distribution system. • Evaluation of compliance of electrical distribution installation to California Code of Regulations Title 24, Part 3, California Electrical Code (CEC), NFPA 70, National Electric Code (NEC), or local codes. • Evaluation of workmanship of electrical distribution system installation. • Evaluation of the material condition of the electrical distribution system components. 1.3 Analytical Software The software package used for modeling the system and performing all of the studies was SKM Power Tools, version 7.0.4.4. Page 4 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 1.4 Study Notes and Assumptions • • • SKM did not have a library file in the program for the XHHW conductors specified for this project. Copper conductors with THHN/THWN insulation were used for circuits 600V and below unless otherwise noted. The variance concerns the type of insulation used over the conductor; not the conductor itself, and will not significantly affect the results of the studies presented in this report. The 1600A model LCL fuses used in the 1600A disconnect are shown in the study reports as “Federal Pacific”. Federal Pacific’s fuse line was acquired by Edison Fuse Products, which was later acquired by Cooper/Eaton. Eaton is providing the electrical equipment for this project, including the LCL fuses. The time-current characteristics have not changed for this particular model of fuse. All overcurrent protective devices will perform as designed by the manufacturer, and operate according to the manufacturer’s published time-current curves. Page 5 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 2.0 SHORT CIRCUIT STUDY 2.1 General The purpose of the Short Circuit Study is to determine the levels of bolted fault current that can flow in an electrical system when a fault occurs at a specific location in that system. Arc flash calculations use this level of bolted fault current for determining arcing fault current and incident energy levels. Circuit breakers and fuses must have an interrupting rating which exceeds the maximum bolted fault current available at its location. Equipment such as switchboards and panelboards must have a withstand rating of equal or greater value than the calculated bolted fault current. The Short Circuit Study models the electrical system impedance by determining an equivalent impedance for all system components and then calculates bolted fault current at various busses. The short-circuit duty is a function of the utility short circuit capacity, on-site source contributions such as motors and generators, and system impedance from cables and transformers. Bus locations may be identified by referring to the one-line diagram in Appendix G of this report. Two short circuit study cases were calculated: The first case uses the short circuit current calculated by Solar City and the design engineer of record, the second case uses the short circuit current calculated by Southern California Edison (SCE) in 2013. The value of current calculated by Solar City was 64,174A at 480V. The values calculated by SCE were 25,500A 3phase, 27,300A single phase to ground, at 480V. As long as the main service switchboard or service equipment is not upgraded, the short circuit values calculated by SCE should still be valid. The much larger value of short circuit current provided by Solar City is most likely based on an infinite bus value of the largest utility transformer sized for the full 3,000A rating of the existing 480V switchboard. Short circuit values using the infinite bus method yield conservatively high values of current, and will be the “worst case” values calculated. The values provided by SCE are based on the rating of the utility service transformer presently installed, which is frequently rated less than the full-load rating of the customer switchboard. Refer to Appendix D for values calculated by SCE. Utilities typically install a smaller-rated transformer due to the fact that most customers have a peak electrical demand much less than the full-load rating of the customer’s main service. Even though the short circuit value provided by Solar City may be higher than what can be provided with presently installed service equipment, the value is useful for specifying interrupting ratings of equipment. If the utility service is upgraded in the future, the equipment installed for the photovoltaic system will still have an adequate interrupting rating, and will not require component replacement as long as the EMWD switchboard is not upgraded. PES ran four study cases which considered the short circuit duties calculated by SCE and Solar city, as well as short circuit current contribution from the photovoltaic arrays: Page 6 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 1. Short circuit values calculated by Solar City, no photovoltaic contribution. 2. Short circuit values calculated by SCE, no photovoltaic contribution. 3. Short circuit values calculated by Solar City, photovoltaic contribution per the inverter datasheet. Per the inverter datasheet, the maximum short circuit contribution from the inverter is 69.6A three-phase, 52.9A single line to ground. The inverter will only conduct short circuit current for one cycle. After a maximum of 20ms, the inverter will stop conducting current. Refer to Appendix F for the short circuit contribution from the inverter. 4. Short circuit values calculated by Solar City, photovoltaic contribution per the inverter datasheet. Per the inverter datasheet, the maximum short circuit contribution from the inverter is 69.6A three-phase, 52.9A single line to ground. The inverter will only conduct short circuit current for one cycle. After a maximum of 20ms, the inverter will stop conducting current. Refer to Appendix F for the short circuit contribution from the inverter. 2.2 Short Circuit Model Simplifications A number of conventional simplifying assumptions were used to establish a system model that reasonably represents the magnitude of fault current the system is capable of producing. The assumptions generally produce a conservative or worst case set of values. The major assumptions utilized in this study include the following: • • • • • • 2.3 Fault current calculations include initial symmetrical fault with ½ cycle asymmetrical contribution. Available fault current values at the utility services were obtained from Southern California Edison and Solar City construction drawings, and are assumed to be valid for the system model and conditions of this study. Protective device impedances and equipment bus impedances were neglected. Pre-fault voltages were set at 1.0 per unit. Impedance elements remain constant during a system fault. Reported fault levels represent three-phase and single-line-to-ground bolted faults. Short Circuit Study Results The results of the short circuit study identified that all components included in this study were suitably rated for the available fault current under both study cases. Using both the short circuit values calculated by Solar City, and the values calculated by SCE, each device had a withstand or interrupting rating that met or exceeded the calculated available fault current, in accordance with California Electrical Code 110.9. For complete results of the Short Circuit study, including source and impedance ratings input into the model and calculation results, refer to Appendix A of this report. Bus locations may be identified by referring to the one-line diagram in Appendix G of this report. Page 7 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 3.0 PROTECTIVE DEVICE COORDINATION STUDY 3.1 General The primary function of electrical power system fault protective devices is to detect a fault current and to isolate the fault by activating the proper interrupting device. A fault should be removed as quickly as possible by the closest upstream protective device to minimize fault damage, maintain maximum service continuity, and protect property and personnel. 3.2 Calibration and Testing of Protective Devices Current transformer ratios and sensor devices must be verified before making any changes to protective device settings. After verification, protective devices can be set to provide the characteristic curves shown in the appropriate TCC. In general, the specified settings will provide operation of the devices as shown. However, equipment tolerances and possible defects in device operation may result in deviations from the desired operating times. Therefore the device settings should be calibrated by field tests to help assure the desired response. Coordination depends on operation of the protective devices as shown, though the devices may be normally inactive for long periods. To assure continuing device coordination, it is essential that all protective devices are maintained, tested, and calibrated at regular intervals, as recommended by the manufacturer. 3.3 Recommended Protective Device Settings Recommended settings are provided below for all adjustable circuit breakers. Non-adjustable circuit breakers and fuses are not listed below. The recommended settings will minimize arc flash incident energy by minimizing breaker trip time, while maintaining device coordination between main and feeder protective devices. These recommended protective device settings should be programmed during equipment testing and commissioning. Relay/Breaker Description Settings Existing Recommended MSB2 Main Circuit Breaker (In Existing Main Switchboard) Square D SE, 3000A Micrologic LIG Trip Unit LTPU LTD INST GFPU GFD 1 11 5 1200A, I2t OFF 0.5 1 11 3 1200A, I2t OFF 0.5 Relay/Breaker Description Settings Existing Recommended EPPDP2 Circuit Breaker (In Existing Main Switchboard) Square D NE, 1200A Micrologic LI Trip Unit LTPU LTD INST 1 24 8 1 24 6 Page 8 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Relay/Breaker New PNL-2 Main Circuit Breaker Description Cutler-Hammer SBS-616, 1600A RMS520 LSI Trip Unit Settings LTPU LTD STPU STD INST GFPU GFD 2 Recommended 1 4 6 0.4, I t 10 0.75 0.4, I2T (1600A) OFF (1200A) OFF Breaker Description Settings Recommended LC-06 Feeder Circuit Breaker (In PNL-2) Cutler-Hammer HKD, RMS310+ LS trip unit, 400AF, 300AT LTPU (IR) LTD (tR) STPU (Isd) E (300) 10 10 Relay/Breaker New PNL-1 Main Circuit Breaker (In PNL-2) Description Cutler-Hammer NGH, 1000A RMS 310+ LSI Trip Unit Settings LTPU LTD STPU STD INST (IR) (tR) (Isd) (tsd) Recommended G 4 8 300ms, I2t 12 (1000A) OFF Breaker Description Settings Recommended LC-01 Feeder Circuit Breaker (In PNL-1) Cutler-Hammer HJD, 225A Magnetic Trip 10 (2250A) Breaker Description Settings Recommended LC-02 Feeder Circuit Breaker (In PNL-1) Cutler-Hammer HJD, 225A Magnetic Trip 10 (2250A) Breaker Description Settings Recommended LC-03 Feeder Circuit Breaker (In PNL-1) Cutler-Hammer HJD, 175A Magnetic Trip 10 (1750A) Breaker Description Settings Recommended LC-04 Feeder Circuit Breaker (In PNL-1) Cutler-Hammer HJD, 175A Magnetic Trip 10 (1750A) Page 9 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Breaker Description Settings Recommended LC-05 Feeder Circuit Breaker (In PNL-1) Cutler-Hammer HJD, 175A Magnetic Trip 10 (1750A) Time-Current Curve plots of protective devices analyzed in this study are included in Appendix B of this report. Page 10 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 4.0 ARC FLASH HAZARD STUDY 4.1 General The arc flash hazard study determines the incident energy and flash hazard boundary resulting from an arcing fault. Required PPE is then selected based on incident energy levels. Warning labels are then produced that identify arc flash hazards, approach boundaries, and PPE ratings to be worn by personnel working on the equipment while it is energized. Work on energized parts exceeding 50 volts to ground may only be done in accordance with Article 130.2 of the 2015 NFPA 70E. “Energized electrical conductors and circuit parts shall be put into an electrically safe work condition before an employee performs work if any of the following conditions exist: (1) The employee is within the limited approach boundary. (2) The employee interacts with equipment where conductors or circuit parts are not exposed but an increased likelihood of injury from an exposure to an arc flash hazard exists.” The Arc Flash module of SKM Power Tools was used for calculation of incident energy. The IEEE 1584 calculation method was used, along with the guidelines in the 2015 edition of NFPA 70E as a basis for this study. Arc flash calculations require available three-phase bolted fault current values and protective device clearing times. SKM utilizes the three-phase bolted fault values computed in the short circuit study, and then determines arcing fault current. This arcing fault current is used to determine protective device clearing time based on time-current curves issued by the device manufacturer and stored in the SKM CAPTOR library. The SKM Arc Flash module scans the entire system topology, starting from the faulted bus out, to find the first protective device with an over-current trip curve. The upstream protective device(s) was also included in the search by selecting the "Check upstream devices for miscoordination" option within the SKM Arc Flash module. Upstream refers to the flow of power from the primary sources to the faulted location from the perspective of standing at the fault location. If there are multiple contributions to the faulted bus, the search process will be repeated until each contribution is cleared by its protective device, or the search reaches the end of the topology. Protection devices with a function name of "Ground" or "Neutral" were excluded from the protective device search. Using the arcing fault current and protective device clearing time, incident energy values are calculated by SKM based on IEEE 1584 and NFPA 70E standards. Page 11 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 4.2 SKM Arc Flash Module Calculation Assumptions • • • • • • • • • • • • Arc Flash calculations were performed using the short circuit current calculated by Solar City, and the values calculated by SCE. The worst-case incident energies from both cases were used. Calculation results are listed in Appendix C, along with a note describing which case produced the worst-case incident energy values. The trip time is determined from the TCC curves stored in the SKM CAPTOR library for all protective devices located in the branch that contains the faulted bus, and the device with the fastest trip time for the given arcing fault current is used. A constant working distance is assumed. The worker is stationary during the entire arc flash incident. When applying generic current-limiting fuse representation, the current-limiting range is assumed to start where the fuse clearing curve drops below 0.01 sec. When applying generic current-limiting fuse representation, fuses operating in the current limiting range are assumed to clear in ½ cycle for currents 1 to 2 times the current where the current-limiting range begins, and ¼ cycle for currents higher than 2 times the current where the current-limiting range begins. For purposes of the arc flash study, the interrupting device is rated for the available short circuit current. No equipment damage is considered due to the available fault current exceeding the protective device’s interrupting rating. Equipment that is underrated for the available bolted fault current should be replaced with devices that meet or exceed the available bolted fault current in order to prevent equipment damage and injury to personnel. The next upstream protective devices were included in the search. The device that clears the arcing fault fastest is used. Ground fault and motor over load devices are excluded. For multi-function protective devices, only time and instantaneous phase overcurrent protective devices (ANSI devices 50 and 51) are used to determine the trip time. Only the larger incident energy based on low or high protective device tolerances is reported. When the total fault current cleared is less than the threshold percent specified in the study setup, or no upstream protective device is found, the bus is labeled as Dangerous and the incident energy and flash boundary are not reported. If the trip time obtained from the time current curve is larger than the maximum protection trip time defined in the study setup, the maximum protection trip time is used. Page 12 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 4.3 SKM Arc Flash Module Study Options Page 13 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 4.4 Arc Flash Hazard Study Results The following equipment had calculated incident energies above 8.0 cal/cm2. Incident energies above 8.0 cal/cm2 require personnel to wear arc flash hazard suits with an arc rating that matches or exceeds the incident energy calculated and printed on the arc flash warning label. Equipment ACDS-1 PNL-1 PNL-2 TR-1 Secondary TR-2 Primary (480V) Incident Energy Value 23 34 21 35 15 For all equipment, personnel must use PPE with an arc rating that meets or exceeds the incident energy printed on the arc flash warning label. Note that the arc flash incident energies are valid only when the recommended circuit breaker settings in Section 3.3 are applied. The incident energies in the table above can not be reduced due to the impedance of transformers TR-1 and TR-2 reducing the available fault current, which increases the time required for protective devices to interrupt the arc. Incident energies at the equipment above also can not be reduced due to the lack of adjustable settings on devices such as thermalmagnetic circuit breakers or fuses. The relatively high hazard risk category at TR-1 and TR-2 exists on the exposed 480V lugs. In the event of an arc flash on the transformer 480V lugs, the Page 14 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF transformer’s 12kV fuses would be called upon to interrupt the arc. The transformer’s impedance results in a lower magnitude of fault current seen by the primary fuses, which results in an increased opening time of the fuses, longer arc duration, and more heat energy released from the arc. The Hazard Risk Category can not be reduced because the transformer primary fuses have been selected by the manufacturer. The primary fuses must be properly sized to accommodate the transformer’s inrush current. Smaller fuses may not withstand the inrush current of the transformer. Replacement of the backup current-limiting fuses requires transformer disassembly. Therefore, reduction of the Hazard Risk Category by changing the protective devices is not feasible. Installation of insulating shields over the exposed 480V terminals within the transformer compartment will help prevent accidental contact with exposed energized parts, and reduce the chances of an arc flash occurring within the transformer’s 480V compartment. Insulating boots can be installed over the transformer lugs, or a sheet of insulating material such as fiberglass could be installed in the compartment. Drop-on insulating boots that cover the transformer 480V terminals are available from manufacturers such as Thomas and Betts. The Arc Flash Hazard at the transformer 480V terminals can also be avoided by de-energizing the transformer from an upstream disconnect. At PNL-1 and PNL-2, insulating shields that protect the terminals of the main circuit breakers are available from Eaton/Cutler-Hammer, the manufacturer of the equipment installed as part of this project. Insulating shields should be installed over the circuit breaker terminals if they are not already provided from the factory. Since the photovoltaic system will be tapped into the line side of Switchboard MSB main breaker, there is no 480V protection at this tap. The tap, from the point of connection to the 1600A fused disconnect, should NOT be exposed while the systems are energized. Warning labels advising against access to the tap while the system is energized should be affixed at the point of the tap. Southern California Edison (SCE) should be contacted to disconnect service prior to starting work on the tap at the line side of the 1600A disconnect. SCE requirements for the interconnection of the photovoltaic system may require this tap to be sealed by the utility, preventing access by facility personnel. No energized work shall be performed on the service entrance equipment and conductors, or the line side of the main circuit breaker. Contact Southern California Edison to perform deenergization of services before starting work on the line side of a service main circuit breaker. In order for the Arc Flash Hazard study results to be valid, the recommended protective device settings for the main circuit breaker should be programmed and tested by a qualified electrical testing company. Refer to Appendix C of this report for complete Arc Flash calculations performed at each equipment location included in this study. Page 15 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 5.0 PROJECT RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Apply Recommended Protective Device Settings It is recommended to program circuit breaker settings given in Section 3.3 of this report. Applying the recommended protective device settings in Section 3.3 of this report will provide optimal device coordination between the main and feeder circuit breakers, while minimizing arc flash incident energies. 2. De-energized Electrical Work Policy Establish the policy of working on electrical equipment that has been de-energized whenever feasible. The directive for avoiding work on energized equipment is listed in NFPA 70E - Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace -Justification for Work. “Live parts to which an employee might be exposed shall be put into an electrically safe work condition before an employee works on or near them, unless the employer can demonstrate that de-energizing produces additional or increased hazards or is infeasible due to equipment design or operational limitations.” Working on electrical equipment that has been established as being in an electrically safe condition, in accordance with NFPA 70E, Article 120, eliminates the Arc Flash hazard and electrical shock hazard for most electrical equipment. By working on de-energized equipment whenever feasible, the exposure of personnel to Arc Flash and shock hazards is reduced. 3. Develop Arc Flash Hazard Management Program 1) PPE with a minimum Arc Thermal Performance Value (ATPV) of 8 calories is recommended as daily wear for qualified employees routinely involved in electrical maintenance. 2) PPE suitable for work on equipment with higher incident energies than 8 calories must be provided. 3) Determine training requirements for various employee work responsibilities. Identify qualified employees versus unqualified employees, and develop electrical safety training tailored to the qualifications of employees. 4) Determine and publish Arc Flash Hazards Management Program policies. 5) Implement program. Page 16 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 4. Require and implement PPE and Protective Measure Policies against Arc Flash Hazards Provide and require employees to practice and implement policies for use of proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for work in all areas of Arc Flash hazards, as required by the facility Arc Flash Hazard Management Program. Qualified employees properly wearing PPE according to the calculated incident energy will mitigate injuries experienced by an arc flash. “Employers must provide workers with appropriate PPE as per the OSHA 29 1910.132 (h)(1) PPE payment requirement, i.e., (PPE) used to comply with this part, shall be provided by the employer at no cost to employees. Paragraph (h) became effective February 13, 2008, and employers must implement the PPE payment requirements no later than May 15, 2008.” Provide clearly visible Arc Flash boundary markings so personnel know when they are entering an Arc Flash zone and the PPE required prior to entering the Arc Flash zone (movable cones, tape, etc.). Boundary markings will help prevent unqualified personnel from entering an Arc Flash or shock hazard boundary while work is performed on energized equipment. 5. Project Validation and Maintenance In order to maintain a safe and compliant facility, it is imperative that the Arc Flash study is updated as changes are made to the electrical distribution system. Changes in the electrical system including impedance, protective device settings, and short circuit duties will affect the incident energy values calculated in this report. As a result, changes in the electrical system will invalidate these values. Procedures for keeping this analysis up-to-date include, but are not limited to, updating the single-line diagrams for the electrical distribution system, recalculating the Short Circuit Study, the Coordination Study and the Arc Flash Hazard Assessment and updating the equipment warning labels to incorporate the latest results. Perform a complete review of all engineering studies performed as part of this Power System Analysis at a minimum of every 5 years, or as required by future NFPA 70E requirements. The review should include all recorded changes to the electrical infrastructure. If there are changes to hazard levels, then equipment should be re-labeled appropriately. Inaccurate incident energies and insufficient PPE can result in serious injury to personnel. By keeping the Arc Flash Hazard Analysis valid and up-to-date, personnel can use proper safety equipment to mitigate hazards. The risk of injury to personnel is minimized when employees have the knowledge of the dangers in the workplace and utilize the right safety equipment to diminish those dangers. Page 17 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 6. Provide Training of Arc Flash/Shock Hazards to Workers Provide adequate training and rules governing the work and hazards on all electrical equipment for both Qualified and Unqualified employees. Personnel must be adequately trained to read Arc Flash/Shock hazard warnings and how to prepare themselves for the dangers of an Arc Flash/Shock hazard. By providing training, hazard notification, and PPE, the electrical system will be compliant with OSHA and NFPA regulations regarding Arc Flash hazards as of this report date. The risk of injury to employees as a result of shock/arc flash will be mitigated when employees are aware of hazards and have taken necessary precautions for working on electrical equipment, including, but not limited to, wearing proper PPE and establishing approach boundaries. 7. Develop an Overcurrent Protective Device (OCPD) Management Program Implement a comprehensive OCPD Management Program. Establish a Circuit Breaker Maintenance program in accordance with manufacturer’s recommendations for testing and maintenance. Require all future maintenance and replacement of fuses and circuit breakers to use the same make and model number for replacement components. The Arc Flash Hazard study depends on operation of the protective devices as shown on the manufacturer’s TCC curves. These devices may be normally inactive for long periods. It is essential that all protective devices and associated relays and sensors are tested and calibrated at regular intervals, as recommended by the manufacturer. The calculated Arc Flash hazard levels in the facility electrical distribution system are dependent on the fault clearing times of the actual fuse types (UL Classifications) and circuit breaker types and their trip settings installed in the system. All maintenance changes to OCPDs must be recorded in writing, i.e., red-lined drawings and drawing revisions. In order to maintain the integrity of this Arc Flash Study, all changes to OCPDs will require future re-calculation of incident energy levels to determine new hazard levels. OCPD coordination in the electrical distribution system is dependent on the fuses, circuit breakers and trip settings currently installed, and recommended. Replacement of protective devices with units that are not identical will affect system protection device coordination, and may adversely affect incident energies calculated in this report. A documented program of scheduled circuit breaker testing and maintenance will ensure that the circuit breakers are in operational condition and that they will function properly during a short circuit condition. Periodic testing of circuit breakers and associated relays ensures proper operation of the circuit breaker’s protective function. Without circuit breaker maintenance, Arc Flash Hazards can increase significantly over time due to slow opening response times of dirty or worn mechanisms, even with no changes to the electrical system. Page 18 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF 8. Equipment Maintenance Buildup of debris in equipment enclosures poses a risk of a short circuit, flashover, and/or equipment failure. In addition, electrical connections can become loose over time. Loose electrical connections can cause high-resistance heating of conductors and connecting devices, and pose a fire hazard. The protective device operating mechanism must be lubricated and exercised to assure proper operation. Periodically de-energize and operate protective equipment and perform maintenance as recommended in 2013 NFPA 70B, “Recommended Practice for Electrical Equipment Maintenance.” Clean interior of equipment enclosures. Check bolted connections for proper torque, that all electrical connections are secure, and perform any other maintenance per manufacturer’s instructions. Maintain a log of maintenance and inspections performed. Page 19 of 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF APPENDIX A SHORT CIRCUIT INPUT DATA, CALCULATION RESULTS DAPPER Fault Analysis Input Report (English) – CASE 1 Utilities Contribution From Name Bus Name TEMEC SCE SERVICE BUS-0048 In/Out Nominal Voltage In 480 -------- Contribution Data -------Duty Units X/R 3P: SLG: 64,174 Amps 64,174 Amps 3.53 4.16 PU (100 MVA Base) R PU X PU Pos: 0.511 Zero: 0.293 1.803 1.860 Cables Cable Name From Bus To Bus In/Out Qty Service /Ph Length Feet ------ Cable Description -----Per Unit (100 MVA Base) Size Cond. Type Duct Type Insul R pu jX pu BUS-TEMEC MSB2 BUS-0048 TEMEC MAIN S In 1 2 1600 Copper Busway Epoxy Pos: Zero: 0.0080 0.0475 0.0042 0.0223 BUS-TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC ACDS-1 TEMEC PNL-2 In 1 3 1600 Copper Busway Epoxy Pos: Zero: 0.0120 0.0712 0.0063 0.0335 CBL-TEMEC AC-01 TEMEC TR-1 SEC TEMEC PNL-1 In 4 50 300 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.2517 0.7932 0.2675 0.6586 CBL-TEMEC AC-02 TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC TR-2 S In 4 50 300 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.2517 0.7932 0.2675 0.6586 CBL-TEMEC AC-03 BUS-0048 TEMEC ACDS-1 In 5 20 500 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.0510 0.1608 0.0809 0.1991 CBL-TEMEC AC-MV TEMEC TR-2 PRI TEMEC TR-1 PR In 1 1,300 1 Copper Non-Magnetic EPR Pos: Zero: 0.1444 0.2296 0.0488 0.1240 CBL-TEMEC GATEW TEMEC MONITOR In TEMEC GATEWA 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC INV 1A TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1A In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1B TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1B In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1C TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1C In 1 45 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.9453 6.2715 0.9121 2.3203 CBL-TEMEC INV 1D TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1D In 1 45 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.9453 6.2715 0.9121 2.3203 CBL-TEMEC INV 1E TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1E In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1F TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1F In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 Page A - 1 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF CBL-TEMEC INV 1G TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1G In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1H TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1H In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1I TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1I In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1J TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1J In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1K TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1K In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1L TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1L In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1 TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1M In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1N TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1N In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1O TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1O In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1P TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1P In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1Q TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1Q In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1R TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1R In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1S TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1S In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1T TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1T In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1U TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1U In 1 240 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 21.0417 Zero: 33.4479 4.8646 12.3750 CBL-TEMEC INV 1V TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1V In 1 270 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 23.6719 Zero: 37.6289 5.4727 13.9219 CBL-TEMEC INV 2A TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2A In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 2B TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2B In 1 35 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 7.7474 Zero: 12.3396 0.8325 2.1176 CBL-TEMEC INV 2C TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2C In 1 65 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 14.3880 Zero: 22.9165 1.5460 3.9327 CBL-TEMEC INV 2D TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2D In 1 95 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 21.0286 Zero: 33.4933 2.2595 5.7478 Page A - 2 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF CBL-TEMEC INV 2E TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2E In 1 125 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 27.6693 Zero: 44.0701 2.9731 7.5629 CBL-TEMEC INV 2F TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2F In 1 155 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 34.3099 Zero: 54.6469 3.6866 9.3780 CBL-TEMEC INV 2G TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2G In 1 170 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 37.6302 Zero: 59.9353 4.0434 10.2856 CBL-TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-01 In 1 40 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 1.1111 3.5017 0.8628 2.1250 CBL-TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-02 In 1 160 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 4.4444 Zero: 14.0069 3.4514 8.5000 CBL-TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-03 In 1 305 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.4722 Zero: 26.7007 6.5792 16.2031 CBL-TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-04 In 1 405 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 11.2500 Zero: 35.4551 8.7363 21.5156 CBL-TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-05 In 1 505 350 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.2852 Zero: 26.1048 10.7619 26.4993 CBL-TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC LC-06 In 1 50 400 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.7726 2.4349 1.0634 2.6172 CBL-TEMEC METE TEMEC METER TEMEC TR-2 S In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC MON TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC MONITOR In 1 15 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 12.1745 Zero: 38.3685 0.5924 1.4590 CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 MO TEMEC PNL-1 G In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 M In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 2-Winding Transformers Xformer Name In/Out Service ------------------Primary & Secondary--------------Bus Conn. Volts FLA Nominal kVA Z PU (100 MVA Base) R pu jX pu TEMEC GATEWAY XF In TEMEC GATEWAY DI D TEMEC GATEWAY WG 480 240 2 5 2.0 Pos: 824.3500 Zero: 824.3500 1,600.150 1,600.150 TEMEC PNL-1 GATEW In TEMEC PNL-1 GATEW D TEMEC PNL-1 GATE WG 480 240 2 5 2.0 Pos: 824.3500 Zero: 824.3500 1,600.150 1,600.150 TEMEC TR-1 In TEMEC TR-1 PRIMAR D TEMEC TR-1 SECON WG 12,000 480 40 1,010 750.0 Pos: Zero: 1.4321 1.4321 7.5045 7.5045 TEMEC TR-2 In TEMEC TR-2 PRIMAR D TEMEC TR-2 SECON WG 12,000 480 40 1,010 750.0 Pos: Zero: 1.4296 1.4296 7.4915 7.4915 Page A - 3 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF ***************** F A U L T A N A L Y S I S S U M M A R Y – CASE 1***************** --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------BUS NAME VOLTAGE AVAILABLE FAULT CURRENT L-L 3 PHASE X/R LINE/GRND X/R TEMEC ACDS-1 480. 61173.3 3.4 64203.85 3.6 TEMEC GATEWAY DISC SW 480. 5710.8 0.1 3386.36 0.1 TEMEC INV 1A 480. 6015.9 2.5 6716.15 2.0 TEMEC INV 1B 480. 5856.5 2.2 6433.29 1.7 TEMEC INV 1C 480. 5645.6 2.1 6075.24 1.7 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1D 1E 1F 1G 1H 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 5645.6 5425.6 5068.8 4552.2 4552.2 2.1 1.9 2.0 1.4 1.4 6075.24 5720.39 4979.44 4288.91 4288.91 1.7 1.5 1.4 1.1 1.1 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1I 1J 1K 1L 1M 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 4611.9 4611.9 4231.5 4131.2 3838.9 1.6 1.6 1.6 1.5 1.3 4368.83 4368.83 3751.52 3637.59 3321.93 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.1 1.0 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1N 1O 1P 1Q 1R 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 3838.9 3790.0 3705.7 3461.3 3461.3 1.3 1.5 1.4 1.2 1.2 3321.93 3197.02 3111.17 2872.20 2872.20 1.0 1.1 1.0 0.9 0.9 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1S 1T 1U 1V 2A 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 3760.3 3688.4 2557.6 2437.6 25156.8 2.0 1.8 1.0 0.9 0.9 3263.49 3186.12 2105.96 2001.30 20513.36 1.5 1.4 0.9 0.8 0.8 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 2B 2C 2D 2E 2F 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 12210.6 7349.8 5235.4 4061.5 3316.3 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.2 0.2 9969.97 6036.44 4314.07 3353.46 2741.84 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.2 0.2 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV 2G LC-01 LC-02 LC-03 LC-04 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 3037.4 6312.4 5323.9 4433.6 3961.5 0.2 3.5 2.5 1.9 1.7 2512.54 7268.77 5360.66 3991.86 3378.07 0.2 2.9 1.8 1.3 1.2 480. 3902.4 2.3 3421.86 1.7 TEMEC LC-05 Page A - 4 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF ***************** F A U L T A N A L Y S I S S U M M A R Y – CASE 1***************** --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------BUS NAME VOLTAGE AVAILABLE FAULT CURRENT L-L 3 PHASE X/R LINE/GRND X/R TEMEC LC-06 480. 37052.3 2.2 31093.84 1.8 TEMEC MAIN SWGR 480. 63962.5 3.5 67572.37 3.8 TEMEC METER 480. 12934.5 0.3 8018.47 0.2 TEMEC MONITOR J-BOX 480. 9261.0 0.2 5568.83 0.1 TEMEC PNL-1 480. 6704.2 4.3 8138.36 4.1 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWAY DISC SW PNL-1 MONITOR J-BOX PNL-2 TR-1 PRIMARY TR-1 SECONDARY TEMEC TR-2 PRIMARY TEMEC TR-2 SECONDARY 480. 480. 480. 12000. 480. 4403.3 5560.0 60881.2 481.6 6824.7 0.9 1.5 3.3 4.0 4.5 12000. 480. 485.5 52058.5 4.3 2.6 3438.45 5242.17 63652.48 0.5 0.9 3.5 8414.10 4.6 52948.31 2.6 *********************** FAULT ANALYSIS REPORT COMPLETED ********************************* Page A - 5 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF DAPPER Fault Analysis Input Report (English) – CASE 2 Utilities Contribution From Name Bus Name TEMEC SCE SERVICE BUS-0048 In/Out Nominal Voltage In 480 -------- Contribution Data -------Duty Units X/R 3P: SLG: 25,500 Amps 27,300 Amps 5.25 6.22 PU (100 MVA Base) R PU X PU Pos: 0.883 Zero: 0.333 4.634 3.783 Cables Cable Name From Bus To Bus In/Out Qty Service /Ph Length Feet ------ Cable Description -----Per Unit (100 MVA Base) Size Cond. Type Duct Type Insul R pu jX pu BUS-TEMEC MSB2 BUS-0048 TEMEC MAIN S In 1 2 1600 Copper Busway Epoxy Pos: Zero: 0.0080 0.0475 0.0042 0.0223 BUS-TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC ACDS-1 TEMEC PNL-2 In 1 3 1600 Copper Busway Epoxy Pos: Zero: 0.0120 0.0712 0.0063 0.0335 CBL-TEMEC AC-01 TEMEC TR-1 SEC TEMEC PNL-1 In 4 50 300 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.2517 0.7932 0.2675 0.6586 CBL-TEMEC AC-02 TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC TR-2 S In 4 50 300 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.2517 0.7932 0.2675 0.6586 CBL-TEMEC AC-03 BUS-0048 TEMEC ACDS-1 In 5 20 500 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.0510 0.1608 0.0809 0.1991 CBL-TEMEC AC-MV TEMEC TR-2 PRI TEMEC TR-1 PR In 1 1,300 1 Copper Non-Magnetic EPR Pos: Zero: 0.1444 0.2296 0.0488 0.1240 CBL-TEMEC GATEW TEMEC MONITOR In TEMEC GATEWA 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC INV 1A TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1A In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1B TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1B In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1C TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1C In 1 45 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.9453 6.2715 0.9121 2.3203 CBL-TEMEC INV 1D TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1D In 1 45 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.9453 6.2715 0.9121 2.3203 CBL-TEMEC INV 1E TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1E In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1F TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1F In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1G TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1G In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1H TEMEC LC-02 In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC 6.6406 0.7135 Page A - 6 Pos: September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF TEMEC INV 1H Zero: 10.5768 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1I TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1I In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1J TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1J In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1K TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1K In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1L TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1L In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1 TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1M In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1N TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1N In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1O TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1O In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1P TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1P In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1Q TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1Q In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1R TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1R In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1S TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1S In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1T TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1T In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1U TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1U In 1 240 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 21.0417 Zero: 33.4479 4.8646 12.3750 CBL-TEMEC INV 1V TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1V In 1 270 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 23.6719 Zero: 37.6289 5.4727 13.9219 CBL-TEMEC INV 2A TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2A In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 2B TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2B In 1 35 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 7.7474 Zero: 12.3396 0.8325 2.1176 CBL-TEMEC INV 2C TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2C In 1 65 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 14.3880 Zero: 22.9165 1.5460 3.9327 CBL-TEMEC INV 2D TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2D In 1 95 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 21.0286 Zero: 33.4933 2.2595 5.7478 CBL-TEMEC INV 2E TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2E In 1 125 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 27.6693 Zero: 44.0701 2.9731 7.5629 Page A - 7 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF CBL-TEMEC INV 2F TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2F In 1 155 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 34.3099 Zero: 54.6469 3.6866 9.3780 CBL-TEMEC INV 2G TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2G In 1 170 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 37.6302 Zero: 59.9353 4.0434 10.2856 CBL-TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-01 In 1 40 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 1.1111 3.5017 0.8628 2.1250 CBL-TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-02 In 1 160 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 4.4444 Zero: 14.0069 3.4514 8.5000 CBL-TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-03 In 1 305 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.4722 Zero: 26.7007 6.5792 16.2031 CBL-TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-04 In 1 405 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 11.2500 Zero: 35.4551 8.7363 21.5156 CBL-TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-05 In 1 505 350 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.2852 Zero: 26.1048 10.7619 26.4993 CBL-TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC LC-06 In 1 50 400 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.7726 2.4349 1.0634 2.6172 CBL-TEMEC METE TEMEC METER TEMEC TR-2 S In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC MON TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC MONITOR In 1 15 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 12.1745 Zero: 38.3685 0.5924 1.4590 CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 MO TEMEC PNL-1 G In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 M In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 2-Winding Transformers Xformer Name In/Out Service ------------------Primary & Secondary--------------Bus Conn. Volts FLA Nominal kVA Z PU (100 MVA Base) R pu jX pu TEMEC GATEWAY XF In TEMEC GATEWAY DI D TEMEC GATEWAY WG 480 240 2 5 2.0 Pos: 824.3500 Zero: 824.3500 1,600.150 1,600.150 TEMEC PNL-1 GATEW In TEMEC PNL-1 GATEW D TEMEC PNL-1 GATE WG 480 240 2 5 2.0 Pos: 824.3500 Zero: 824.3500 1,600.150 1,600.150 TEMEC TR-1 In TEMEC TR-1 PRIMAR D TEMEC TR-1 SECON WG 12,000 480 40 1,010 750.0 Pos: Zero: 1.4321 1.4321 7.5045 7.5045 TEMEC TR-2 In TEMEC TR-2 PRIMAR D TEMEC TR-2 SECON WG 12,000 480 40 1,010 750.0 Pos: Zero: 1.4296 1.4296 7.4915 7.4915 Page A - 8 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF ***************** F A U L T A N A L Y S I S S U M M A R Y – CASE 2***************** --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------BUS NAME VOLTAGE AVAILABLE FAULT CURRENT L-L 3 PHASE X/R LINE/GRND X/R TEMEC ACDS-1 480. 25027.0 5.0 29232.58 5.2 TEMEC GATEWAY DISC SW 480. 5469.8 0.3 3335.38 0.2 TEMEC INV 1A 480. 5282.1 2.8 6100.36 2.2 TEMEC INV 1B 480. 5166.1 2.4 5876.65 1.9 TEMEC INV 1C 480. 5003.9 2.3 5578.59 1.8 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1D 1E 1F 1G 1H 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 5003.9 4838.2 4549.4 4150.0 4150.0 2.3 2.1 2.2 1.6 1.6 5578.59 5287.19 4650.76 4061.04 4061.04 1.8 1.6 1.6 1.2 1.2 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1I 1J 1K 1L 1M 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 4190.4 4190.4 3872.8 3792.6 3555.7 1.8 1.8 1.8 1.7 1.4 4123.72 4123.72 3571.28 3470.65 3188.84 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.2 1.0 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1N 1O 1P 1Q 1R 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 3555.7 3504.4 3435.3 3232.7 3232.7 1.4 1.6 1.5 1.3 1.3 3188.84 3068.70 2991.30 2774.12 2774.12 1.0 1.2 1.1 1.0 1.0 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1S 1T 1U 1V 2A 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 3467.4 3408.7 2439.0 2331.9 16724.7 2.1 2.0 1.1 1.0 1.5 3118.04 3049.04 2053.95 1955.21 15707.14 1.6 1.5 0.9 0.9 1.3 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 2B 2C 2D 2E 2F 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 10415.0 6797.2 4985.3 3922.5 3228.8 0.7 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.3 9030.29 5747.02 4181.37 3278.80 2694.39 0.6 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.3 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV 2G LC-01 LC-02 LC-03 LC-04 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 2965.7 5496.5 4742.1 4032.7 3643.6 0.2 3.8 2.7 2.1 1.8 2473.48 6531.11 4968.05 3781.72 3230.84 0.2 3.1 1.9 1.4 1.3 480. 3582.6 2.4 3258.47 1.8 TEMEC LC-05 Page A - 9 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF ***************** F A U L T A N A L Y S I S S U M M A R Y – CASE 2***************** --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------BUS NAME VOLTAGE AVAILABLE FAULT CURRENT L-L 3 PHASE X/R LINE/GRND X/R TEMEC LC-06 480. 19934.2 3.4 19996.75 2.7 TEMEC MAIN SWGR 480. 25469.8 5.2 29744.62 5.4 TEMEC METER 480. 11181.2 0.6 7636.78 0.3 TEMEC MONITOR J-BOX 480. 8497.4 0.4 5405.09 0.2 TEMEC PNL-1 480. 5787.3 4.6 7214.08 4.4 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWAY DISC SW PNL-1 MONITOR J-BOX PNL-2 TR-1 PRIMARY TR-1 SECONDARY TEMEC TR-2 PRIMARY TEMEC TR-2 SECONDARY 480. 480. 480. 12000. 480. 4071.4 4967.3 24983.0 375.0 5876.2 1.0 1.6 5.0 4.5 4.8 12000. 480. 377.3 23447.0 4.8 4.2 3334.09 4930.42 29162.75 0.6 1.0 5.1 7428.23 4.8 27266.34 4.1 *********************** FAULT ANALYSIS REPORT COMPLETED ********************************* Page A - 10 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF DAPPER Fault Analysis Input Report (English) – CASE 3 Utilities Contribution From Name Bus Name In/Out Nominal Voltage -------- Contribution Data -------Duty Units X/R PU (100 MVA Base) R PU X PU INVERTER 1A SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1A In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1B SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1B In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1C SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1C In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1D SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1D In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1E SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1E In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1F SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1F In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1G SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1G In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1H SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1H In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1I SC CONTRIB TEMEC INV 1I In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1J SC CONTRIB TEMEC INV 1J In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1K SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1K In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1L SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1L In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1M SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1M In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1N SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1N In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1O SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1O In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1P SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1P In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1Q SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1Q In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 Page A - 11 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF INVERTER 1R SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1R In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1S SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1S In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1T SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1T In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1U SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1U In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1V SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1V In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2A SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2A In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2B SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2B In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2C SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2C In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2D SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2D In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2E SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2E In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2F SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2F In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2G SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2G In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 TEMEC SCE SERVICE In 480 3P: SLG: 64,174 Amps 64,174 Amps 3.53 4.16 Pos: 0.511 Zero: 0.293 BUS-0048 1.803 1.860 Cables Cable Name From Bus To Bus In/Out Qty Service /Ph Length Feet ------ Cable Description -----Per Unit (100 MVA Base) Size Cond. Type Duct Type Insul R pu jX pu BUS-TEMEC MSB2 BUS-0048 TEMEC MAIN S In 1 2 1600 Copper Busway Epoxy Pos: Zero: 0.0080 0.0475 0.0042 0.0223 BUS-TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC ACDS-1 TEMEC PNL-2 In 1 3 1600 Copper Busway Epoxy Pos: Zero: 0.0120 0.0712 0.0063 0.0335 CBL-TEMEC AC-01 TEMEC TR-1 SEC TEMEC PNL-1 In 4 50 300 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.2517 0.7932 0.2675 0.6586 CBL-TEMEC AC-02 TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC TR-2 S In 4 50 300 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.2517 0.7932 0.2675 0.6586 CBL-TEMEC AC-03 BUS-0048 TEMEC ACDS-1 In 5 20 500 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.0510 0.1608 0.0809 0.1991 Page A - 12 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF CBL-TEMEC AC-MV TEMEC TR-2 PRI TEMEC TR-1 PR In 1 1,300 1 Copper Non-Magnetic EPR 0.1444 0.2296 0.0488 0.1240 CBL-TEMEC GATEW TEMEC MONITOR In TEMEC GATEWA 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC INV 1A TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1A In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1B TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1B In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1C TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1C In 1 45 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.9453 6.2715 0.9121 2.3203 CBL-TEMEC INV 1D TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1D In 1 45 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.9453 6.2715 0.9121 2.3203 CBL-TEMEC INV 1E TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1E In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1F TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1F In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1G TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1G In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1H TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1H In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1I TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1I In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1J TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1J In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1K TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1K In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1L TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1L In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1 TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1M In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1N TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1N In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1O TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1O In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1P TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1P In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1Q TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1Q In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1R TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1R In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 Page A - 13 Pos: Zero: September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF CBL-TEMEC INV 1S TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1S In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1T TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1T In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1U TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1U In 1 240 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 21.0417 Zero: 33.4479 4.8646 12.3750 CBL-TEMEC INV 1V TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1V In 1 270 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 23.6719 Zero: 37.6289 5.4727 13.9219 CBL-TEMEC INV 2A TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2A In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 2B TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2B In 1 35 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 7.7474 Zero: 12.3396 0.8325 2.1176 CBL-TEMEC INV 2C TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2C In 1 65 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 14.3880 Zero: 22.9165 1.5460 3.9327 CBL-TEMEC INV 2D TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2D In 1 95 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 21.0286 Zero: 33.4933 2.2595 5.7478 CBL-TEMEC INV 2E TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2E In 1 125 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 27.6693 Zero: 44.0701 2.9731 7.5629 CBL-TEMEC INV 2F TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2F In 1 155 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 34.3099 Zero: 54.6469 3.6866 9.3780 CBL-TEMEC INV 2G TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2G In 1 170 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 37.6302 Zero: 59.9353 4.0434 10.2856 CBL-TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-01 In 1 40 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 1.1111 3.5017 0.8628 2.1250 CBL-TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-02 In 1 160 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 4.4444 Zero: 14.0069 3.4514 8.5000 CBL-TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-03 In 1 305 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.4722 Zero: 26.7007 6.5792 16.2031 CBL-TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-04 In 1 405 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 11.2500 Zero: 35.4551 8.7363 21.5156 CBL-TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-05 In 1 505 350 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.2852 Zero: 26.1048 10.7619 26.4993 CBL-TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC LC-06 In 1 50 400 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.7726 2.4349 1.0634 2.6172 CBL-TEMEC METE TEMEC METER TEMEC TR-2 S In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC MON TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC MONITOR In 1 15 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 12.1745 Zero: 38.3685 0.5924 1.4590 Page A - 14 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 MO TEMEC PNL-1 G In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 M In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 2-Winding Transformers Xformer Name In/Out Service ------------------Primary & Secondary--------------Bus Conn. Volts FLA Nominal kVA Z PU (100 MVA Base) R pu jX pu TEMEC GATEWAY XF In TEMEC GATEWAY DI D TEMEC GATEWAY WG 480 240 2 5 2.0 Pos: 824.3500 Zero: 824.3500 1,600.150 1,600.150 TEMEC PNL-1 GATEW In TEMEC PNL-1 GATEW D TEMEC PNL-1 GATE WG 480 240 2 5 2.0 Pos: 824.3500 Zero: 824.3500 1,600.150 1,600.150 TEMEC TR-1 In TEMEC TR-1 PRIMAR D TEMEC TR-1 SECON WG 12,000 480 40 1,010 750.0 Pos: Zero: 1.4321 1.4321 7.5045 7.5045 TEMEC TR-2 In TEMEC TR-2 PRIMAR D TEMEC TR-2 SECON WG 12,000 480 40 1,010 750.0 Pos: Zero: 1.4296 1.4296 7.4915 7.4915 Page A - 15 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF ***************** F A U L T A N A L Y S I S S U M M A R Y – CASE 3***************** --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------BUS NAME VOLTAGE AVAILABLE FAULT CURRENT L-L 3 PHASE X/R LINE/GRND X/R TEMEC ACDS-1 480. 62769.8 3.2 65433.27 3.5 TEMEC GATEWAY DISC SW 480. 5711.0 0.1 3386.21 0.1 TEMEC INV 1A 480. 6999.8 1.9 7519.94 1.6 TEMEC INV 1B 480. 6751.9 1.7 7132.16 1.4 TEMEC INV 1C 480. 6468.0 1.6 6695.43 1.4 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1D 1E 1F 1G 1H 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 6468.0 6154.3 5818.2 5090.6 5090.6 1.6 1.5 1.6 1.2 1.2 6695.43 6244.95 5471.37 4617.74 4617.74 1.4 1.2 1.2 0.9 0.9 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1I 1J 1K 1L 1M 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 5193.7 5193.7 4784.8 4647.9 4260.6 1.3 1.3 1.4 1.3 1.1 4731.06 4731.06 4076.36 3939.32 3566.63 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.0 0.9 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1N 1O 1P 1Q 1R 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 4260.6 4275.1 4162.4 3843.9 3843.9 1.1 1.3 1.2 1.0 1.0 3566.63 3480.03 3377.79 3097.21 3097.21 0.9 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.8 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1S 1T 1U 1V 2A 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 4266.3 4167.2 2766.9 2628.4 25486.7 1.6 1.5 0.9 0.8 0.9 3573.57 3478.76 2239.95 2125.14 20724.91 1.3 1.3 0.8 0.8 0.8 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 2B 2C 2D 2E 2F 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 12309.0 7419.3 5298.1 4121.6 3375.0 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.2 0.2 10043.46 6090.31 4362.92 3400.24 2787.55 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.2 0.2 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV 2G LC-01 LC-02 LC-03 LC-04 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 3095.7 7484.4 6202.2 5067.5 4508.8 0.2 2.5 1.9 1.6 1.4 2557.89 8317.60 5967.86 4370.16 3698.23 0.2 2.3 1.5 1.2 1.1 480. 4465.9 1.9 3770.22 1.5 TEMEC LC-05 Page A - 16 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF ***************** F A U L T A N A L Y S I S S U M M A R Y – CASE 3***************** --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------BUS NAME VOLTAGE AVAILABLE FAULT CURRENT L-L 3 PHASE X/R LINE/GRND X/R TEMEC LC-06 480. 37908.9 2.1 31626.13 1.8 TEMEC MAIN SWGR 480. 65533.5 3.3 68790.51 3.7 TEMEC METER 480. 12960.5 0.3 8022.58 0.2 TEMEC MONITOR J-BOX 480. 9263.7 0.2 5568.76 0.1 TEMEC PNL-1 480. 8017.6 2.9 9475.04 3.0 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWAY DISC SW PNL-1 MONITOR J-BOX PNL-2 TR-1 PRIMARY TR-1 SECONDARY TEMEC TR-2 PRIMARY TEMEC TR-2 SECONDARY 480. 480. 480. 12000. 480. 4650.4 6162.2 62481.4 531.4 8124.7 0.7 1.1 3.2 3.3 3.0 12000. 480. 535.0 53568.7 3.5 2.5 3485.01 5481.00 64876.42 0.4 0.7 3.4 9772.68 3.3 54007.04 2.5 *********************** FAULT ANALYSIS REPORT COMPLETED ********************************* Page A - 17 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF DAPPER Fault Analysis Input Report (English) – CASE 4 Utilities Contribution From Name Bus Name In/Out Nominal Voltage -------- Contribution Data -------Duty Units X/R PU (100 MVA Base) R PU X PU INVERTER 1A SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1A In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1B SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1B In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1C SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1C In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1D SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1D In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1E SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1E In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1F SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1F In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1G SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1G In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1H SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1H In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1I SC CONTRIB TEMEC INV 1I In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1J SC CONTRIB TEMEC INV 1J In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1K SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1K In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1L SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1L In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1M SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1M In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1N SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1N In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1O SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1O In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1P SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1P In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1Q SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1Q In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 Page A - 18 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF INVERTER 1R SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1R In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1S SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1S In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1T SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1T In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1U SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1U In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 1V SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 1V In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2A SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2A In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2B SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2B In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2C SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2C In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2D SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2D In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2E SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2E In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2F SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2F In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 INVERTER 2G SC CONTRI TEMEC INV 2G In 480 3P: SLG: 70 Amps 53 Amps 1.00 1.00 Pos: 1,222. 1,222.0 Zero: 2,379. 2,379.3 TEMEC SCE SERVICE In 480 3P: SLG: 25,500 Amps 27,300 Amps 5.25 6.22 Pos: 0.883 Zero: 0.333 BUS-0048 4.634 3.783 Cables Cable Name From Bus To Bus In/Out Qty Service /Ph Length Feet ------ Cable Description -----Per Unit (100 MVA Base) Size Cond. Type Duct Type Insul R pu jX pu BUS-TEMEC MSB2 BUS-0048 TEMEC MAIN S In 1 2 1600 Copper Busway Epoxy Pos: Zero: 0.0080 0.0475 0.0042 0.0223 BUS-TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC ACDS-1 TEMEC PNL-2 In 1 3 1600 Copper Busway Epoxy Pos: Zero: 0.0120 0.0712 0.0063 0.0335 CBL-TEMEC AC-01 TEMEC TR-1 SEC TEMEC PNL-1 In 4 50 300 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.2517 0.7932 0.2675 0.6586 CBL-TEMEC AC-02 TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC TR-2 S In 4 50 300 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.2517 0.7932 0.2675 0.6586 CBL-TEMEC AC-03 BUS-0048 TEMEC ACDS-1 In 5 20 500 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.0510 0.1608 0.0809 0.1991 Page A - 19 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF CBL-TEMEC AC-MV TEMEC TR-2 PRI TEMEC TR-1 PR In 1 1,300 1 Copper Non-Magnetic EPR 0.1444 0.2296 0.0488 0.1240 CBL-TEMEC GATEW TEMEC MONITOR In TEMEC GATEWA 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC INV 1A TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1A In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1B TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1B In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1C TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1C In 1 45 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.9453 6.2715 0.9121 2.3203 CBL-TEMEC INV 1D TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1D In 1 45 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.9453 6.2715 0.9121 2.3203 CBL-TEMEC INV 1E TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV 1E In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1F TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1F In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1G TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1G In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1H TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1H In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1I TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1I In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1J TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV 1J In 1 60 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 5.2604 8.3620 1.2161 3.0938 CBL-TEMEC INV 1K TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1K In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1L TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1L In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1 TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1M In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1N TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV 1N In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1O TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1O In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1P TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1P In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1Q TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1Q In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 CBL-TEMEC INV 1R TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV 1R In 1 30 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 6.6406 Zero: 10.5768 0.7135 1.8151 Page A - 20 Pos: Zero: September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF CBL-TEMEC INV 1S TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1S In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 1T TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1T In 1 15 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 3.3203 5.2884 0.3568 0.9076 CBL-TEMEC INV 1U TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1U In 1 240 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 21.0417 Zero: 33.4479 4.8646 12.3750 CBL-TEMEC INV 1V TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV 1V In 1 270 2 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 23.6719 Zero: 37.6289 5.4727 13.9219 CBL-TEMEC INV 2A TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2A In 1 10 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 2.2135 3.5256 0.2378 0.6050 CBL-TEMEC INV 2 TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2B In 1 35 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 7.7474 Zero: 12.3396 0.8325 2.1176 CBL-TEMEC INV 2C TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2C In 1 65 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 14.3880 Zero: 22.9165 1.5460 3.9327 CBL-TEMEC INV 2D TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2D In 1 95 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 21.0286 Zero: 33.4933 2.2595 5.7478 CBL-TEMEC INV 2E TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2E In 1 125 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 27.6693 Zero: 44.0701 2.9731 7.5629 CBL-TEMEC INV 2F TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2F In 1 155 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 34.3099 Zero: 54.6469 3.6866 9.3780 CBL-TEMEC INV 2G TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV 2G In 1 170 6 Copper Non-Magnetic PVC Pos: 37.6302 Zero: 59.9353 4.0434 10.2856 CBL-TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-01 In 1 40 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 1.1111 3.5017 0.8628 2.1250 CBL-TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-02 In 1 160 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 4.4444 Zero: 14.0069 3.4514 8.5000 CBL-TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-03 In 1 305 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.4722 Zero: 26.7007 6.5792 16.2031 CBL-TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-04 In 1 405 4/0 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 11.2500 Zero: 35.4551 8.7363 21.5156 CBL-TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC LC-05 In 1 505 350 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.2852 Zero: 26.1048 10.7619 26.4993 CBL-TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC LC-06 In 1 50 400 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: Zero: 0.7726 2.4349 1.0634 2.6172 CBL-TEMEC METE TEMEC METER TEMEC TR-2 S In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC MON TEMEC PNL-2 TEMEC MONITOR In 1 15 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 12.1745 Zero: 38.3685 0.5924 1.4590 Page A - 21 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 MO TEMEC PNL-1 G In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 M In 1 10 12 Copper Magnetic PVC Pos: 8.1163 Zero: 25.5790 0.3950 0.9727 2-Winding Transformers Xformer Name In/Out Service ------------------Primary & Secondary--------------Bus Conn. Volts FLA Nominal kVA Z PU (100 MVA Base) R pu jX pu TEMEC GATEWAY XF In TEMEC GATEWAY DI D TEMEC GATEWAY WG 480 240 2 5 2.0 Pos: 824.3500 Zero: 824.3500 1,600.150 1,600.150 TEMEC PNL-1 GATEW In TEMEC PNL-1 GATEW D TEMEC PNL-1 GATE WG 480 240 2 5 2.0 Pos: 824.3500 Zero: 824.3500 1,600.150 1,600.150 TEMEC TR-1 In TEMEC TR-1 PRIMAR D TEMEC TR-1 SECON WG 12,000 480 40 1,010 750.0 Pos: Zero: 1.4321 1.4321 7.5045 7.5045 TEMEC TR-2 In TEMEC TR-2 PRIMAR D TEMEC TR-2 SECON WG 12,000 480 40 1,010 750.0 Pos: Zero: 1.4296 1.4296 7.4915 7.4915 Page A - 22 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF ***************** F A U L T A N A L Y S I S S U M M A R Y – CASE 4***************** --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------BUS NAME VOLTAGE AVAILABLE FAULT CURRENT L-L 3 PHASE X/R LINE/GRND X/R TEMEC ACDS-1 480. 26557.3 4.3 30643.80 4.6 TEMEC GATEWAY DISC SW 480. 5466.7 0.3 3332.43 0.1 TEMEC INV 1A 480. 6312.1 1.9 6981.19 1.7 TEMEC INV 1B 480. 6114.8 1.7 6652.32 1.5 TEMEC INV 1C 480. 5882.8 1.7 6271.93 1.4 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1D 1E 1F 1G 1H 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 5882.8 5627.8 5351.6 4744.8 4744.8 1.7 1.5 1.6 1.2 1.2 6271.93 5880.65 5195.89 4431.32 4431.32 1.4 1.3 1.3 1.0 1.0 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1I 1J 1K 1L 1M 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 4827.4 4827.4 4474.4 4357.3 4022.8 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.3 1.1 4529.76 4529.76 3928.33 3802.65 3458.40 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.0 0.9 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1N 1O 1P 1Q 1R 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 4022.8 4031.7 3933.5 3653.7 3653.7 1.1 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.1 3458.40 3374.83 3279.73 3017.35 3017.35 0.9 1.0 1.0 0.9 0.9 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 1S 1T 1U 1V 2A 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 4015.7 3929.4 2672.1 2544.2 17355.9 1.6 1.5 0.9 0.8 1.4 3455.56 3367.81 2198.68 2088.54 16095.05 1.4 1.3 0.8 0.8 1.2 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV INV INV INV INV 2B 2C 2D 2E 2F 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 10594.0 6885.6 5054.4 3985.4 3289.2 0.7 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.3 9138.47 5808.92 4233.22 3327.16 2741.15 0.6 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.3 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC INV 2G LC-01 LC-02 LC-03 LC-04 480. 480. 480. 480. 480. 3025.3 6696.5 5666.8 4714.6 4234.1 0.3 2.5 2.0 1.6 1.5 2519.75 7651.58 5633.04 4196.25 3576.92 0.3 2.3 1.5 1.2 1.1 480. 4189.0 1.9 3636.98 1.5 TEMEC LC-05 Page A - 23 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF ***************** F A U L T A N A L Y S I S S U M M A R Y – CASE 4***************** --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------BUS NAME VOLTAGE AVAILABLE FAULT CURRENT L-L 3 PHASE X/R LINE/GRND X/R TEMEC LC-06 480. 21036.0 3.0 20778.76 2.5 TEMEC MAIN SWGR 480. 26986.7 4.4 31140.42 4.7 TEMEC METER 480. 11280.0 0.5 7644.34 0.3 TEMEC MONITOR J-BOX 480. 8512.5 0.4 5400.91 0.2 TEMEC PNL-1 480. 7113.8 2.9 8613.19 3.0 TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWAY DISC SW PNL-1 MONITOR J-BOX PNL-2 TR-1 PRIMARY TR-1 SECONDARY TEMEC TR-2 PRIMARY TEMEC TR-2 SECONDARY 480. 480. 480. 12000. 480. 4379.5 5644.7 26515.5 426.0 7190.8 0.8 1.2 4.3 3.4 3.0 12000. 480. 428.0 24948.3 3.5 3.6 3398.43 5228.36 30574.00 0.4 0.8 4.5 8851.69 3.2 28620.44 3.7 *********************** FAULT ANALYSIS REPORT COMPLETED ********************************* Page A - 24 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF PROTECTIVE DEVICE SHORT CIRCUIT EVALUATION – “WORST CASE” FAULT DUTY CALCULATED BY SOLAR CITY, WITH INVERTER SHORT CIRCUIT CONTRIBUTION Device/Bus Status Description Manufacturer CB-MSB2 MAIN TEMEC MAIN SWGR SE & SEH, Micrologic LI, 300-3000AP SQUARE D SE TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES Pass Continuous Amps INT kA Bus/ Device 480 LF/Dev/ Rating% 0.00 Calc/Dev/ Series 68.79 480 3000.00 100.00 CloseLatch kA Calc/ Dev Rating % K Factor Ith Parting Time Volt/INT/ C-L 100.00 3P/SLG Speed Cycles 68.79 0.00 Symm LCL Econolim 480 0.00 65.43 80.00 TEMEC ACDS-1 800-6000A 600 1600.00 200.00 32.72 FEDERAL PACIFIC LCL-1600 TEMEC GATEWAY DISC SW FUSES TEMEC GATEWAY DISC SW Pass Voltage (V) Pass FERRAZ SHAWMUT TEMEC INV-1A BRKR TRS, 600V, Class RK5 0.1-12A 0.00 480 0.00 5.71 80.00 600 6.00 200.00 2.86 TRS 0.00 Symm HFD 480 0.00 8.32 100.00 TEMEC LC-01 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 12.80 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1B BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 8.32 100.00 TEMEC LC-01 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 12.80 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1C BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 8.32 100.00 TEMEC LC-01 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 12.80 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1D BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 8.32 100.00 TEMEC LC-01 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 12.80 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1E BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 8.32 100.00 TEMEC LC-01 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 12.80 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1F BRKR Pass Symm Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 6.20 100.00 TEMEC LC-02 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 9.54 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 Page A - 25 Symm September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Device/Bus Status Description Manufacturer TEMEC INV-1G BRKR Continuous Amps INT kA Bus/ Device LF/Dev/ Rating% Calc/Dev/ Series CloseLatch kA Calc/ Dev Rating % K Factor Ith Parting Time Volt/INT/ C-L 3P/SLG Speed Cycles HFD 480 0.00 6.20 100.00 TEMEC LC-02 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 9.54 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1H BRKR Pass Voltage (V) HFD 480 0.00 6.20 100.00 TEMEC LC-02 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 9.54 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1I BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 6.20 100.00 TEMEC LC-02 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 9.54 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1J BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 6.20 100.00 TEMEC LC-02 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 9.54 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1K BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 5.07 100.00 TEMEC LC-03 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 7.80 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1L BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 5.07 100.00 TEMEC LC-03 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 7.80 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1M BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 5.07 100.00 TEMEC LC-03 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 7.80 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1N BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 5.07 100.00 TEMEC LC-03 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 7.80 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1O BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 4.51 100.00 TEMEC LC-04 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 6.94 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1P BRKR Pass Symm Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 4.51 100.00 TEMEC LC-04 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 6.94 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 Page A - 26 Symm September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Device/Bus Status Description Manufacturer TEMEC INV-1Q BRKR Continuous Amps INT kA Bus/ Device LF/Dev/ Rating% Calc/Dev/ Series CloseLatch kA Calc/ Dev Rating % K Factor Ith Parting Time Volt/INT/ C-L 3P/SLG Speed Cycles HFD 480 0.00 4.51 100.00 TEMEC LC-04 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 6.94 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1R BRKR Pass Voltage (V) HFD 480 0.00 4.51 100.00 TEMEC LC-04 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 6.94 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1S BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 4.47 100.00 TEMEC LC-05 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 6.87 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1T BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 4.47 100.00 TEMEC LC-05 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 6.87 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1U BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 4.47 100.00 TEMEC LC-05 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 6.87 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-1V BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 4.47 100.00 TEMEC LC-05 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 6.87 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-2A BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 37.91 100.00 TEMEC LC-06 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 58.32 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-2B BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 37.91 100.00 TEMEC LC-06 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 58.32 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-2C BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 37.91 100.00 TEMEC LC-06 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 58.32 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-2D BRKR Pass Symm Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 37.91 100.00 TEMEC LC-06 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 58.32 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 Page A - 27 Symm September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Device/Bus Status Description Manufacturer TEMEC INV-2E BRKR Continuous Amps INT kA Bus/ Device LF/Dev/ Rating% Calc/Dev/ Series CloseLatch kA Calc/ Dev Rating % K Factor Ith Parting Time Volt/INT/ C-L 3P/SLG Speed Cycles HFD 480 0.00 37.91 100.00 TEMEC LC-06 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 58.32 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-2F BRKR Pass Voltage (V) HFD 480 0.00 37.91 100.00 TEMEC LC-06 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 58.32 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC INV-2G BRKR Pass Symm HFD 480 0.00 37.91 100.00 TEMEC LC-06 15-225A 480 45.00 65.00 58.32 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD 0.00 65.00 TEMEC LC-01 BRKR Pass Symm HJD 480 0.00 9.48 100.00 TEMEC PNL-1 70-250A 480 225.00 65.00 14.58 CUTLER-HAMMER HJD TEMEC LC-02 BRKR Pass Symm Symm HJD 480 0.00 9.48 100.00 TEMEC PNL-1 70-250A 480 225.00 65.00 14.58 CUTLER-HAMMER HJD TEMEC LC-03 BRKR Pass 0.00 Symm HJD 480 0.00 9.48 100.00 TEMEC PNL-1 70-250A 480 175.00 65.00 14.58 CUTLER-HAMMER HJD TEMEC LC-04 BRKR Pass 0.00 Symm HJD 480 0.00 9.48 100.00 TEMEC PNL-1 70-250A 480 175.00 65.00 14.58 CUTLER-HAMMER HJD TEMEC LC-05 BRKR Pass 0.00 Symm HJD 480 0.00 9.48 100.00 TEMEC PNL-1 70-250A 480 175.00 65.00 14.58 CUTLER-HAMMER HJD TEMEC LC-06 BRKR Pass 0.00 TEMEC PNL-2 K Frame Series C, Digitrip 310+ LS, 400AS EATON HKD TEMEC METER FUSE TEMEC TR-2 SECONDARY Pass Pass FRS-R, 600V Class RK5 1-600A 0.00 Symm 480 0.00 64.88 100.00 480 400.00 65.00 99.81 0.00 Symm 480 0.00 54.01 80.00 600 1.00 200.00 27.00 Page A - 28 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Device/Bus Status Description Voltage (V) Continuous Amps INT kA Bus/ Device LF/Dev/ Rating% 0.00 Calc/Dev/ Series HFD 480 0.00 64.88 100.00 TEMEC PNL-2 15-225A 480 20.00 65.00 99.81 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD Manufacturer BUSSMANN TEMEC MON BRKR TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR FRS-R Pass Pass TEMEC PNL-2 NG-Frame, Series G 310+ LSI, 1200AF CUTLER-HAMMER NGH TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWAY DISC SW FU TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWAY DISC SW FERRAZ SHAWMUT Pass TEMEC PNL-1 MON BRKR Pass TRS, 600V, Class RK5 0.1-12A CloseLatch kA Calc/ Dev Rating % K Factor Ith Parting Time Volt/INT/ C-L 3P/SLG Speed Cycles Symm 0.00 Symm 480 0.00 64.88 100.00 480 1000.00 65.00 99.81 0.00 Symm 480 0.00 4.65 80.00 600 6.00 200.00 2.33 TRS 0.00 Symm HFD 480 0.00 9.48 100.00 TEMEC PNL-1 15-225A 480 20.00 65.00 14.58 CUTLER-HAMMER HFD TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN Pass TEMEC PNL-2 CUTLER-HAMMER TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE TEMEC TR-1 PRIMARY Bay-O-Net Current Sensing Fuse Link, 23kV C4-C17 COOPER 353C14 TEMEC TR-1 CLF Pass Magnum SB, DT 520 LSI, 1600AF, 200-1600AP SBS-616 TEMEC TR-1 PRIMARY ELSP, 15.5kV, (2/03) 30-300A COOPER ELSP TEMEC TR-2 BAY FUSE Pass TEMEC TR-2 PRIMARY Bay-O-Net Current Sensing Fuse Link, 23kV C4-C17 COOPER 353C14 TEMEC TR-2 CLF Pass Pass ELSP, 15.5kV, (2/03) 0.00 Symm 480 0.00 64.88 94.49 508 1600.00 65.00 99.81 0.00 Symm 12000 0.00 0.53 0.61 77.42 15500 65.00 2.50 4.00 21.26 0.00 15.16 12000 0.00 0.53 0.61 77.42 15500 125.00 50.00 76.08 1.06 0.00 0.80 12000 0.00 0.53 0.62 77.42 15500 65.00 2.50 4.00 21.40 0.00 12000 Page A - 29 0.00 15.41 0.53 0.62 77.42 Symm Symm Symm September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Device/Bus Status Description Manufacturer TEMEC TR-2 PRIMARY 30-300A COOPER ELSP Voltage (V) Continuous Amps INT kA Bus/ Device 15500 LF/Dev/ Rating% 125.00 Calc/Dev/ Series 50.00 0.00 Page A - 30 CloseLatch kA Calc/ Dev 76.08 Rating % K Factor Ith Parting Time Volt/INT/ C-L 1.07 3P/SLG Speed Cycles 0.81 Symm September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF APPENDIX B - SELECTED TIME-CURRENT CURVES Page B - 1 TEMEC LC-06 BRKR 100K 10K 10 1K 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES 1000 FEDERAL PACIFIC Type LCL Econolim Frame/Model LCL-1600 Trip 1600.0 A EATON Type K Frame Series C, Digitrip 310+ Frame/Model HKD Trip 400.0 A Settings Phase LTPU (A-H) E (300) (300A) LTD (2 - 24s) 10 STPU (2 - 12 x Ir) 10 (3000A) STD I2T Fixed (I^2t On) INST OR Fixed (4400A) TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN - Phase CUTLER-HAMMER Type Magnum SB, DT 520 Frame/Model SBS-616 Trip 1600.0 A Plug 1600.0 A Settings Phase Ir, (0.4-1.0 x P) 1 (1600A) LTD, (2 - 24 Sec.) 4 STPU, (2-10 x Ir) 6 (9600A) STD, (0.1-0.5 Sec.) 0.4 (I^2t Off) INST, (2-14 x P) 10 (16000A) INST OR, (Fixed) 18 x ln (28800A) TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type NG-Frame, Series G 310+ Frame/Model NGH Trip 1200.0 A Plug 1000.0 A Settings Phase Ir (A-H) G (1000) (1000A) LTD (2 - 24s) 4 STPU (2 - 9 x Ir) 8 (8000A) STD FLAT (Inst-300ms) 300ms (P,Q,R) INST (6-12 x In) 12 (14400A) INST OR Fixed (14400A) 100 10 TIME IN SECONDS 1 TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES 0.10 TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN TEMEC LC-06 BRKR TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-ACDS-1, PNL-2 Current Scale x 1 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Reference Voltage: 480 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 2 10K 10 1K 1 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES 1000 TEMEC TR-2 CBL-TEMEC AC-02 TEMEC TR-2 TEMEC TR-2 BAY FUSE COOPER Type Bay-O-Net Current Sensing Fuse Link, 23kV Frame/Model 353C14 Trip 65.0 A Settings Phase 65.0 Amps TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type NG-Frame, Series G 310+ Frame/Model NGH Trip 1200.0 A Plug 1000.0 A Settings Phase Ir (A-H) G (1000) (1000A) LTD (2 - 24s) 4 STPU (2 - 9 x Ir) 8 (8000A) STD FLAT (Inst-300ms) 300ms (P,Q,R) INST (6-12 x In) 12 (14400A) INST OR Fixed (14400A) 100 TEMEC TR-2 CLF TEMEC LC-01 BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HJD Frame/Model HJD Trip 225.0 A Settings Phase Thermal Curve (Fixed) INST (5-10 x Trip) 10 (2250A) 10 TIME IN SECONDS COOPER Type ELSP, 15.5kV, (2/03) Frame/Model ELSP Trip 125.0 A Settings Phase 125.0 Amps CBL-TEMEC AC-02 QtyPerPhase 4 CableSize 300 kcmil 1 TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR CBL-TEMEC AC-02 TEMEC TR-2 TX Inrush S P TEMEC TR-2 CLF 0.10 TEMEC TR-2 BAY FUSE CBL-TEMEC AC-MV TEMEC LC-01 BRKR 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-12KV XFMRS Current Scale x 1 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Reference Voltage: 12000 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 3 CBL-TEMEC MON 1M 100K 10K 10 1K 1 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN - Phase CUTLER-HAMMER Type Magnum SB, DT 520 Frame/Model SBS-616 Trip 1600.0 A Plug 1600.0 A Settings Phase Ir, (0.4-1.0 x P) 1 (1600A) LTD, (2 - 24 Sec.) 4 STPU, (2-10 x Ir) 6 (9600A) STD, (0.1-0.5 Sec.) 0.4 (I^2t Off) INST, (2-14 x P) 10 (16000A) INST OR, (Fixed) 18 x ln (28800A) 1000 100 TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES FEDERAL PACIFIC Type LCL Econolim Frame/Model LCL-1600 Trip 1600.0 A 10 TIME IN SECONDS TEMEC MON BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HFD Frame/Model HFD Trip 20.0 A Settings Phase Fixed CBL-TEMEC MON 1 QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 12 AWG TEMEC GATEWAY DISC SW FUSES FERRAZ SHAWMUT Type TRS, 600V, Class RK5 Frame/Model TRS Trip 6.0 A TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN TEMEC MON BRKR 0.10 CBL-TEMEC MON TEMEC GATEWAY DISC SW FUSES P S TEMEC GATEWAY XFMR 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-PNL-2-MONITOR BRKR Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 480 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 4 TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN - Phase CBL-TEMEC LC-06 CUTLER-HAMMER Type Magnum SB, DT 520 Frame/Model SBS-616 Trip 1600.0 A Plug 1600.0 A Settings Phase Ir, (0.4-1.0 x P) 1 (1600A) LTD, (2 - 24 Sec.) 4 STPU, (2-10 x Ir) 6 (9600A) STD, (0.1-0.5 Sec.) 0.4 (I^2t Off) INST, (2-14 x P) 10 (16000A) INST OR, (Fixed) 18 x ln (28800A) 100K 10K 10 1K 1 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES 1000 FEDERAL PACIFIC Type LCL Econolim Frame/Model LCL-1600 Trip 1600.0 A 100 TEMEC LC-06 BRKR EATON Type K Frame Series C, Digitrip 310+ Frame/Model HKD Trip 400.0 A Settings Phase LTPU (A-H) E (300) (300A) LTD (2 - 24s) 10 STPU (2 - 12 x Ir) 10 (3000A) STD I2T Fixed (I^2t On) INST OR Fixed (4400A) CBL-TEMEC LC-06 QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 400 kcmil 10 TIME IN SECONDS TEMEC INV-2A BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HFD Frame/Model HFD Trip 45.0 A Settings Phase Fixed 1 TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN 0.10 TEMEC LC-06 BRKR CBL-TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV-2A BRKR 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-PNL-2-LC-06 BRKR Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 480 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 5 TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES 10K 10 1K 1 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES 1000 TEMEC TR-2 CBL-TEMEC AC-02 FEDERAL PACIFIC Type LCL Econolim Frame/Model LCL-1600 Trip 1600.0 A TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN - Phase CUTLER-HAMMER Type Magnum SB, DT 520 Frame/Model SBS-616 Trip 1600.0 A Plug 1600.0 A Settings Phase Ir, (0.4-1.0 x P) 1 (1600A) LTD, (2 - 24 Sec.) 4 STPU, (2-10 x Ir) 6 (9600A) STD, (0.1-0.5 Sec.) 0.4 (I^2t Off) INST, (2-14 x P) 10 (16000A) INST OR, (Fixed) 18 x ln (28800A) 100 CBL-TEMEC AC-02 TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR 10 TIME IN SECONDS QtyPerPhase 4 CableSize 300 kcmil CUTLER-HAMMER Type NG-Frame, Series G 310+ Frame/Model NGH Trip 1200.0 A Plug 1000.0 A Settings Phase Ir (A-H) G (1000) (1000A) LTD (2 - 24s) 4 STPU (2 - 9 x Ir) 8 (8000A) STD FLAT (Inst-300ms) 300ms (P,Q,R) INST (6-12 x In) 12 (14400A) INST OR Fixed (14400A) TEMEC TR-2 1 TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES TX Inrush TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN 0.10 TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR CBL-TEMEC AC-02 TEMEC TR-2 S P 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-PNL-2-TR-2 BRKR Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 12000 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 6 100K 10K 10 1K 1 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES 1000 CBL-TEMEC LC-06 CBL-TEMEC INV 2A TEMEC LC-06 BRKR EATON Type K Frame Series C, Digitrip 310+ Frame/Model HKD Trip 400.0 A Settings Phase LTPU (A-H) E (300) (300A) LTD (2 - 24s) 10 STPU (2 - 12 x Ir) 10 (3000A) STD I2T Fixed (I^2t On) INST OR Fixed (4400A) TEMEC INV-2A BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HFD Frame/Model HFD Trip 45.0 A Settings Phase Fixed 100 CBL-TEMEC LC-06 QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 400 kcmil 10 TIME IN SECONDS CBL-TEMEC INV 2A QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 6 AWG 1 TEMEC LC-06 BRKR CBL-TEMEC LC-06 0.10 TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC INV-2A BRKR CBL-TEMEC INV 2A TEMEC INV 2A 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-LC-06-TYPICAL BRKRS Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 480 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 7 1M 100K 10K 10 1K 1 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES 1000 TEMEC TR-1 CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWY DISC SW TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE COOPER Type Bay-O-Net Current Sensing Fuse Link, 23kV Frame/Model 353C14 Trip 65.0 A Settings Phase 65.0 Amps 100 TEMEC TR-1 TEMEC TR-1 CLF 10 TEMEC PNL-1 MON BRKR TIME IN SECONDS COOPER Type ELSP, 15.5kV, (2/03) Frame/Model ELSP Trip 125.0 A Settings Phase 125.0 Amps 1 CUTLER-HAMMER Type HFD Frame/Model HFD Trip 20.0 A Settings Phase Fixed TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWY DISC SW TEMEC TR-1 CLF P S TX Inrush TEMEC TR-1 0.10 TEMEC PNL-1 QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 12 AWG TEMEC PNL-1 MON BRKR CBL-TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWY DISC SW TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWAY DISC SW FU TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWAY DISC SW FU FERRAZ SHAWMUT Type TRS, 600V, Class RK5 Frame/Model TRS Trip 6.0 A 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-PNL-1 MONITOR BRKR Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 480 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 8 100K 10K 10 1K 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES 1000 TEMEC TR-1 CBL-TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE TEMEC TR-1 CLF COOPER Type Bay-O-Net Current Sensing Fuse Link, 23kV Frame/Model 353C14 Trip 65.0 A Settings Phase 65.0 Amps COOPER Type ELSP, 15.5kV, (2/03) Frame/Model ELSP Trip 125.0 A Settings Phase 125.0 Amps 100 TEMEC LC-01 BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HJD Frame/Model HJD Trip 225.0 A Settings Phase Thermal Curve (Fixed) INST (5-10 x Trip) 10 (2250A) 10 TIME IN SECONDS TEMEC TR-1 TEMEC INV-1A BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HFD Frame/Model HFD Trip 45.0 A Settings Phase Fixed CBL-TEMEC LC-01 QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 4/0 AWG 1 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE TEMEC TR-1 CLF TX Inrush P S 0.10 TEMEC TR-1 TEMEC LC-01 BRKR CBL-TEMEC LC-01 TEMEC INV-1A BRKR 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-PNL-1 LC-01 BRKR Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 480 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 9 100K 10K 10 1K 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES 1000 TEMEC TR-1 CBL-TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE COOPER Type Bay-O-Net Current Sensing Fuse Link, 23kV Frame/Model 353C14 Trip 65.0 A Settings Phase 65.0 Amps 100 TEMEC TR-1 CLF COOPER Type ELSP, 15.5kV, (2/03) Frame/Model ELSP Trip 125.0 A Settings Phase 125.0 Amps TEMEC LC-02 BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HJD Frame/Model HJD Trip 225.0 A Settings Phase Thermal Curve (Fixed) INST (5-10 x Trip) 10 (2250A) 10 TIME IN SECONDS TEMEC TR-1 TEMEC INV-1F BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HFD Frame/Model HFD Trip 45.0 A Settings Phase Fixed CBL-TEMEC LC-02 QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 4/0 AWG 1 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE TEMEC TR-1 CLF TX Inrush P S 0.10 TEMEC TR-1 TEMEC LC-02 BRKR CBL-TEMEC LC-02 TEMEC INV-1F BRKR 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-PNL-1 LC-02 BRKR Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 480 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 10 100K 10K 10 1K 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES 1000 TEMEC TR-1 CBL-TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE COOPER Type Bay-O-Net Current Sensing Fuse Link, 23kV Frame/Model 353C14 Trip 65.0 A Settings Phase 65.0 Amps TEMEC TR-1 CLF 100 COOPER Type ELSP, 15.5kV, (2/03) Frame/Model ELSP Trip 125.0 A Settings Phase 125.0 Amps TEMEC INV-1K BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HFD Frame/Model HFD Trip 45.0 A Settings Phase Fixed 10 TIME IN SECONDS TEMEC TR-1 TEMEC LC-03 BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HJD Frame/Model HJD Trip 175.0 A Settings Phase Thermal Curve (Fixed) INST (5-10 x Trip) 10 (1750A) CBL-TEMEC LC-03 QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 4/0 AWG 1 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE TEMEC TR-1 CLF TX Inrush P S 0.10 TEMEC TR-1 TEMEC LC-03 BRKR CBL-TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC INV-1K BRKR 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-PNL-1 LC-03 BRKR Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 480 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 11 100K 10K 10 1K 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES 1000 TEMEC TR-1 CBL-TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE COOPER Type Bay-O-Net Current Sensing Fuse Link, 23kV Frame/Model 353C14 Trip 65.0 A Settings Phase 65.0 Amps 100 TEMEC TR-1 CLF COOPER Type ELSP, 15.5kV, (2/03) Frame/Model ELSP Trip 125.0 A Settings Phase 125.0 Amps TEMEC INV-1O BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HFD Frame/Model HFD Trip 45.0 A Settings Phase Fixed 10 TIME IN SECONDS TEMEC TR-1 TEMEC LC-04 BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HJD Frame/Model HJD Trip 175.0 A Settings Phase Thermal Curve (Fixed) INST (5-10 x Trip) 10 (1750A) CBL-TEMEC LC-04 QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 4/0 AWG 1 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE TEMEC TR-1 CLF P S TX Inrush TEMEC TR-1 0.10 TEMEC LC-04 BRKR CBL-TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC INV-1O BRKR 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-PNL-1 LC-04 BRKR Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 480 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 12 100K 10K 10 1K 100 CURRENT IN AMPERES 1000 TEMEC TR-1 CBL-TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE COOPER Type Bay-O-Net Current Sensing Fuse Link, 23kV Frame/Model 353C14 Trip 65.0 A Settings Phase 65.0 Amps TEMEC TR-1 CLF COOPER Type ELSP, 15.5kV, (2/03) Frame/Model ELSP Trip 125.0 A Settings Phase 125.0 Amps 100 TEMEC INV-1S BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HFD Frame/Model HFD Trip 45.0 A Settings Phase Fixed 10 TIME IN SECONDS TEMEC TR-1 TEMEC LC-05 BRKR CUTLER-HAMMER Type HJD Frame/Model HJD Trip 175.0 A Settings Phase Thermal Curve (Fixed) INST (5-10 x Trip) 10 (1750A) CBL-TEMEC LC-05 QtyPerPhase 1 CableSize 350 kcmil 1 TEMEC TR-1 BAY FUSE TEMEC TR-1 CLF P S TX Inrush TEMEC TR-1 0.10 TEMEC LC-05 BRKR CBL-TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC INV-1S BRKR 0.01 TCC Name: TCC-PNL-1 LC-05 BRKR Current Scale x 1 Reference Voltage: 480 Overcurrent Protective Device Settings September 25, 2015 Power Engineering Services, Inc. Page B - 13 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF APPENDIX C ARC FLASH CALCULATIONS A table of arc flash calculations performed at each equipment bus is included on the following pages. The columns in the table are described as follows, reading from left to right: Bus Name Fault location for report. For line side and load side report options the bus refers to the equipment where the line side and load side protective devices are connected. Protective Device Name Lists the protective device that clears the arcing fault. Bus kV Bus voltage at the fault location, given in kilo-volts. Bus Bolted Fault Current (kA) The magnitude of current flowing to a bus fault that occurs between two or more conductors or bus bars, where the impedance between the conductors or bus bars is zero. Bus Arcing Fault (kA) The calculated arcing current on the faulted bus. Protective Device Arcing Fault Current (kA) The arcing fault current flowing through each protective device feeding the arc fault. Note that the total arc fault current may flow through several parallel sources to the arc location. Trip / Delay Time The time required for the protective device to operate for the given fault condition. In the case of a relay, the breaker opening time is entered separately from the relay trip time. For fuses, the trip time is assumed to be the total clearing curve or high tolerance of the published clearing curve. Breaker Opening Time The time required for a breaker to open after receiving a signal from the trip unit to operate. The combination of the Trip/Delay time and the Breaker Opening time determines the total time required to clear the fault. This column does not apply when a fuse operates to clear the fault. Duration of Arc The summation of Trip/Delay Time and Breaker Opening Time. Arc Type Identifies whether the fault location is in an enclosure or in open air. In open air the arc energy will radiate in all directions whereas an enclosure will focus the energy toward the enclosure opening. The In Box / Air selection is available when the NFPA 70E study option is selected. For the IEEE 1584 Page C - 1 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF study selection the In Box or In Air is determined automatically from the Equipment Type specification. Arc Flash Boundary The distance from exposed live parts within which a person could receive a 2nd degree, curable, burn. Working Distance The distance between the arc source and the worker’s face or chest. Incident Energy Incident energy is calculated in calories per square centimeter (cal/cm2). This value is a function of working distance, system voltage, available bolted fault current, arc current, and the time required for circuit protective devices to clear the fault and extinguish the arc. Required Protective FR Clothing Category/PPE Level Level of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) necessary to protect a person from the Arc Flash energy calculated for the specific location and working distance. Page C - 2 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF APPENDIX C – ARC FLASH CALCULATIONS – WORST CASE INCIDENT ENERGIES REPORTED Bus Name Protective Bus Bus Device kV Name Bolted Prot Dev Bolted Prot Dev Arcing Delay Opening Fault Fault Fault Time Time/Tol (kA) (kA) (kA) (sec.) (sec.) (in) TEMEC ACDS-1 TEMEC ACDS-1 FUSES 0.48 26.56 25.03 14.23 TEMEC GATEWAY DISC SW TEMEC MON BRKR 0.48 5.71 5.71 4.06 TEMEC INV 1A TEMEC INV-1A BRKR 0.48 7.00 6.93 TEMEC INV 1B TEMEC INV-1B BRKR TEMEC INV-1C BRKR TEMEC INV-1D BRKR TEMEC INV-1E BRKR TEMEC INV-1F BRKR TEMEC INV-1G BRKR 0.48 6.75 0.48 TEMEC INV-1H BRKR TEMEC INV-1I BRKR TEMEC INV-1J BRKR TEMEC LC-03 BRKR TEMEC LC-03 BRKR TEMEC INV-1M BRKR TEMEC INV 1C TEMEC INV 1D TEMEC INV 1E TEMEC INV 1F TEMEC INV 1G TEMEC INV 1H TEMEC INV 1I TEMEC INV 1J TEMEC INV 1K TEMEC INV 1L TEMEC INV 1M Trip/ Breaker Ground Equip Gap Type (mm) Arc Working Incident Flash Distance Energy Boundary (in) (cal/cm2) PPE Level / Notes (*N) 0.000 Yes PNL 25 110 18 23 0.015 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.19 (*S2) 4.79 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 7 18 0.24 (*S2) 6.68 4.64 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 7 18 0.23 (*S2) 6.47 6.40 4.47 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.22 (*S2) 0.48 6.47 6.40 4.47 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.22 (*S2) 0.48 6.15 6.09 4.28 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.21 (*S2) 0.48 5.82 5.75 4.08 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.21 (*S2) 0.48 5.09 5.02 3.63 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.19 (*S2) 0.48 5.09 5.02 3.63 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.19 (*S2) 0.48 5.19 5.12 3.70 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.19 (*S2) 0.48 5.19 5.12 3.70 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.19 (*S2) 0.48 4.78 4.72 3.44 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.17 (*N5) (*S2) 0.48 4.65 4.58 3.36 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.17 (*N5) (*S2) 0.48 4.26 4.19 3.11 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.16 (*S2) Page C - 3 (*N4) (*S3) September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Bus Name Protective Bus Bus Device kV Name TEMEC INV 1N TEMEC INV 1O TEMEC INV 1P TEMEC INV 1Q TEMEC INV 1R TEMEC INV 1S TEMEC INV 1T TEMEC INV 1U TEMEC INV 1V TEMEC INV 2A TEMEC INV 2B TEMEC INV 2C TEMEC INV 2D TEMEC INV 2E TEMEC INV 2F TEMEC INV 2G TEMEC LC-01 Bolted Prot Dev Bolted Prot Dev Arcing Trip/ Breaker Delay Opening Fault Fault Fault Time Time/Tol (kA) (kA) (kA) (sec.) (sec.) Ground Equip Gap Type (mm) Arc Working Incident Flash Distance Energy Boundary (in) (cal/cm2) PPE Level / Notes (*N) (in) TEMEC INV-1N BRKR TEMEC INV-1O BRKR 0.48 4.26 4.19 3.11 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.16 (*S2) 0.48 4.28 4.21 3.12 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.16 (*S2) TEMEC INV-1P BRKR TEMEC INV-1Q BRKR 0.48 4.16 4.09 3.05 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.16 (*S2) 0.48 3.84 3.77 2.85 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.15 (*S2) TEMEC INV-1R BRKR TEMEC INV-1S BRKR TEMEC INV-1T BRKR TEMEC INV-1U BRKR TEMEC INV-1V BRKR 0.48 3.84 3.77 2.85 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.15 (*S2) 0.48 4.27 4.20 3.12 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.16 (*S2) 0.48 4.17 4.10 3.05 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.16 (*S2) 0.48 2.77 2.70 2.13 0.019 0.000 Yes PNL 25 4 18 0.12 (*S2) 0.48 2.63 2.56 2.04 0.019 0.000 Yes PNL 25 4 18 0.12 (*S2) TEMEC LC-06 BRKR TEMEC INV-2B BRKR TEMEC INV-2C BRKR TEMEC INV-2D BRKR TEMEC INV-2E BRKR TEMEC INV-2F BRKR TEMEC INV-2G BRKR 0.48 25.49 25.42 14.54 0.011 0.000 Yes PNL 25 11 18 0.53 (*N5) (*S2) 0.48 12.31 12.24 7.79 0.014 0.000 Yes PNL 25 9 18 0.37 (*S2) 0.48 7.42 7.36 5.04 0.015 0.000 Yes PNL 25 7 18 0.25 (*S2) 0.48 5.30 5.24 3.77 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.19 (*S2) 0.48 4.12 4.06 3.03 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.16 (*S2) 0.48 3.38 3.32 2.55 0.018 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.14 (*S2) 0.48 3.10 3.04 2.36 0.018 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.13 (*S2) TEMEC LC-01 BRKR 0.48 7.48 7.17 4.90 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 7 18 0.25 (*S2) Page C - 4 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Bus Name Protective Bus Bus Device kV Name TEMEC LC-02 Bolted Prot Dev Bolted Prot Dev Arcing Trip/ Breaker Delay Opening Fault Fault Fault Time Time/Tol (kA) (kA) (kA) (sec.) (sec.) Ground Equip Gap Type (mm) Arc Working Incident Flash Distance Energy Boundary (in) (cal/cm2) PPE Level / Notes (*N) (in) TEMEC LC-02 BRKR TEMEC LC-03 BRKR TEMEC LC-04 BRKR TEMEC LC-05 BRKR TEMEC LC-06 BRKR CB-MSB2 MAIN 0.48 6.20 5.87 4.13 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.22 (*S2) 0.48 5.07 4.80 3.47 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.18 (*S2) 0.48 4.51 4.24 3.12 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.17 (*S2) 0.48 4.47 4.20 3.10 0.017 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.17 (*S2) 0.48 37.91 37.46 20.23 0.009 0.000 Yes PNL 25 12 18 0.65 (*S2) 0.48 65.53 65.53 32.67 0.038 0.000 Yes PNL 25 41 18 4.5 (*S2) TEMEC METER FUSE TEMEC MON BRKR 0.48 12.96 12.96 8.18 0.004 0.000 Yes PNL 25 4 18 0.11 (*S2) 0.48 9.26 9.26 6.14 0.014 0.000 Yes PNL 25 7 18 0.28 (*S2) TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR TEMEC PNL-1 MON BRKR 0.48 8.02 6.71 4.54 2 0.000 Yes PNL 25 139 18 34 0.48 4.65 4.65 3.41 0.016 0.000 Yes PNL 25 5 18 0.16 (*N5) (*N9) (*S2) (*S2) TEMEC PNL-1 MON BRKR 0.48 6.16 6.16 4.34 0.015 0.000 Yes PNL 25 6 18 0.20 (*S2) 0.48 26.52 24.98 14.21 0.4 0.000 Yes PNL 25 102 18 21 (*S3) TEMEC TR-1 PRIMARY TEMEC PNL-2 MAIN TEMEC TR-2 BAY FUSE 12.00 0.53 0.48 0.48 0.266 0.000 No SWG 152 34 36 1.0 (*N11) (*S2) TEMEC TR-1 SECONDARY TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR 0.48 8.12 6.83 4.62 2 0.000 Yes PNL 25 140 18 35 (*N5) (*N9) (*S2) TEMEC TR-2 PRIMARY TEMEC TR-2 BAY FUSE 12.00 0.53 0.49 0.49 0.263 0.000 No SWG 152 33 36 1.0 (*N11) (*S2) TEMEC TR-2 SECONDARY TEMEC PNL-1 BRKR 0.48 24.95 23.79 13.65 0.3 0.000 Yes PNL 25 83 18 15 (*S3) TEMEC LC-03 TEMEC LC-04 TEMEC LC-05 TEMEC LC-06 TEMEC MAIN SWGR TEMEC METER TEMEC MONITOR J-BOX TEMEC PNL-1 TEMEC PNL-1 GATEWAY DISC SW TEMEC PNL-1 MONITOR J-BOX TEMEC PNL-2 Page C - 5 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Bus Name Protective Bus Bus Device kV Name Bolted Prot Dev Bolted Prot Dev Arcing Trip/ Breaker Ground Equip Gap Type (mm) Arc Working Delay Opening Fault Fault Fault Time Time/Tol (kA) (kA) (kA) (sec.) (sec.) (in) Incident Flash Distance Energy Boundary (in) (cal/cm2) #Equip Eval Failed = 0 #Bus Equip Eval Failed = 0 PPE Level / Notes (*N) (*N11) - Out of IEEE 1584 Range, Lee Equation Used. Applicable for Open Air only. (*N4) Equipment Specific Equations Used (*N5) Miscoordinated, Upstream Device Tripped (*N9) - Max Arcing Duration Reached NFPA 70E 2015 Annex D.4 IEEE 1584 Bus Report ( - 80% Cleared Fault Threshold, miscoordination checked Worst Case: (*S0) - Solar City Fault Current (*S1) - SCE Fault Current (*S2) - Solar City Fault Current-PV Page C - 6 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Bus Name Protective Bus Bus Device kV Name Bolted Prot Dev Bolted Prot Dev Arcing Trip/ Breaker Ground Equip Gap Type (mm) Arc Working Delay Opening Fault Fault Fault Time Time/Tol (kA) (kA) (kA) (sec.) (sec.) (in) Incident Flash Distance Energy Boundary (in) (cal/cm2) PPE Level / Notes (*N) (*S3) - SCE Fault CurrentPV Page C - 7 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF APPENDIX D-UTILITY SHORT CIRCUIT DUTY Page D - 1 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Page D - 2 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF APPENDIX E GLOSSARY Term Arc Blast Arc Flash Arc Flash Hazard Assessment Arc Flash Protection Boundary ATPV Calorie Current-Limiting Overcurrent Protective Device Deenergized Electrical Hazard Electrical Hazard Assessment Definition A pressure wave created by the heating, melting, vaporization, and expansion of conducting material and surrounding gases or air. The sudden release of heat energy and intense light at the point of an arc. Can be considered a short-circuit in the air, usually created by accidental contact between live conductors. A study that analyzes potential exposure to Arc flash hazards. The outcome of the study establishes Incident Energy levels, Hazard Risk Categories, Arc Flash Protection Boundary and required level of PPE. A protection boundary established to protect personnel from Arc flash hazards. This boundary is the distance at which an unprotected worker can receive a second-degree burn to bare skin. Arc Thermal Performance Value which is defined in ASTM F 1959, Standard Test Method for Clothing, as the incident energy on a material or multilayer system of materials that result in a 50% probability that sufficient heat transfer through the tested specimen is predicted to cause the onset of a second degree skin burn injury based on the Stoll curve, cal/cm². The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius. 1 cal/cm² is equivalent to the exposure on the tip of a finger by a cigarette lighter for one second. A device that, when interrupting current in its current limiting range, reduces the current flowing in the faulted circuit to a magnitude substantially less than that obtainable in the same circuit if the device were replaced with a solid conductor having comparable impedance. Equipment or components that have had all possible energy sources removed. A dangerous condition caused by equipment failure or contact with an energized conductor or circuit part. Hazards include shock, Arc flash, burns and arc-blast. A study to identify the potential electrical hazards that may be exposed to personnel. The assessment should address both shock and Arc flash hazards. Page E - 1 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Term Electrically Safe Work Condition Electrical Safety Program Flame-Resistant (FR) Glove Class Hazard Risk Category Incident Energy Interrupting Rating Limited Approach Boundary Live Parts Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Definition Condition where the equipment and or circuit components have been disconnected from all electrical energy sources, locked/tagged out, and tested to verify all sources of power are removed. A documented program that identifies policies, procedures, principles and safe work practices to protect workers exposed to electrical energy. The property of material whereby combustion is prevented, terminated, or inhibited following the application of a flaming or non-flaming source of ignition, with or without subsequent removal of the ignition source. Flame resistance can be inherent to the material or applied by a specific treatment. The Glove Class is based on the voltage level only. The following Glove Class table is published in ASTM D 120-95. Glove Class Voltage 00 500 V 0 1000 V 1 7500 V 2 17,000 V 3 26,500 V 4 36,000 V A means of classifying the hazard to personnel as defined by NFPA 70E. Each category (0-4) requires PPE and is related to incident energy levels. The amount of thermal energy impressed on a surface generated during an electrical arc at a certain distance from the arc. This is typically measured in cal/cm². The highest rms symmetrical current, at specified test conditions, which the device is rated to interrupt. The difference between Interrupting Capacity and Interrupting Rating is in the test circuits used to establish the ratings. An approach boundary to protect personnel from shock. A boundary distance is established from an energized part based on system voltage. To enter this boundary, unqualified persons must be accompanied by a qualified person and must use PPE. Energized electrical conductive components or circuit parts Equipment used to protect personnel which can include clothing, tools, etc. Page E - 2 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF Term Prohibited Approach Boundary Protective Device Coordination Study Qualified Person Restricted Approach Boundary Shock Shock Hazard Assessment Short-Circuit Current Rating Short-Circuit Study Single-Line Diagram Unqualified Person Working Distance Definition An approach boundary to protect personnel from shock. Work in this boundary is considered the same as making direct contact with an energized part. Only qualified persons are allowed to enter this boundary and they must use PPE. This analysis will determine the opening time of the protective devices relative to the time-current curves as issued by the fuse and/or circuit breaker manufacturer. Protective device settings are recorded and recommendations are provided for better protective device coordination (where applicable). One who has the skills and knowledge related to the construction and operation of the electrical equipment and installations and has received safety training to recognize and avoid the hazards involved. An approach boundary to protect personnel from shock. A boundary distance is established from an energized part based on system voltage. Only qualified persons are allowed to enter this boundary and they must use PPE. A trauma subjected to the body by electrical current. When personnel come in contact with energized conductors, it can result in current flowing through their body often causing serious injury or death. A study that analyzes potential exposure to electrical Shock hazards. The outcome of the study establishes circuit voltage and shock protection boundaries. The prospective symmetrical fault current at a nominal voltage to which an apparatus or system is able to be connected without sustaining damage exceeding defined acceptance. A study which analyzes and determines the available phase and ground fault duties for all buses and equipment. The analysis outputs will indicate fault currents available and device interruption ratings required at each bus. Any equipment which is not rated for the available fault current is also identified. A diagram that shows, by means of single lines and graphic symbols, the course of an electric circuit or system of circuits and the component devices or parts used in the circuit or system. A person that does not possess all the skills and knowledge or has not been trained for a particular task. Closest distance a worker’s body, excluding arms and hands, would be exposed to the arc. Page E - 3 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF APPENDIX F - INVERTER TECHNICAL DATA, WITH SHORT CIRCUIT CONTRIBUTION Page F - 1 September 30, 2015 PES No. 4863B-15 EMWD/Arc Flash Temecula Valley RWRF APPENDIX G SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS DEVELOPED FOR STUDIES [PAGE LEFT INTENTIONALLY BLANK]