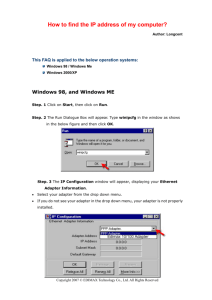
_
V1.1
Hardware Reference
ST SPC58 B Line Emulation Adapter
ST SPC58 B Line Emulation Adapter System
ST SPC58 B line emulation adapter primary use case is providing Nexus trace functionality
for the SPC58 B line devices in the QFP64 and the QFP100 packages, where Nexus trace port
is not available. The emulation adapter is based on the 144-pin superset device and provides
the adaptation to 64-pin and 100-pin QFP target package.
Alternative use case is also a standalone operation. In this case customer can start developing
and testing the application while his target may not be available yet.
ST SPC58 B line emulation adapter is based on the SPC582B60E5 device in the QFP 144
package, only in which the Nexus trace port is exposed and available. It’s a superset device
with 1MB program flash and can emulate all ST SPC58 B line devices in smaller packages.
Complete emulation adapter is split into individual parts which makes it flexible when support
for different target packages is required. A typical setup in conjunction with the target
contains:
IEA-SPC582B (Microcontroller part)
Pin Count Conversion Board
Solder Part
iSYSTEM, July 2016
1/12
Optional is a power supply part, which is used for emulation adapter standalone operation
without the target or when there are problems with the target supplying the power.
Minimally the IEA-SPC582B (Emulation Adapter) and the IEA-PS (Power Supply) items are
required for standalone operation without the target.
Minimal setup for standalone operation
Ordering Code:
IEA-SPC582B
IEA-PS
QFP100
IEA-SPC582B-TQ100
IA100TQ-SOLDER
QFP64
IEA-SPC582B-ATQ64
IA64ATQ-SOLDER
Description:
Emulation Adapter
Emulation Adapter Power Supply (optional)
100-Pin Count Conversion Board
Solder Part TQ100QFP (14x14)
64-Pin Count Conversion Board
Solder Part TQ64QFP (10x10)
The emulation adapter can be used in conjunction with iSYSTEM iC5000, iC5500 and
iC6000 debug and test tool or any other third party tool supporting ST SPC58 B line Nexus
trace port. Debug tool connects to the standard 38-pin Mictor connector (P6) providing debug
and Nexus trace interface connection.
iSYSTEM, July 2016
2/12
Jumper configuration
J1: target reset configuration
Jumper J1 connects the reset line between the emulation device and the target. By default J1 is
populated.
J2 and J3: clock source configuration
Jumpers J2 and J3 select clock source for the emulation device.
Per default, both jumpers are set to position 1-2, which yields the clock source being used
from the target.
Note that the emulation adapter may not operate when crystal circuit is used in the target.
Typical design guideline is that the crystal should be as close as possible to the
microcontroller. However, it may happen that the target crystal may not oscillate in
conjunction with the emulation adapter since clock lines (XTAL, EXTAL) between the target
and the emulation device on the emulation adapter can become too long consequentially too
much affecting the impedance of the crystal circuit. There should be no problem if the
oscillator is used in the target.
If an oscillator in the target is not an option and the target crystal doesn’t oscillate in
conjunction with the emulation adapter, clock from the emulation adapter must be used (J2 &
J3 position 2-3). In this case, a crystal circuit must be assembled on the emulation adapter.
Crystal circuit
Note: Crystal circuit is located in the corner of the emulation adapter, next to the 38-pin
Mictor connector P6.
Per default 10pF capacitors are populated for C1 and C2 and the crystal Q1 is not populated.
Note that C1 and C2 values are valid for 40MHz crystal only. If different crystal is used, the
default 10 pF capacitors must be replaced with proper value.
iSYSTEM, July 2016
3/12
J4 & J6: GND connecting points
Real target microcontroller in the QFP package provides an exposed
GND pad in the middle of the microcontroller at the bottom side of the
package. This provides GND connection between the microcontroller
and the target.
In case of the emulation adapter usage, the solder part (IA100TQSOLDER or IA64ATQ-SOLDER) is soldered instead of the
microcontroller. Note that the available solder parts at the introduction of
this emulation adapter, did not provide support for the exposed GND
pad. For this reason, user must ensure replacement GND connection between the
emulation adapter and the target using a dedicated GND wire. Without this connection,
the system will not work. Use provided GND wire which comes along the emulation adapter
and plug it to the pin J6 (see picture above) on the emulation adapter. Connect the other side
to the ground potential on the target - as close as possible to the microcontroller respectively
solder part being soldered instead of the microcontroller. This connection must be quality and
reliable otherwise debugging and tracing over the Nexus trace port may not work.
Alternatively, GND connection can be also established over the J4 ground bridge.
P5: power selection
The P5 header row is used for power supply selection.
Refer to the microcontroller user manual for more details which power supply designation
belongs to which power supply.
Signal
direction
target
target
target
target
target
Signal
Pin Pin
NC
VDD_HV_OSC
VDD_HV_ADV
VDD_HV_ADR_S
VDD_HV_IO_MAIN
VDD_HV_FLA
NC
NC
NC
NC
GND
GND
GND
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
Signal
2
NC
4
CVDD_HV_OSC
6
CVDD_HV_ADV
8
CVDD_HV_ADR_S
10 CVDD_HV_IO_MAIN
12
CVDD_HV_FLA
14
NC
16
NC
18
NC
20
NC
22
GND
24
GND
26
GND
Signal
direction
CPU
CPU
CPU
CPU
CPU
P5 signal description
By default jumpers are set and connect target power supply coming from the target to the
microcontroller residing on the emulation adapter. If a different power source is to be used
(e.g. in case of standalone operation), jumpers must be removed, and power source must be
applied to CVDD_HV_OSC (pin 4), CVDD_HV_ADV (pin 6), CVDD_HV_ADR_S (pin 8),
CVDD_HV_IO_MAIN (pin 10), CVDD_HV_FLA (pin 12) and GND (pins 22, 24, 26)
signals.
iSYSTEM, July 2016
4/12
Optional emulation adapter power supply (ordering code: IEA-PS), which can provide 3.3V
or 5V voltage, connects on top of the emulation adapter directly to the P5 header row and
allows standalone usage of the emulation adapter. This is convenient when the target is not
available or it’s not adjusted for the emulation adapter connection yet.
IEA-PS (optional emulation adapter power supply
IEA-SPC582B Emulation Adapter
iSYSTEM, July 2016
5/12
Next picture shows a pinout of the four connectors P1-P4 on the bottom side of the emulation
adapter.
GND GND 109 111 113
GND GND 110 112 nc
nc
105
103
nc
nc
97
nc
nc
nc
nc
nc
85
83
81
nc
nc
nc
nc
GND
GND
115 nc 119 121 123 125 nc 129 131 133 nc 137 139 nc 143
nc 118 nc 122 nc nc 128 130 132 134 nc 138 nc 142 144
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
nc
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
nc
nc
nc
23
nc
nc
nc
nc
nc
nc
30
31
32
33
nc
nc
36
GND GND
GND GND
108
106
104
102
nc
98
96
nc
nc
nc
nc
86
84
82
80
78
nc
nc
GND
GND
GND GND nc
GND GND 72
69
nc
67
68
65
66
63
64
nc
nc
59
nc
57
nc
55
56
53
54
nc
nc
nc
nc
47
48
45
46
43
44
41
42
39
40
nc – Not Connected
Optionally, the user could also design his target directly providing connection to the
emulation adapter via P1-P4 connectors. Connectors being used on the emulation adapter are
female Tyco Electronics connectors, part number 0-0104652-4 (40 pin).
Bottom side of the IEA-SPC582B
iSYSTEM, July 2016
6/12
37
38
QFP100 Adaptation
IEA-SPC582B-TQ100 100-Pin Count Conversion Board
This part connects between the IEA-SPC582B emulation adapter and the solder part
IA100TQ-SOLDER being soldered on the target side.
IA100TQ-SOLDER (TET solder part)
Solder part, which is being soldered to the target.
Recommended (by TET) PCB footprint size:
(Unit: mm)
A
B
C
D
E
K
L
16.5
1.125
17.0
17.0
2.15
19.55
19.55
When it’s meant soldering the solder part manually, it’s highly recommended prolonging the
dimension E on the outer side (e.g. for 1.5-2 mm) during the PCB design. Note that without
this modification it’s very difficult to solder the solder part manually.
iSYSTEM, July 2016
7/12
IA100TQ-SOLDER dimensions
User must be familiar with the SMT (Surface Mount Technology) soldering in order to solder
the IA100TQ-SOLDER to the PCB instead of the original microcontroller. On request,
iSYSTEM can provide this service too.
QFP64 Adaptation
IEA-SPC582B-ATQ64 64-Pin Count Conversion Board
This part connects between the IEA-SPC582B emulation adapter and the solder part
IA64ATQ-SOLDER being soldered on the target side.
iSYSTEM, July 2016
8/12
IA64ATQ-SOLDER (TET solder part)
Solder part, which is being soldered to the target.
Recommended (by TET) PCB footprint size:
(Unit: mm)
A
B
C
D
E
K
L
12
1.505
13.0
13.0
2.3
14
14
When it’s meant soldering the solder part manually, it’s highly recommended prolonging the
dimension E on the outer side (e.g. for 1.5-2 mm) during the PCB design. Note that without
this modification it’s very difficult to solder the solder part manually.
IA64ATQ-SOLDER dimensions
User must be familiar with the SMT (Surface Mount Technology) soldering in order to solder
the IA64ATQ-SOLDER to the PCB instead of the original microcontroller. On request,
iSYSTEM can provide this service too.
iSYSTEM, July 2016
9/12
Schematic
iSYSTEM, July 2016
10/12
Notes:
iSYSTEM, July 2016
11/12
Disclaimer: iSYSTEM assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear in this
document, reserves the right to change devices or specifications detailed herein at any time
without notice, and does not make any commitment to update the information herein.
iSYSTEM. All rights reserved.
iSYSTEM, July 2016
12/12