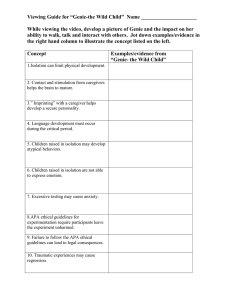
What is Isolation
advertisement

Circuit Isolation Techniques & TI Isolation Technology Industrial Interface Products iif_bdm@list.ti.com 4Q 2013 Agenda Technical Review Markets and Applications Competitive Advantages Product Q&A TI Information – Selective Disclosure Technical Review Signal Isolation The Real World mC Speed Position Flow TRANSCEIVERS RS-485/ CAN Pressure Sound ADC ISOLATION Temperature PLC DSP Light Humidity TI Information – Selective Disclosure DIGITAL INTELLIGENCE Why is Isolation Used? • Is a means of preventing DC or uncontrolled transient current from flowing between two communicating points. • Is used in two general situations. Isolation 1. Where there is the potential for voltage surges that may damage equipment or harm humans 2. Where interconnections involve large ground potential differences (GPDs) and disruptive ground loops are to be avoided. In both cases isolation is used to tolerate or protect from hazardous voltages, yet allows for data or power flow between the two points. TI Information – Selective Disclosure Different Isolation Techniques Galvanic Isolation •Isolated circuits exchange signals without DC current flow between the isolated domains. Transformer Isolation •A form of Galvanic isolation using transformers to provide an AC coupled data path with coil separation providing the isolation. •The same topology can also be used to transfer power. Junction Isolation •Typically found in low voltage applications. •Highest breakdown processes available can reach 1200v (International Rectifier). Amplifier Isolation •Instrumentation Amplifiers and Differential Amplifiers comprise this area. •High levels of Common Mode signal rejection (isolation) while maintaining or amplifying the signals of interest. •Typically low-voltage (10s of volts). Frequency dependency can be a weakness. Wireless Technology •Recently also focused on power transmission, “The Holy Grail” of power electronics. •Dielectric thickness is variable and Frequency dependencies must be specified per application. TI Information – Selective Disclosure What is Isolation Voltage Supply 1 Voltage Supply 2 1) Electrical Installation can cause large GPDs (ground potential difference) Circuit 2 between two remote nodes. Circuit 1 ISOLATOR Signal & Signal & Return Path Return Path Ground Loop 2) A direct ground connection between the nodes closes the ground loop. 3) Noise sources (i.e. electric motors) injecting large currents into the ground modulate the ground loop current. 4) This ground noise then appears in the signal path. 5) An isolator breaks the ground loop, thus removing signal path noise. GPD Ground 1 With Isolation No Isolation TI Information – Selective Disclosure Ground 2 6) The GPD yet still exists and the isolator must be robust enough to withstand the large voltage differences. Why Isolate?? - Other reasons 120 Ω 120 Ω Data SN65HVD233 CAN CAN SN65HVD233 Group loop isolation ISO ISO7221C ISO7221C ISO Noise isolation TMP101 Sensor Fan DSP TMS 320 F2810 DSP with CAN Controller DSP 120V TI Information – Selective Disclosure ADS1255 24-Bit ISO7241A OPA333 SN75477 LVC2G06 Amp ISO ISO ISO721 Block High Voltage Amp ISO ISO7220M Amp Motor 480V Data Isolation: Common-Mode Transient Event Signals referenced to GND2 CMTI – The change in ground 1 relative ground 2. Measured in kV / μSec. TI Information – Selective Disclosure Isolation history Capacitive based isolation Ewald Georg von Kleist invented the first recorded capacitor 1745 Inductive based isolation Michael Faraday demonstrated the transformer principle in 1831 Opto-coupler based isolation Zarlink Invented the opto-coupler (1968) Others… Sound, RF, light, Mechanical, etc TI Information – Selective Disclosure Isolation Techniques Capacitive Inductive GMR Optical A. Capacitive Capacitive Inductive GMR Optical ISO72X ADuM1xx IL7x HCPL-07xx CIO 1 pF 1 pF Isolation Dielectric SiO2 Polyimide Which is capacitive coupled? B. Inductive 1.1 pF C. GMR D. Optical Polyimide 0.6 pF Mold compound E. All of the above TI Information – Selective Disclosure Source: TI App note SLLA198 www.ti.com/iso721 (Click on above link for web info) Some History “ Burr Brown Announces Industry-First Isolated Digital Coupler Using Capacitive Barrier Technology.” Article from: Business Wire Dated: August 19, 1998 Coplanar Capacitor Technology Technical Innovation by TI with regard to capacitive isolation technology improvements is impressive!! TI Information – Selective Disclosure How are they constructed? Cross Sectional View Transmit Chip Chip Transmit Receive Chip Receive Chip Mold compound Bond wire Top plate = Al High Voltage Capacitor Detail Inter Level Dielectric (Tons of SiO2) Bottom Plate = Silicon Substrate (doped) TI Information – Selective Disclosure 8-14 mm Internal Construction ISO72x: Integrated at process level Optical: Isolation functionality added at package level Inductive: Integrated at process level TI Information – Selective Disclosure How do they work? Isolation Barrier OSC Low – Frequency Channel (DC...100 kbps) LPF PWM VREF OUT IN DCL High – Frequency Channel (100 kbps...200Mbps) VREF The LF channel assures correct output signal polarity during loss of input signal (i.e. wire-break) HF and LF channels use differential signaling for high noise immunity In the new architecture, all signal transitions go through the High-Frequency Channel. TI Information – Selective Disclosure High-Frequency Channel (50:50 duty cycle) 1 2 A 3 4 CLOCK TRANSFER B (Duty Cycle = 50:50 ) C D 1 IN’ VREF A C A 1. 2. 3. 4. B Initial Staging RC Differentiator Stage Comparator Stage Flip Flop Stage C C D D L L H H L H L H S H L L S L H L S = store previous condition TI Information – Selective Disclosure A ( IN’) D B 2 B C 3 C D 4 D Low Frequency Channel A B OSC C D IN’ PWM IN” VREF C A B D IN’ CLK IN” Between A and D, the LF-channel works in the same way the HF channel does. A B The only differences are the pulse-width modulation at the beginning and the demodulation at the end. C D TI Information – Selective Disclosure E DEMOD E Terminology Working or Operating Voltage (Vrms): • Voltage that may be applied continuously across the Isolation barrier, ranges from 300Vrms to 1500Vrms Isolation or Transient Voltage (Vrms): • Voltage that may occur temporarily across the barrier tested for 1 minute during qualification. • Ranges from 2.5kVrms to 6kVrms Basic or Functional Isolation: • Assumes a single level of isolation of certain strength • Is applicable for most industrial applications and AC-equipment ≤ 400Vrms, and for consumer electronics. • Is mostly rated at 560Vpk continuous, 4kVpk transient voltage. Reinforced Isolation: • Assumes a single level of isolation providing the same reliability as a two-layer isolation. • Is applicable for most medical applications and AC-equipment > 400Vrms. • For component-level reinforced rating, VDE requires certification testing at a 10 kVpk surge voltage level. Common Mode Transient Immunity: • CMTI is the quick change in Reference potential from primary to secondary. • Given as the dV/dt up to which no false toggling of the output will occur (e.g. 35kV/us) Partial Discharge (PD): • Is a phenomena exhibited by insulator material when subjected to high electrical stresses, and is caused by the localized dielectric breakdown of voids or imperfections present within, which does not immediately bridge the space between two conductors. • It is measured in pico-coulombs using ‘Apparent Charge’ method. 100% units are production-tested for PD. • SiO2 is a very resilient insulation material. TI Information – Selective Disclosure Creepage and Clearance Discusses the surface-distance that may conduct if wet/polluted, respectively the air-distance. For 560V/4kV mostly 5mm is sufficient, for 890V/6kV mostly 8mm is needed. Depends on pollution degree Creepage distance Clearance distance Surface Air Shortest distance between two conductive leads, across isolation barrier, measured along surface of insulation. Package/ designation TI Package Specs Narrow body SOIC/ D Gull wing / DUB Wide body SOIC/ DW TI Information – Selective Disclosure QSOP / DBQ Shortest distance between two conductive leads , across isolation barrier, measured through air. Creepage mm Clearance mm 4 4 6.8 6.1 8 8 3.7 3.7 Discovery Questions… … to allow educated solution-proposals 1. 2. Isolation strength: basic/reinforced? What certifications? Isolation & working voltage: 4kVpeak, 560Vpk continuous? 6kVpeak, 890Vpk continuous? 3. Stand-alone isolation or integration (Transceiver, Gate-Driver, Data-Converter)? 4. Supply Voltages? 5. Channel-count & channel direction? 6. What is the transient immunity requirement? (CMTI) TI Information – Selective Disclosure Markets/Applications TI Information – Selective Disclosure Applications utilizing Isolation Industrial: • Robotics • PLC input/output isolation • Industrial networks • Motor control • Power supplies Primary Task: •Isolation between High-Power and Control Signals •Isolation of Bus-Nodes to prevent Corruption of the complete Bus & Common Mode Rejection TI Information – Selective Disclosure Applications utilizing Isolation Medical: Communications: • • • • • PBX (Private Branch Exchange) and central office • Telephone terminal equipment • Telephone switching equipment • Modems • ISDN • Ethernet / PoE Microwave therapy Patient monitoring Electrocardiographs Defibrillators Primary Task: Communications: •Isolation between Power and Caller •Isolation of Bus-Nodes to prevent Corruption of the complete Bus TI Information – Selective Disclosure Medical: • Isolation between Power and Patient Applications utilizing Isolation Consumer Electronics: • • • • Video (TV, VCR, etc.) Plasma displays Electronic gaming Home appliances Computers & Office Equipment • Isolated I/O • Printers and plotters • Fax machines Primary Task: • Isolation between High-Power and User TI Information – Selective Disclosure Competitive Analysis TI Information – Selective Disclosure Specs and Reliability Comparison Opto (Avago) Magnetic (ADI) Capacitive (Si Labs) Capacitive (TI) Max Data Rate (Mbps) 50 150 150 150 Typ Power Consumed/Ch @ 25Mbps & 3.3V (mA) 16 3.4 2.7 2 Max Propagation Delay Time (ns) 22 32 13 12 Pulse Width Distortion (ns) 2 2 4.5 1.5 Channel-to-Channel skew (ns) 16 2.0 2.5 1.6 Part-to-Part Skew (ns) 20 10 4.5 2 ESD on all Pins (kV) ±2 ±2 ±4 ±4 Minimum CM Transient Immunity (kV/us) 20 25 25 25 -45..125 -40..125 -40..125 -40..125 6.92E+04 3.17E+07 - 1.65E+09 14391 31.55 - 0.6 Radiated Electromagnetic-Field Immunity IEC61000-4-3 (80MHz-1000MHz) MIL-STD 461E RS103 (30MHz-1000MHz) - Fails* Fails* Fails* Fails* Complies Complies High-Voltage Lifetime Expectancy (yrs) - < 10 > 60* > 28 Temperature Range (oC) MTBF @ 125oC, 90% Confidence (Hrs) FIT@ 125oC, 90% Confidence (per 1E+09 hrs) * Devices passed the minimum criteria set by some standards. See details later in the presentation. TI Information – Selective Disclosure Competitive Analysis – ICC1 ICC1 COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS @ 3.3V 35 30 ICC1 (mA) 25 ISO7641FM 20 ISO7641FC Si8641BD 15 ADuM4401C 10 5 0 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 Data Rate (Mbps) TI Isolators have excellent power consumption throughout its operating range. Data shown above is taken in the lab on the same setup to ensure apples-toapples comparison. TI Information – Selective Disclosure Competitive Analysis – ICC2 ICC2 COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS @ 3.3V 30 25 ICC2 (mA) 20 ISO7641FM ISO7641FC 15 Si8641BD ADuM4401C 10 5 0 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 Data Rate (Mbps) TI Isolators have excellent power consumption throughout its operating range. Data shown above is taken in the lab on the same setup to ensure apples-toapples comparison. TI Information – Selective Disclosure Competitive Analysis – Propagation Delay Propagation Delay @ 3.3V 35.00 Prop Delay (ns) 30.00 25.00 ADuM4401C 20.00 Si8641BD ISO7641FC 15.00 ISO7641FM 10.00 5.00 0.00 Device Type TI has isolators with very fast propagation delays (M-grade) and devices with integrated input noise filters (C-grade). Data shown above is taken in the lab on the same setup to ensure apples-toapples comparison. TI Information – Selective Disclosure Dielectric Materials Used for Isolation • SiO2: ISO72x Typical BV is 800 Vpeak/um – Inorganic – Highly Stable (over temperature, moisture, time), high quality – Used extensively and for long time as dielectric in semiconductor (low defect rates) – Deposited in a controlled semiconductor process • Polyimide: ADI Transformer core Typical BV is 250 Vpeak/um – Organic – Retains moisture – affects lifetime especially at high voltages – Used in semiconductor mainly for stress relief & now as isolation barrier • Epoxy: Opto-couplers: Typical BV is 50 Vpeak/um – Uses filler materials – Leaky (higher partial discharge) – Applied at packaging as mold compound – Voids and anomalies are common TI Information – Selective Disclosure High Voltage Lifetime – TDDB (time dependent dielectric breakdown) TI Information – Selective Disclosure High Voltage Lifetime Temperature and Voltage Effect Tj = 150C 70 Lifetime in Years 60 Tj = 100C Tj = 85C 59 50 43 40 30 31 28 20 23 20 15 11 10 0 500 600 700 800 Vpeak (Working Voltage) TI Information – Selective Disclosure 900 1000 E-field immunity Test Report TI Information – Selective Disclosure EN55022 Class B Radiations Testing 1Mbps: Comparison of Radiated Noise Spectrum – Antenna Horizontal ADuM1201: 1Mbps operation @ 5V Vcc ISO7221: 1Mbps operation @ 5V Vcc TI Information – Selective Disclosure EN55022 Class B Radiation Testing 25Mbps: Comparison of Radiated Noise Spectrum – Antenna Horizontal ADuM1201: 25Mbps operation @ 5V Vcc ISO7221: 25Mbps operation @ 5V Vcc TI Information – Selective Disclosure E-field susceptibility Test Report TI Isolator ADI Isolator TI Information – Selective Disclosure Roadmap and Products (Click Link for presentation) TI Information – Selective Disclosure Thank You!