Generation of New Restrictive Conditionally Immortalized
Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Line
Anatoliy Koval , Zoe Damian , Alex Batchelor , Kaushik Shah ; Thomas J. Abbruscato
1
1
1
2
2
Lonza Walkersville, Inc. 8830 Biggs Ford Rd, Walkersville, MD, 21793-0127
2
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, 1300 Coulter Drive, Amarillo, Texas 79106
1
Abstract
Paracellular permeability assay and TEER measurements.
Previously, we were able to immortalize a variety of human primary cells including skeletal muscle
myoblasts, subcutaneous preadipocytes, human fetal hepatocyte precursors, donor matched
blood and lymph microvascular endothelial cells, epidermal keratinocytes, dermal fibroblasts,
and coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Most recently, we were able to develop a conditionally
immortalized human brain microvascular endothelial cell line termed HH8.
50,000 cells/well were plated in 0.4 µm transwell inserts (Corning collagen coated PTFE membrane,
Sigma-Aldrich, cat.# CLS3493). Cells were incubated at 33°C for 7-8 days and TEER was measured
during the last 2 days of incubation. For paracellular permeability, 0.5ml of fresh EGM®-2 MV
containing 1 µCi/ml of 14C-sucrose or 3H-mannitol (all from Perkin Elmer, cat.#NEC100X250UC
and NET101250UC, respectively) were added to the upical side of the inserts. 10 µl aliquots
were taken from 1.5 ml of media on the basolateral chamber of the transwells every 0, 30, 60,
90, and 120 min and counted using Beckman LS 65400 liquid scintillation counter (Beckman
Instruments, Inc., Fullerton, CA). The apparent permeability coefficient (PC) was calculated in
cm/min as described in Yang et al., 2007.
Human primary brain microvascular endothelial cells were immortalized by co-expression of
temperature sensitive SV40 Large T antigen and human telomerase. Resulting cells are cloned,
truly immortal and are able to proliferate for more then 160 population doublings (PD) with an
average proliferation rate of 40 h/PD at 33°C. Cells possess healthy, primary cell-like spindle
shape morphology, express a number of endothelial cell markers (CD34 +, CD146+, CD105+, CD90–,
CD31+, VEGF-RI+, VWF+), maintain contact inhibition and form homogeneous cell monolayers.
Upon confluency, cells display specific submembranous expression of tight junction proteins
ZO-1, Cadherin-5, β-Catenin, γ-Catenin, and p120 Catenin. Expression analysis of approximately
400 genes associated with toxicology reveals high expression levels of P-gp, MRP-1, -3, -4, ABCD3,
IGF-IR, SLC-2, -16,-27 and other transporters. Pgp and MRP1 activities are easily discriminated
using Calcein-AM uptake assay. More importantly, our cells demonstrate paracellular permeability
values (2-4E-04 cm/min for Sucrose and 3-4E-04 cm/min for Mannitol) that are more restrictive
than primary cultures of bovine brain microvessel endothelial cells or many existing immortalized
or transformed brain endothelial cell lines.
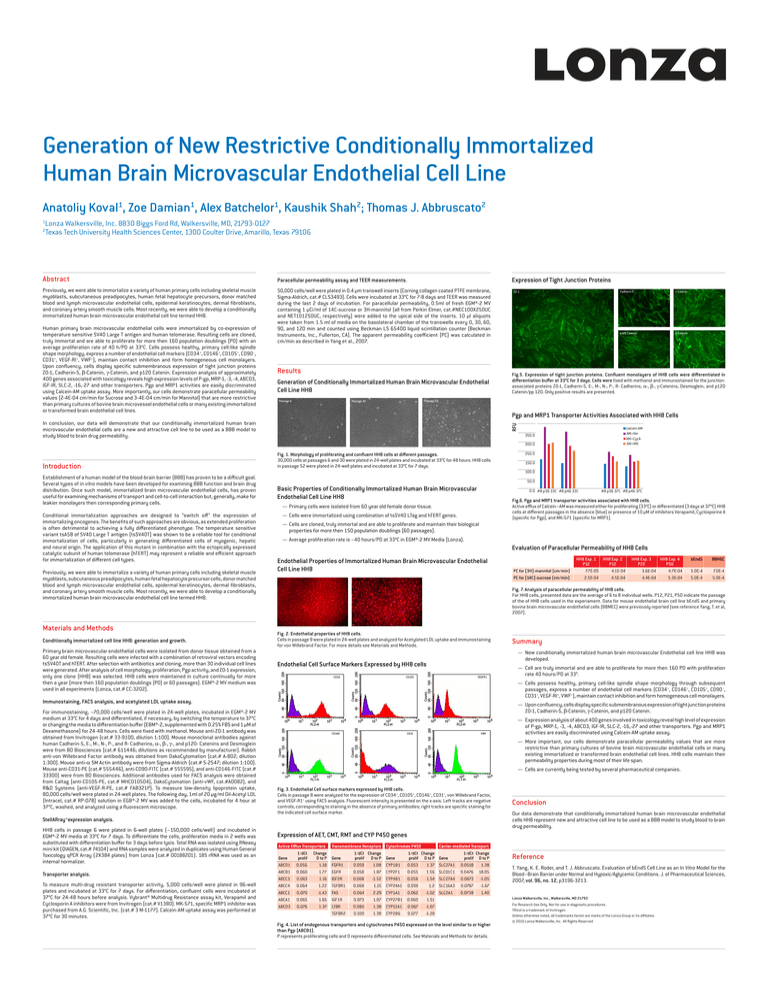
Expression of Tight Junction Proteins
Results
Generation of Conditionally Immortalized Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial
Cell Line HH8
Passage 6
ZO-1
Cadherin-5
γ-Catenin
p120 Catenin
β-Catenin
Fig.5. Expression of tight junction proteins. Confluent monolayers of HH8 cells were differentiated in
differentiation buffer at 33°C for 3 days. Cells were fixed with methanol and immunostained for the junctionassociated proteins ZO-1, Cadherin-5, E-, M-, N-, P-, R- Cadherins, α-, β-, γ-Catenins, Desmoglein, and p120
Catenin/pp 120. Only positive results are presented.
Passage 52
Passage 30
Pgp and MRP1 Transporter Activities Associated with HH8 Cells
RFU
In conclusion, our data will demonstrate that our conditionally immortalized human brain
microvascular endothelial cells are a new and attractive cell line to be used as a BBB model to
study blood to brain drug permeability.
calcein AM
AM+Ver
AM+CycA
AM+MK
350.0
300.0
Introduction
Establishment of a human model of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) has proven to be a difficult goal.
Several types of in vitro models have been developed for examining BBB function and brain drug
distribution. Once such model, immortalized brain microvascular endothelial cells, has proven
useful for examining mechanisms of transport and cell-to-cell interaction but, generally, make for
leakier monolayers then corresponding primary cells.
Conditional immortalization approaches are designed to “switch off” the expression of
immortalizing oncogenes. The benefits of such approaches are obvious, as extended proliferation
is often detrimental to achieving a fully differentiated phenotype. The temperature sensitive
variant tsA58 of SV40 Large T antigen (tsSV40T) was shown to be a reliable tool for conditional
immortalization of cells, particularly in generating differentiated cells of myogenic, hepatic
and neural origin. The application of this mutant in combination with the ectopically expressed
catalytic subunit of human telomerase (hTERT) may represent a reliable and efficient approach
for immortalization of different cell types.
Previously, we were able to immortalize a variety of human primary cells including skeletal muscle
myoblasts, subcutaneous preadipocytes, human fetal hepatocyte precursor cells, donor matched
blood and lymph microvascular endothelial cells, epidermal keratinocytes, dermal fibroblasts,
and coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Most recently, we were able to develop a conditionally
immortalized human brain microvascular endothelial cell line termed HH8.
Materials and Methods
Conditionally immortalized cell line HH8: generation and growth.
Primary brain microvascular endothelial cells were isolated from donor tissue obtained from a
60 year old female. Resulting cells were infected with a combination of retroviral vectors encoding
tsSV40T and hTERT. After selection with antibiotics and cloning, more than 30 individual cell lines
were generated. After analysis of cell morphology, proliferation, Pgp activity, and ZO-1 expression,
only one clone (HH8) was selected. HH8 cells were maintained in culture continually for more
then a year (more then 160 population doublings (PD) or 60 passages). EGM®-2 MV medium was
used in all experiments (Lonza, cat.# CC-3202).
Fig. 1. Morphology of proliferating and confluent HH8 cells at different passages.
30,000 cells at passages 6 and 30 were plated in 24-well plates and incubated at 33°C for 48 hours. HH8 cells
in passage 52 were plated in 24-well plates and incubated at 33°C for 7 days.
50.0
Basic Properties of Conditionally Immortalized Human Brain Microvascular
Endothelial Cell Line HH8
0.0 #8 p36 33C #8 p46 33C
Transporter analysis.
To measure multi-drug resistant transporter activity, 5,000 cells/well were plated in 96-well
plates and incubated at 33°C for 7 days. For differentiation, confluent cells were incubated at
37°C for 24-48 hours before analysis. Vybrant® Multidrug Resistance assay kit, Verapamil and
Cyclosporin A inhibitors were from Invitrogen (cat.# V1380). MK-571, specific MRP1 inhibitor was
purchased from A.G. Scientific, Inc. (cat.# 3 M-1177). Calcein-AM uptake assay was performed at
37°C for 30 minutes.
#8 p36 37C #8 p46 37C
Fig.6. Pgp and MRP1 transporter activities associated with HH8 cells.
Active efflux of Calcein–AM was measured either for proliferating (33°C) or differentiated (3 days at 37°C) HH8
cells at different passages in the absence (blue) or presence of 10 µM of inhibitors Verapamil, Cyclosporine A
(specific for Pgp), and MK-571 (specific for MRP1).
—— Primary cells were isolated from 60 year old female donor tissue.
—— Cells were immortalized using combination of tsSV40 LTag and hTERT genes.
—— Cells are cloned, truly immortal and are able to proliferate and maintain their biological
properties for more then 150 population doublings (60 passages).
—— Average proliferation rate is ~40 hours/PD at 33°C in EGM®-2 MV Media (Lonza).
Evaluation of Paracellular Permeability of HH8 Cells
Endothelial Properties of Immortalized Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial
Cell Line HH8
PC for [3H]-mannitol (cm/min)
PC for [14C]-sucrose (cm/min)
HH8 Exp. 1 HH8 Exp. 2
P12
P12
7.7E-05
4.1E-04
2.5E-04
4.5E-04
HH8 Exp. 3
HH8 Exp. 4
P23
P50
3.6E-04
4.7E-04
4.4E-04
5.3E-04
bEnd5
BBMEC
5.0E-4
5.0E-4
7.0E-4
5.0E-4
Fig. 7. Analysis of paracellular permeability of HH8 cells.
For HH8 cells, presented data are the average of 6 to 8 individual wells. P12, P21, P50 indicate the passage
of the of HH8 cells used in the experiament. Data for mouse endothelial brain cell line bEnd5 and primary
bovine brain microvascular endothelial cells (BBMEC) were previously reported (see reference Yang, T. et al,
2007).
Fig. 2. Endothelial properties of HH8 cells.
Cells in passage 9 were plated in 24-well plates and analyzed for Acetylated LDL uptake and immunostaining
for von Willebrand Factor. For more details see Materials and Methods.
Endothelial Cell Surface Markers Expressed by HH8 cells
CD34
Summary
—— New conditionally immortalized human brain microvascular Endothelial cell line HH8 was
developed.
CD105
VEGFR1
—— Cell are truly immortal and are able to proliferate for more then 160 PD with proliferation
rate 40 hours/PD at 33°.
—— Cells possess healthy, primary cell-like spindle shape morphology through subsequent
passages, express a number of endothelial cell markers (CD34 +, CD146+, CD105+, CD90–,
CD31+, VEGF-RI+, VWF+), maintain contact inhibition and form homogeneous cell monolayers.
—— Upon confluency, cells display specific submembranous expression of tight junction proteins
ZO-1, Cadherin-5, β-Catenin, γ-Catenin, and p120 Catenin.
CD146
CD31
VWF
—— Expression analysis of about 400 genes involved in toxicology reveal high level of expression
of P-gp, MRP-1, -3, -4, ABCD3, IGF-IR, SLC-2, -16,-27 and other transporters. Pgp and MRP1
activities are easily discriminated using Calcein-AM uptake assay.
—— More important, our cells demonstrate paracellular permeability values that are more
restrictive than primary cultures of bovine brain microvascular endothelial cells or many
existing immortalized or transformed brain endothelial cell lines. HH8 cells maintain their
permeability properties during most of their life span.
—— Cells are currently being tested by several pharmaceutical companies.
Fig. 3. Endothelial Cell surface markers expressed by HH8 cells.
Cells in passage 8 were analyzed for the expression of CD34+, CD105+, CD146+, CD31+, von Willebrand Factor,
and VEGF-R1+ using FACS analysis. Fluorescent intensity is presented on the x-axis. Left tracks are negative
controls, corresponding to staining in the absence of primary antibodies; right tracks are specific staining for
the indicated cell surface marker.
StellARray™expression analysis.
HH8 cells in passage 6 were plated in 6-well plates (~150,000 cells/well) and incubated in
EGM®-2 MV media at 33°C for 7 days. To differentiate the cells, proliferation media in 2 wells was
substituted with differentiation buffer for 3 days before lysis. Total RNA was isolated using RNeasy
mini kit (QIAGEN, cat.# 74104) and RNA samples were analyzed in duplicates using Human General
Toxicology qPCR Array (2X384 plates) from Lonza (cat.# 00188201). 18S rRNA was used as an
internal normalizer.
150.0
100.0
Immunostaining, FACS analysis, and acetylated LDL uptake assay.
For immunostaining, ~70,000 cells/well were plated in 24-well plates, incubated in EGM®-2 MV
medium at 33°C for 4 days and differentiated, if necessary, by switching the temperature to 37°C
or changing the media to differentiation buffer (EBM®-2, supplemented with 0.25% FBS and 1 µM of
Dexamethasone) for 24-48 hours. Cells were fixed with methanol. Mouse anti-ZO-1 antibody was
obtained from Invitrogen (cat.# 33-9100, dilution 1:100). Mouse monoclonal antibodies against
human Cadherin-5, E-, M-, N-, P-, and R- Cadherins, α-, β-, γ-, and p120- Catenins and Desmoglein
were from BD Biosciences (cat.# 611446; dilutions as recommended by manufacturer). Rabbit
anti-von Willebrand Factor antibody was obtained from DakoCytomation (cat.# A-802; dilution
1:300). Mouse anti-α SM Actin antibody were from Sigma-Aldrich (cat.# S-2547; dilution 1:100).
Mouse anti-CD31-PE (cat.# 555446), anti-CD90-FITC (cat.# 555595), and anti-CD146-FITC (cat.#
33300) were from BD Biosciences. Additional antibodies used for FACS analysis were obtained
from Caltag (anti-CD105-PE, cat.# MHCD10504), DakoCytomation (anti-vWF, cat.#A0082), and
R&D Systems (anti-VEGF-R-PE, cat.# FAB321P). To measure low-density lipoprotein uptake,
80,000 cells/well were plated in 24-well plates. The following day, 1ml of 20 µg/ml DiI-Acetyl LDL
(Intracel, cat.# RP-078) solution in EGB®-2 MV was added to the cells, incubated for 4 hour at
37°C, washed, and analyzed using a fluorescent microscope.
250.0
Conclusion
Our data demonstrate that conditionally immortalized human brain microvascular endothelial
cells HH8 represent new and attractive cell line to be used as a BBB model to study blood to brain
drug permeability.
Expression of AET, CMT, RMT and CYP P450 genes
Active Efflux Transporters
Gene
ABCD1
ABCB1
ABCC3
ABCC4
ABCC1
ABCA1
ABCD3
1/dCt
prolif
0.056
0.060
0.063
0.064
0.070
0.065
0.076
Change
D to P
1.18
1.77
1.16
1.22
-1.43
1.65
1.37
Transmembrane Receptors Cytochromes P450
Gene
FGFR1
EGFR
IGF2R
TGFBR1
FAS
IGF1R
LTBR
TGFBR2
1/dCt Change
prolif D to P Gene
0.059
1.08 CYP1B1
0.058
1.87 CYP2F1
0.068
-1.52 CYP4B1
0.068
1.15 CYP24A1
0.064
2.29 CYP1A1
0.073
1.07 CYP27B1
0.080
1.38 CYP51A1
0.100
1.38 CYP2B6
Carrier-mediated Transport
1/dCt Change
prolif D to P Gene
0.053
1.37 SLC27A1
0.055
1.56 SLC01C1
0.056
1.54 SLC27A4
0.059
1.2 SLC16A3
0.062
-1.02 SLC2A1
0.060
1.51
0.067
-1.07
0.077
-1.28
1/dCt Change
prolif D to P
0.0518
1.38
0.0476 18.05
0.0673 -1.05
0.0787 -1.67
0.0738
1.40
Fig. 4. List of endogenous transporters and cytochromes P450 expressed on the level similar to or higher
than Pgp (ABCB1).
P represents proliferating cells and D represents differentiated cells. See Materials and Methods for details.
Reference
T. Yang, K. E. Roder, and T. J. Abbruscato. Evaluation of bEnd5 Cell Line as an In Vitro Model for the
Blood–Brain Barrier under Normal and Hypoxic/Aglycemic Conditions. J. of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
2007, vol. 96, no. 12, p3196-3213.
Lonza Walkersville, Inc., Walkersville, MD 21793
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
TRIzol is a trademark of Invitrogen
Unless otherwise noted, all trademarks herein are marks of the Lonza Group or its affiliates.
© 2010 Lonza Walkersville, Inc. All Rights Reserved