COMPOUND CIRCUITS
advertisement

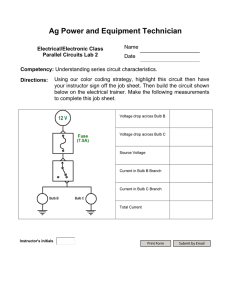
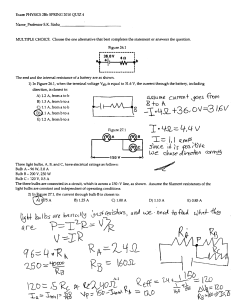
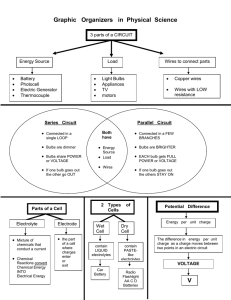
COMPOUND CIRCUITS LOGGING ON Go to www.ExploreLearning.com and log in using your Username and Password. Select “Browse Gizmos” icon at the upper left. Select “Grades 9 – 12 Physics” Select “Electricity and Magnetism” Select “Advanced Circuits” and Launch the Gizmo. GETTING STARTED To build a simple circuit with a single bulb and battery, use the cursor to drag a battery, two wires, and a bulb. Notice the light bulb glows. The “slider” at the bottom of the circuit board adjusts the voltage. Remove one of the wires and replace it with a switch. Turn the switch on and off. MEASURING VOLTAGE AND CURRENT 1. Build a simple circuit with one bulb, one battery, a switch and a wire. Set the voltage to 10 volts. 2. Using the cursor, drag the positive terminal of the volt meter to the positive side of the bulb and the negative terminal of the meter to the negative side of the bulb. The voltage in the circuit is displayed at the bottom left of the Gizmo. The voltmeter must be placed “across” the bulb. (see diagram to the right) 3. Using the cursor, drag the ammeter and place it near one of the connections in the circuit. The current (in amperes) is displayed below the voltage. The ammeter must be placed “in series” with the bulb. (see diagram to the right) PART I: SERIES CIRCUITS Construct a circuit with two bulbs in series. Set the voltage to 10.0 volts. Measure the overall voltage in the circuit by placing the appropriate terminal of the voltmeter at the terminals of the battery. Measure the voltage across each bulb. Next, place the ammeter in the circuit to determine the current at the designated points within the circuit. Record your data in the tables. Voltage (volts) A Across Bulb A Across Bulb B Across the Battery Between Battery & A Current (amperes) Between A&B Between Battery & B B Building Circuits 1 Construct a circuit with three bulbs in series and measure the voltage and current as you did above. Voltage (volts) Across Across Bulb B Bulb C Across Bulb A A B Across the Battery C Current (amperes) Between Battery & A Between A&B Between B&C Between Battery & C Compare the voltage across the battery (total voltage) and the voltage at each bulb for the two circuits. Write a generalized statement that describes the relationship between the total voltage and the voltage at each bulb for a series circuit. Compare the current at the battery (total current) and the current at each bulb. Write a generalized statement that describes the relationship between the total current and the current at each bulb. CALCULATING RESISTANCE Using Ohm’s Law ( V voltage = I current x R resistance ), calculate the resistance in Ohms at the various points within the circuit. The unit for resistance, Ohm, is symbolized by the Greek letter omega (Ω). Express your answers to 3 significant figures. Resistance (Ohms) Resistance (Ohms) Bulb A Bulb B Battery Bulb A Bulb B Bulb C Battery Building Circuits 2 MEASURING RESISTANCE Reconstruct the series circuit with two bulbs without a battery. The Ohmmeter will only function when there is no current running through the circuit. To check the total resistance in the circuit, place the Ohmmeter where the battery would normally be located. Then, place the Ohmmeter at opposite terminals for each bulb to measure the resistance of the bulb. Then, reconstruct the series circuit with three bulbs and check the total resistance and the resistance of each bulb. Resistance (Ohms) Bulb A Bulb B Resistance (Ohms) Total Bulb A Bulb B Bulb C Total Write a generalized statement that describes the relationship between the total resistance in the circuit (as measured where the battery would be located) and the resistance at each bulb. How does the total resistance in a series circuit change when increasing the number of bulbs? Does the resistance of each bulb change when increasing the number of bulbs in the circuit? PART II: PARALLEL CIRCUITS Construct a circuit with two bulbs in parallel and set the voltage to 10.0 volts. Measure the overall voltage in the circuit by placing the appropriate terminal of the voltmeter at the terminals of the battery. Measure the voltage across each bulb. Next, place the ammeter in the circuit to determine the current at the designated points within the circuit. Record your data in the tables. Voltage (volts) A Across Bulb A Across Bulb B Across the Battery Between Battery & A Current (amperes) Between A&B Between Battery & B B Building Circuits 3 Construct a circuit with three bulbs in parallel and measure the voltage and current as you did above. Across Bulb A B A Voltage (volts) Across Across Bulb B Bulb C Across the Battery C Current (amperes) Between Battery & A Between A&B Between B&C Between Battery & C Compare the voltage across the battery (total voltage) and the voltage at each bulb for the two circuits. Write a generalized statement that describes the relationship between the total voltage and the voltage at each bulb. Compare the current at the battery (total current) and the current at each bulb. Write a generalized statement that describes the relationship between the total current and the current at each bulb. CALCULATING RESISTANCE Using Ohm’s Law ( V = I R ), calculate the resistance for each bulb in the two circuits. Resistance (Ohms) Bulb A Bulb B Resistance (Ohms) Bulb A Bulb B Bulb C CALCULATING TOTAL RESISTANCE FOR PARALLEL CIRCUITS The total resistance of a parallel circuit can also be calculated using the equivalent resistance equation, where the total resistance in a parallel circuit RTOTAL can be calculated from the following formula: 1 Rt 1 RA 1 RB 1 RC ... As you have seen, the total resistance in a series circuit increases as the number of bulbs increases, for a parallel circuit, the total resistance decreases as more bulbs are added. Building Circuits 4 Using the equivalent resistance equation, substitute the values for the resistances of each bulb and calculate the total resistance in each parallel circuit. Show your work below. (Hint: Reduce the fraction rather than calculate.) Total Resistance for Two Parallel Bulbs Total Resistance for Three Parallel Bulbs How does the total resistance in a parallel circuit change when increasing the number of bulbs? PART III: BUILDING COMPOUND CIRCUITS In this part, you will build several examples of compound circuits that combine parallel and series components. Build the circuit shown in the diagram to the right. This circuit should look familiar since it is the compound circuit that was constructed in the previous laboratory. Set the voltage of the battery to 10.0 V. A C Notice that bulbs A & B are in series, and that bulbs A & B are parallel with bulb C. As you have concluded from the previous experiments: B FOR SERIES CIRCUITS The total voltage in the circuit is the sum of the voltages across each bulb. The current is the same anywhere in the circuit. The total resistance in a circuit is the sum of the resistances at each bulb. FOR PARALLEL CIRCUITS The voltage is the same anywhere in the circuit. The total current is the sum of the currents in each circuit. The total resistance of a circuit follows the relationship: 1 Rt 1 RA 1 RB 1 RC ... Building Circuits 5 Use the voltmeter and ammeter to measure the voltage and current at each bulb, A, B & C. Record your values in the table. Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the resistance for each bulb. Bulb Resistance (Ohms) Current (amperes) Voltage (volts) A B C Total DETERMINING TOTAL RESISTANCE, CURRENT & VOLTAGE Using the information from the table above, you will next determine the total current, voltage, and resistance in the compound circuit. To determine the total current: 1. Use the series rule for current for the right-hand circuit (bulbs A & B). Current is the same in both bulbs. 2. Use the parallel rule for current for the entire circuit (right and left hand): Total current is the sum of the currents in each circuit. Total Current = ______________ + ________________ (bulbs A & B) (bulb C) To determine the total voltage: 1. Use the series rule for voltage for the right-hand circuit. Voltage in circuit is the sum of voltages in the bulbs. 2. Use the parallel rule for voltage for the entire circuit (right and left hand). Total voltage is the same as the voltage in each circuit. Total Voltage = ________________ To determine the total resistance: 1. Use the series rule for the resistance for the right-hand circuit: The resistance in this circuit is the sum of the resistances for bulbs A & B Right-hand circuit resistance = _________________ 2. Use the Equivalent Resistance Rule for the entire circuit (right and left hand). 1 / R total = 1 / right hand + 1 / left hand R TOTAL = _____________________ Building Circuits 6 CALCULATING POWER The power of a light bulb, measured in Watts, is determined by the following equation: Power (Watts) = Current (Amperes) x Voltage (Volts) or P = I V Calculate the power (in Watts) for each of the bulbs in the circuit diagram Bulb A Bulb B Bulb C Construct a statement that relates the power of the bulb to its apparent brightness. BUILDING COMPOUND CIRCUITS (CONTINUED) Examine the circuit shown in the diagram to the right. How many different pathways are there for the current A C B D in the compound circuit? __________ Which bulbs does each circuit contain? Left Side: ___________ Right Side: _____________ Are the bulbs in each circuit in series or parallel with each other? _______________ Are the two pathways (Left and Right Side) in series or in parallel with each other? _____________ Notice that some of the values have been included in the table below. The first step in determining the missing values is to assess which bulbs in the circuit are identical to each other. Then, information which is known concerning one bulb can added to the information known about similar bulbs. Using this information fill in the missing data without constructing the circuit. Then, calculate the total current, voltage, and resistance in the compound Voltage Current Resistance circuit. Bulb (Volts) Now, construct and test the circuit using the voltmeter and ammeter to determine the voltage and current at each bulb to confirm your solution. B Bulb B Bulb C D 5.0 0.33 15 Total Power (Watts) Bulb A (Ohms) A C Finally, calculate the power (in Watts) at each light bulb. (Amperes) Bulb D Building Circuits 7 POST LABORATORY PROBLEMS Without using the computer simulation, determine the missing values in the data tables for each of the following circuits. Afterwards, build the circuit and test your answers using the ammeter, voltmeter, and Ohmmeter. Remember to first assess which bulbs in the circuit are identical to each other, then the missing information can be determined from similar bulbs. Circuit 1 Bulb Circuit 1 Voltage Current A Resistance A 0.27 A 2.0 V B C 15 Ω D Total B 10.0 V C Circuit 2 D A Bulb Voltage A B B C D Circuit 2 Current Resistance Power 0.29 A 1.43 V C 15 Ω D E 4.28 V Total E ----- Circuit 3 Bulb A B Voltage A B D Resistance Power 0.13 A 2.0 V C C Circuit 3 Current 15 Ω 6.0 V Total ----- D Building Circuits 8