Centre 7: Electricity
advertisement

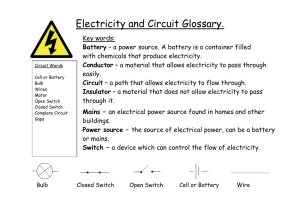
Centre 7: Electricity Electricity 1 12/9/02, 9:24 AM Grade 6 Electricity The theme of this activity centre is Electricity, a topic from the Grade 6 Pan Canada Science Curriculum. These interdisciplinary materials are designed to support your implementation of this unit as well as invite the student to reflect on potential careers that are linked to this topic. WHAT DO YOU SEE? is a Science and Art activity where students draw and label (using a legend with names and descriptor), a small 2.5 volt light bulb and a battery which will be used in some of the remaining activities. IF AT FIRST YOU DON’T SUCCEED is a Science activity where students learn four different ways to make a light bulb light up using just one bulb, one battery and one piece of wire. Overview YES AND NO is a Science activity where students develop their skill of prediction. Students are given nine sketches showing a battery, a bulb and a piece of wire to review. Before they actual try the sketches as shown, they predict whether or not they think the bulb will light up. CONDUCTORS OR NOT? is a Science activity where students test everyday objects to determine if they are conductors or if they are insulators. MAKING CONNECTIONS is a Science activity where students look at a drawing of a mystery card showing two or three connections that will complete a circuit and light up a light bulb. Student test circuits by first predicting which ones will complete the circuit. LOGICAL CONNECTIONS is a Math, Language Arts and Science activity where students generate mystery circuit cards using number combinations (math) or combinations of words (language arts) to set up the circuit combinations WHERE WERE YOU WHEN… is a Language Arts creative writing activity based on a scary incident when the power (lights) went off. ELECTRICAL SHORTHAND is a Science activity where students learn some of the symbols used in electrical drawings. Students are given a picture of a simple circuit and asked to redraw it using only symbols. General Curriculum Links Several subject areas have been drawn upon for the development of these activities. They include: Western Canada Math (Number Operations and Number Concepts Strand) Pan Canada Science (Performing and Recording) Use numbers to describe quantities 205-3 Represents numbers in multiple ways follow a given set of procedures Pan Canada Science (Knowledge) 300-20 compare the conductivity of a variety of solids (and liquids) Experiments with language and forms Understands forms and techniques (create original texts) Page 7.2 303-23 compare a variety of electrical pathways by constructing simple circuits Western Canada Language Arts (General Outcome 1 and 2) Electricity 2 12/9/02, 9:24 AM Activity List of Materials Other What Do You See? light bulb 2.5 volts D cell battery, pencil activity sheet 7.7 If At First You Don’t Succeed light bulb 2.5 volt D cell battery, 20 cm bare wire (20-24 guage), scissors activity sheet 7.8 Yes And No light bulb 2.5 volt D cell battery, 20 cm bare wire (20-24 guage) activity sheet 7.9 activity sheet 7.10 Electrical Shorthand Conductors or Not? Grade 6 Electricity List of Materials 1 battery and battery holder 1 bulb 2.5 volts and a bulb holder, 3 pieces of bare wire (20 cm) Making Connections activity sheet 7.11 activity sheet 7.12 Logical Connections tin foil, index cards, hole punch, tape activity sheet 7.13 Where Were You When… pencil activity sheet 7.14 Answers/Responses negative terminal filament ceramic Activity 7.9 YES AND NO The diagrams which work are letters A, B, D, G, and I. Activity 7.10 ELECTRICAL SHORTHAND case a) b) positive terminal Activity 7.12 MAKING CONNECTIONS lead contact threaded metal base ceramic lead tip Activity 7.8 IF AT FIRST YOU DON’T SUCCEED Overview Activity 7.7 WHAT DO YOU SEE? The light bulb would go off with the following connections – A and D, B and C, B and E, and C and E. Page 7.3 Electricity 3 12/9/02, 9:24 AM Electricity Page 7.4 Progress Chart Class List/Students 4 AT D OY OU CTR I CA LS 12/9/02, 9:24 AM WH ERE WE NO T ? YO UW HE N CTI ON S CTI ON S ON NE RE LO GIC AL C MA KIN GC ON NE OR HO R TH AN D CTO RS CO ND U ELE SEE ? IF A T S U C FIRST Y CE E D OU D ON ’T YES AN DN O WH Grade 6 Electricity Progress Chart WHAT DO YOU SEE? is a Science and Art activity where you will draw and label a small 2.5 volt light bulb and a battery. Grade 6 Electricity Date Completed IF AT FIRST YOU DON’T SUCCEED is a Science activity where you will explore different ways to make a light bulb light up. Student Checklist YES AND NO is a Science activity where you will look at diagrams and determine if a light bulb will light. Then you will test it with a bulb, battery and piece of wire. ELECTRICAL SHORTHAND is a Science activity where you will learn different symbols used in electrical drawings. Page 7.5 Electricity 5 12/9/02, 9:24 AM Grade 6 Electricity Date Completed CONDUCTORS OR NOT? is a Science activity where you will learn about objects that conduct electricity (conductors) and objects that do not conduct electricity (insulators). Student Checklist MAKING CONNECTIONS is a Science activity where you test circuits. You will also try to predict ways of completing a circuit and getting a light bulb to light up. LOGICAL CONNECTIONS is a Math, Language Arts and Science activity where you will create different mystery circuit cards. Other students will use their knowledge of math or language arts to test the circuits. Page 7.6 WHERE WERE YOU WHEN… is a Language Arts creative writing activity based on a scary incident when the power (lights) went off. Electricity 6 12/9/02, 9:24 AM Grade 6 Electricity a) We take it for granted that every time we turn on a light switch the lights will come on. Think of all the people that must be involved in the making of a light bulb and in the delivery of electrical services to your house. b) Have you ever taken a really close look at a light bulb? In this activity, you will make a drawing of your observations of a light bulb as 1. 2. battery. , with clear glass, and a D cell g them using the You will need a small light bulb and the battery and try labellin bulb t ligh the h bot of g win dra Make a detailed of the page. legend (chart) at the bottom Batteries Light Bulb and thin coiled wire that heats up gives off light s small piece of material that hold ceramic not s doe filaments in place and conduct electricity t electricity when lead contact helps to conduc it comes in contact filament Electricity 7 lead tip into a provides support and screws e bas provides a contact point ton positive terminal (+ end) – but shaped case ce holds battery contents in pla shape flat ) negative terminal (- end Try to identify as many careers as possible that might have had something to do with the production of a light bulb and battery. 12/9/02, 9:24 AM Activity 7.7 d) Some Things To Try! How many different types of batteries can you think of? Try making a drawing of each one. threaded metal base What Do You See? c) well as a battery. Sounds easy doesn’t it? Lets see! Grade 6 Electricity Activity 7.8 If At First You Don’t Succeed a) Now that you know what all the parts of a light bulb and battery are, it’s time to shed more light on this subject. Electricity b) You will need: • 1 small 2.5 v light bulb • 1 D cell battery • 1 piece (20 cm) of bare wire (20 to 24 gauge) • Scissors (to cut the wire) c) and one Using one battery, one light bulb s way to get the wire, try to find four different have found four light bulb to light up. When you rt. ways, draw them on this cha 2. 1. 4. 3. d) Some Things To Try! Try to find out what is meant by the “gauge” of a wire. 8 What is the difference between 24 gauge wire and 12 gauge wire? 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity a) Look at each of the diagrams. Write the word YES or NO beside each diagram. 1. 2. Write YES if you think it will work – will make the bulb light up. Write a NO if you think it will not work. Good luck! B C D E F G H I 3. Yes and No A Once you have finished writing yes or no beside each one, take a battery, bulb and small piece of wire and try each one. If you got it right, circle your earlier answer (prediction). If you got it wrong, circle your answer and draw a big “X” through it. Activity 7.9 Electricity 9 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity a) Have you eve seen the types of drawings that electricians, mechanics and repair technicians use? They use symbols to b) Here’s some of the symbols that are used. Symbol represent things. Once you know their language, it’s not so hard to understand. Electrical Component Comments Wire Wires not connected Positive polarity Activity 7.10 Electrical Shorthand Negative polarity Electricity Battery Short line negative Two batteries Long line positive Bulb Switch Open Switch Closed Motor c) circuits Look at the drawing of the simple the only g usin them aw below and redr ve. symbols from abo d) Some Things To Try! Try making electrical drawings for a circuit with more than one light bulb or switch in it. 10 bols. Redraw the simple circuit using sym Try making a circuit drawing for a small appliance such as a toaster or kettle. 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity a) To learn about conductors you will need: • 1 battery and battery holder • 1 2.5 volt bulb and a bulb holder • 3 pieces of bare wire (20 cm) b) Set up a simple circuit as shown in the diagram. Place wires A and B directly on the objects being tested for their conductivity. If the light bulb goes on, you have a completed circuit and that object conducts electricity. That makes it a conductor. Objects that do not conduct electricity are called nonconductors or insulators. c) 1. 2. 3. b uctivity. Test as many objects as you can for their cond l, dime, estions include nails, scissors, penny, nicke You can test any object you like. Some sugg , rocks, keys, tacks, plastic, glass, wood, styrofoam quarter, loonie, toonie, tin foil, wax paper, paper, staples, etc. it will be a conductor or not. Before you actually try one, try to predict if Object to be Tested Prediction (conductor/nonconductor) Test (Yes/No) 1. 2. Conductors or Not? a 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Electricity 11 Research the type of materials used for safety equipment for electricians, power linemen and emergency response teams. 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Activity 7.11 d) Some Things to Try! Try to find some examples of where conductors or insulators are used around you – in the school or at home. Making Connections Grade 6 Electricity A B C D E F a) The picture above is an index card with six holes punched it. The holes are labeled A, B, C, D, E and F. has been covered with tape. All anyone can see is the six holes and they all have a piece of tin foil in them. b) Imagine that the smaller boxes around A and D, B and C, as well as B and E, are actually pieces of tin foil. Also imagine that no one can see the tin foil pieces because the index card c) 1. if you What do you think would happen vity acti from s wire two r connected you tin the to ?) NOT OR RS CTO 7.12 (CONDU ? card x inde the in s hole the foil on two of 2. if you tried What do you think would happen wing follo the g usin s to make connection points of contact: A and B _____ A and C _____ A and D _____ A and E _____ A and F _____ B and C _____ B and D _____ B and E _____ C and D _____ C and E _____ C and F _____ D and E _____ D and F Activity 7.12 B and F Electricity 12 _____ 12/9/02, 9:25 AM _____ Grade 6 Electricity a) Electricians and repair technicians test circuits all the time. They want to make sure that instruments and machines are getting electricity. You can test circuits as well using mystery circuit cards like the ones in Activity 7.12 (MAKING CONNECTIONS). b) Go ahead. Try to make your own mystery card that has one or more ways of making the light bulb light up. (Hint: Using 2 batteries hooked up together with battery holders will make the current stronger and give you better results.) Be sure to: e. 1. Put tin foil over each hol tin foil other than of ces pie 2. Ensure that no ss over one your secret connections cro or you will er oth h eac ch another or tou uit is. circ rt sho a at wh soon discover 3. 4. e) Some Things To Try! Here’s a twist to really make your connection card cool. Try using something you are studying in Language Arts or Math as your contact point. Instead of using A, B, C, D, E and F, try using three sets of words that are tape or a second Cover your index card with t no one can see index card with tape so tha made. the connections that were and write down d car the on e nam Put your here so others the right connections somew can check their answers. opposites, or three sets of numbers that are equivalent fractions. In order to get the light bulb to light up, someone has to match the correct two words or numbers to complete the circuit. Only the ones which are equivalent fractions will light up the bulb. 2/3 12/16 6/8 Logical Connections d) c) To make mystery cards, you will need: • Tin foil • Index cards • Hole puncher • Tape 2/3 and 6/9 12/16 and 6/8 12/16 and 48/64 6/9 48/64 2/4 6/8 and 48/64 (tricky one) Activity 7.13 Electricity 13 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity a) Have you ever heard someone say “Where were you when the lights went out?” Usually they are talking about a power outage – something Northerners are very familiar with. b) Try to imagine the scariest place you could be when the power or lights go out. Where would that be – in an elevator? On a roller coaster at the top of an incline? incident Write a short story about a SCARY there is des, when the power went off! Besi the for wait nothing else to do while you so the power power lineman to fix the problem can come back on. Activity 7.14 Where Were You When... c) Electricity 14 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity son is an Eric Amarouk Hugh an. He lives ici ctr appr entice ele in Baker Lake. Photo Stefan Blake is an apprentice electrician working in Norman Wells. Page 7.15 Electricity 15 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity Page 7.16 Photos Leila McKay is a jour neyperson partsperson working in Hay River. Every day is always different from the last day in her job. Peo ple are always looking for so many different parts for their vehicles and machines. Electricity 16 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity Ryan Schimmelmann is an appren tice electrician. He works at the BHP Billito n Ekati Diamond Mine. He likes the variety and type of work associated with the electrical trades. An electrician apprentice learns about the science related to electrical systems. This includes safety, magnetism, controls and switches, fire alarm systems, circuits, measuring instruments, heating and cooling systems, motors, starters electronics, lighting, and trade mathematics. Apprentices also learn about blueprints and drawings. Electricians lay out, assemble, install, test and repair electrical fixtures, control equipment and wiring needed to supply heat, light and power to all types of buildings. Photos Page 7.17 Electricity 17 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity in Egypt. He is a Yousry Abdelmegid was bor n ning mechanic. refrigeration and air conditio Milan, Italy. He trained in Cairo, Egypt and since 1996. He Yousry has been in the North Yellowknife. He works with JSL Mechanical in trol systems. enjoys working with various con Page 7.18 Photos As a refrigeration and air conditioning mechanic apprentice, you will learn about the science related to changes of state, heat and temperature, properties of coolants, compression, heating systems, electricity, equipment controls, gas laws, and small engines. Training involves ordering, assembling, installing, and testing of industrial and commercial equipment. You would usually work for companies that install and service air conditioning and refrigeration systems. Electricity 18 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity Barry Menard is a po wer lineman working for Northland Utilities in Ye llowknife. He was born in Fort Smith and raised in Frobisher Bay (Iqalu it), Fort Simpson, Fort Re solution and Yellowkn ife. Barry finds that each day brings something new in this job. He als o really likes working with the people at Northlan ds. Barry says that to be a good lineman you really need to know yo ur high school math. Photos Page 7.19 Electricity 19 12/9/02, 9:25 AM Grade 6 Electricity electrician Ted McKnight is an apprentice ys working working in Norman Wells. He enjo tricity. outside and learning all about elec Page 7.20 Photos Shawn Wentz is an electrical engineering technologist. He works for Nor thland Utilities in Yellowknife. In his job he con sults on wiring and electrical needs for buildings. He also monitors the power substations and systems that brings electricity to your home. Sha wn says that the math and physics you learn in high school is a good start to this career. Electricity 20 12/9/02, 9:25 AM