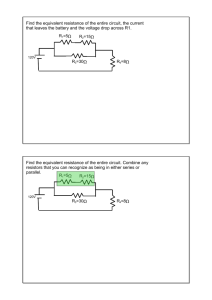
1 R2=15Ω R3=30Ω R4=8Ω Find the equivalent resistance of the
advertisement
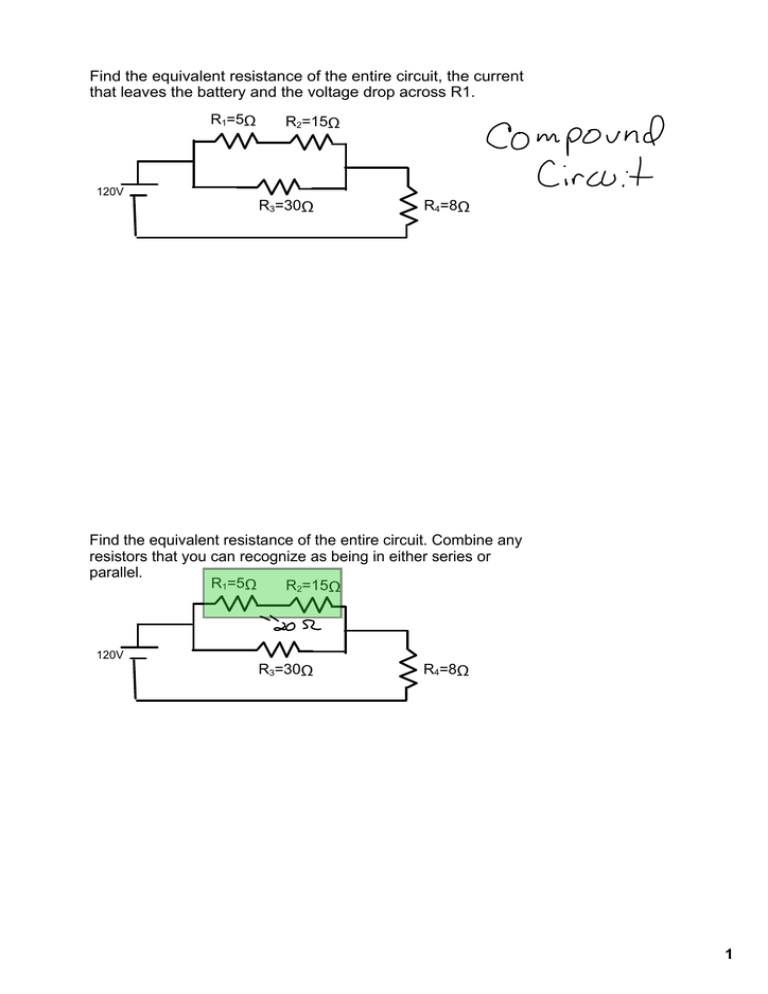
Find the equivalent resistance of the entire circuit, the current that leaves the battery and the voltage drop across R1. R1=5Ω R2=15Ω 120V R3=30Ω R4=8Ω Find the equivalent resistance of the entire circuit. Combine any resistors that you can recognize as being in either series or parallel. R1=5Ω R2=15Ω 120V R3=30Ω R4=8Ω 1 Find the equivalent resistance of the entire circuit. Combine any resistors that you can recognize as being in either series or parallel. R1+2=20Ω 120V R3=30Ω R4=8Ω Find the equivalent resistance of the entire circuit. Combine any resistors that you can recognize as being in either series or 1/R=1/20+1/30=5/60 parallel. R=12 R1+2 and 3=12Ω 120V R4=8Ω 2 Find the equivalent resistance of the entire circuit. Now use Ohm's law to find the current through or voltage dropped across each resistor. 1/R=1/20+1/30=5/60 R=12 R(1+2 and 3) + 4=20Ω 120V Determine whether a single resistor replaced a series or parallel branch. This will determine whether each resistor would have the same current through it or same voltage drop. Then find the other quantity using Ohm's Law. 1/R=1/20+1/30=5/60 R=12 R1+2 and 3=12Ω 120V R4=8Ω 3 Determine whether a single resistor replaced a series or parallel branch. This will determine whether each resistor would have the same current through it or same voltage drop. Then find the other quantity using Ohm's Law. R1+2=20Ω 120V R4=8Ω R3=30Ω Determine whether a single resistor replaced a series or ` parallel branch. This will determine whether each resistor would have the same current through it or same voltage drop. Then find the other quantity using Ohm's Law. R1=5Ω R2=15Ω 120V R3=30Ω R4=8Ω 4