Time Series Analysis and Fourier Transforms
advertisement

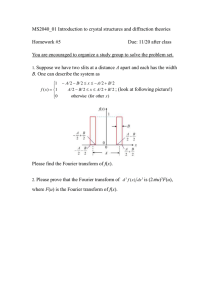
Time Series Data and Fourier Transforms Jason Bailey Quick Summary • Look Time Series Data • See data in Time domain (time series) and Frequency domain (using Fourier Transform) • Application: Filter data/Extract pattern with Fourier Transform • FFT - Fast Fourier Transform Visitors to a Learning Site 1000 800 600 Number of Visits 400 200 0 -200 -400 -600 07-Apr 14-Apr Date 21-Apr What is Time Series Data • A sequence of data points • Typically at successive points in time spaced at uniform time intervals • Used: • statistics, signal processing, pattern recognition, finance, weather forecasting, earthquake prediction, control engineering and communications engineering http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_series What if we want to extract a pattern from time series data? Visitors to a Learning Site 1000 Original Data lunchtime rush unidentified 800 600 Number of Visits 400 200 0 -200 -400 -600 12AM 12AM 12AM Time https://gist.github.com/espeecat/5438953 12AM 12AM A sine wave or sinusoid y(t) = A sin(2πft +ф) Sometimes 2πf written as ω Cosine too Much better to see it in a graph • Use a tool like Matlab – A programmable calculator with good graph/chart abilities • Other tools are available and much cheaper An example of a sinusoid and FFT plot of y=2*sin(2*pi*f*t) f=1Hz Amplitude 2 1 0 -1 -2 0 0.5 1 1.5 Time (seconds) 2 2.5 Abs Amp 800 600 400 200 0 0 5 10 Frequency (Hz) https://gist.github.com/espeecat/5439069 15 20 The Fourier Transform (FFT) • Based on Fourier Series - represent periodic time series data as a sum of sinusoidal components (sine and cosine) • (Fast) Fourier Transform [FFT] – represent time series in the frequency domain (frequency and power) • The Inverse (Fast) Fourier Transform [IFFT] is the reverse of the FFT • Like graphic equaliser on music player Combining Sinusoids 10 5 0 -5 -10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 4 5 6 4 5 6 4 5 6 Time (s) 10 5 0 -5 -10 0 1 2 3 Time (s) 10 5 0 -5 -10 0 1 2 3 Time (s) 10 5 0 -5 -10 0 1 2 3 Time (s) Looking at the Fourier Transforms 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5 6 7 8 5 6 7 8 5 6 7 8 Frequency (Hz) 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 1 2 3 4 Frequency (Hz) 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 1 2 3 4 Frequency (Hz) 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 1 2 3 4 Frequency (Hz) Applications of Fourier Transform • Shazam – “finger printing” using Fourier Transforms • Images – The Gabor Transform for facial recognition? • Filtering data/ Extracting patterns • Sound processing – discarding sound • System Identification The (Fast) Fourier Transform • Discrete-time Fourier Transform –assumes sampled data and limited length • Implementations available in lots of programming languages e.g. http://www.fftw.org/ • Python numpy.fft Filtering Time Series Data 20 10 0 -10 -20 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0 50 100 150 200 250 Frequency Hz. 300 350 400 450 500 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 15 filtered data original data Amplitude 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 Time (s) 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 Original data and filtered data Comparison of original and filtered data 15 filtered data original data 10 Amplitude 5 0 -5 -10 -15 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 Time (s) 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 Thank you Alternative to Matlab • SciLab – https://www.scilab.org/ • Octave http://www.gnu.org/software/octave/ • R - http://www.r-project.org/ • Programming language & graph library Twitter @espeecat www.jasonbailey.net 14 x 10 4 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Discrete-Time Fourier Transform • ω = 2πƒ –angular frequency • Euler Formula used but this represents