Chapter 23 - Capacitors - University of Colorado Boulder
advertisement

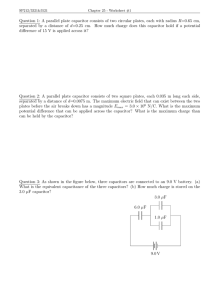
Chapter 23 - Capacitors Capacitors • A capacitor is a pair of conductors, insulated from each other, and used to store charge and energy. • For a “charged” capacitor, one conductor is positively charged and the other is negatively charged (net charge is always zero). • The work used in separating charge is stored as electrostatic energy in the capacitor. • Capacitance is the charge stored per unit potential difference: C = Q/V. • V refers to magnitude of the voltage difference between conductors • Its SI unit is the farad (F): • 1 F = 1 C/V Parallel Plate Capacitor • What is the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor of area A and separation d? • Determine E: 1 E= σ �0 • Determine V in terms of Q 1 1 Qd V = Ed = σd = �0 �0 A Q A C= = �0 V d • Capacitance is always independent of voltage and charge! CT 29.C2 A parallel-plate capacitor has square plates of edge length L, separated by a distance d. If we double the dimension L and halve the dimension d, by what factor have we changed the capacitance? L d A: no change B: up by 2. C: up by 4. D: up by 8 E: none of these ©University of Colorado, Boulder CT 29.C3 How big is a one Farad Capacitor? Assume you have two parallel plates that are separated by 1 mm. If you estimate ε0 ~ 10-11, what is the area of the plates to have a 1.0 Farad capacitance? A) 100 million square meters B) 1 thousand square meters C) 1 square meters D) 0.001 square meters E) None of these is even close. ©University of Colorado, Boulder Example - Spherical capacitor • What is the capacitance of a spherical capacitor, consisting of a a inner shell of radius ra and outer radius r b? Question 29.3 Work and Potential Energy Which group of charges took more work to bring together from a very large initial distance apart? +2 d +1 +1 d +1 Both took the same amount of work. d d +1 Energy stored in a capacitor • Charging a capacitor involves transferring charge between the initially neutral plates. • The work dW involved in moving charge dq is dW=V(q)dq q • For a capacitor, q =C V(q), so dW = dq C • Then the work involved in charging up to a final value of Q is W = � 0 Q q Q2 dq = C 2C • This is therefore the electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor: Q2 1 U =W = = CV 2 2C 2 Practical capacitors • Capacitors are manufactured using a variety of technologies, in capacitances ranging from picofarads (pF; 10–12 F) to several farads. • Most use a dielectric material between their plates. • The dielectric increases capacitance by lowering the electric field and thus the potential difference required for a given charge on the capacitor. • The dielectric constant, is a property of the dielectric material that gives the reduction in field and thus the increase in capacitance. Energy in the electric field • The electrostatic energy associated with a charge distribution is stored in the electric field of the charge distribution. • Considering the uniform field of the parallel-plate capacitor implies that the electric energy density is • This is a universal result: • Every electric field contains energy with this density. 1 U = CV 2 = uE Ad 2 CT 29.C4 A parallel plate capacitor is charged (the plates are isolated so Q cannot change.) The plates are then pulled apart so that the plate separation d increases. The total electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor…. +++++++++++++++++++++++ d +Q E ----------------------------------------- -Q A:increases B:decreases C: stays same ©University of Colorado, Boulder Connecting capacitors: parallel • Capacitors connected in parallel have their top plates connected together and their bottom plates connected together. • Therefore the potential difference across the two capacitors is the same. Q1 Q2 ∆V = = C1 C2 Q1 + Q2 = ∆V (C1 + C2 ) Cparallel = C1 + C2 Connecting capacitors: series • Capacitors connected in series are wired so that one capacitor follows the other. • Why are both capacitors charged the same amount? Q1 Q2 ∆V = ∆V1 + ∆V2 = + C1 C2 1 1 + ) = Q( C1 C2 1 1 1 =⇒ = + Cseries C1 C2