2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2
advertisement

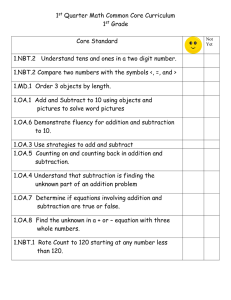
2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Unit 1: Addition and Subtraction Within 20 September 3 – October 17, 2014 Learning Progression In Grade 2, students will: Become fluent in single digit additions and the related subtractions using the mental level 2 and level 3 strategies as needed. Master all addition and subtraction problems and solve one- and two-step word problems. TEACHER TIPS: Read (or re-read) the Introduction to Math Expressions, pg. xvii-xxxvi before starting instruction for the year. Use page xxx Pacing Guide to consider lessons that require more than one day. See the Unit Planning section before each unit to see resources available, materials needed, assessments, CCSS taught (by lessons), differentiated instruction opportunities, and cross-curricular connections. For each unit, please read the Putting Research into Practice, and the Math Background sections provided (including the Mathematical Practices taught in the unit, including a section on Helping Students Avoid Common Errors. Unit 1: Help Students Avoid Common Errors in Lessons 6, 8, 15, and 20 (see p. 1DD) Use each unit’s Test A as pre- and post-test to demonstrate student growth and to guide instruction. Plan for daily formative assessment, possibly using the “Formative Assessment: Check for Understanding” at the end of each MX lesson as exit slip. Remember to use Quick Practice daily in addition to Daily Routines to practice/assess 2.OA.2. Mental Level 2 and Level 3 strategies are used in lessons 1, and in lessons 3-5. SCIENCE LINKS: FOSS Kit Balance and Motion: Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheets 12 & 13, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Pebbles, Sand and Silt: Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.2 Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 15, 2.OA.1 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 17, 2.OA.1 Investigation 3, Math Extension, Student Sheets 18 & 19, 2.OA.1 1|Page 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Common Core Content 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction with 100 to solve one and two step word problems, involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions. 2.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies by end of grade 2 know from memory all sums of two one digit numbers. 2.OA.3 Determine whether a group of objects (up to 20) has an odd or even number of members lessons 6,7,21 2.NBT.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. lessons 9,16 2.NBT.6 Add up to four-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. lessons 9,16 2.NBT.9 Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work, using place value and the properties of operations. lessons 1,3,9 Big Ideas Strategies for Addition and Subtraction (Lessons 1-9) Addition and Subtraction Situations (Lessons 10-16) More Complex Situations (Lessons 17-21) CCSS Mathematical Practices Habits of Mind/Interaction Mathematical Practices: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. To address the Common Core Mathematical Practices, select those you will use during this unit. Habits of Mind: Make Sense Justify Why Generalize Regularity, Patterns, Structure Mathematical Representations Formative Assessments Summative Assessments Use Unit 1 Test A as a Pre-test Unit 1 Test Form A Quick Quiz 1 and Fluency Check 1 (after Lesson 9) Use Unit 1 Performance Assessment from Assessment Guide. (Use as needed). Quick Quiz 2 and Fluency Check 2 (after Lesson 16) Quick Quiz 3 and Fluency Check 3 (after Lesson 21) Formative Assessment Check Understanding-at the end of each MX lesson-use as needed. PARCC (optional) Report Card Represents and solves addition and subtraction one and two step word problems within 100. 2.OA.1 Uses mental strategies to add and subtract within 20. 2.OA.2 Work with equal groups of objects to gain foundations for multiplication. (even/odd, arrays) 2.OA.3-4 (partial) Uses place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract within 1000. 2.NBT.5-9 (partial) 2|Page 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Unit 1 Vocabulary: Addends Equation Unit 1 Strategies: Addition doubles Doubles minus 1 Doubles minus 2 Metacognition and Reflection Connections Mistakes and Stuck points Persevere and Seek More Habits of Interaction: Private Reasoning Time Listen to Understand Explain Genuine Questions Multiple Pathways Compare the Logic of our Ideas Critique and Debate Math Reasoning is the Authority Even Fewer Is equal to (=) Doubles plus 1 Doubles plus 2 Equation chain Make a ten Is not equal to (≠) More Odd Partners Total Vertical form Math mountain Comparison Bars Situation equation Solution equation Subtraction Doubles Unknown Literature Links: Rumble Bus by Larry Dane Brimmer Even Steven and Odd Todd by Kathryn Cristaldi 3|Page 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Unit 2: Addition Within 200 October 20 – November 25, 2014 Learning Progression and Big Ideas In Grade 2, students will: Extend base ten understanding to hundreds. Compute sums within 1000 using place value and the Commutative and Associative Properties of Addition. Become fluent with addition within 100 TEACHER TIPS: Remember to use Quick Practice daily in addition to Daily Routines to practice/assess 2.OA.2. Use page xxx Pacing Guide to consider lessons that require more than one day. See the Unit Planning section before each unit to see resources available, materials needed, assessments, CCSS taught (by lessons), differentiated instruction opportunities, and cross-curricular connections. For each unit, please read the Putting Research into Practice, and the Math Background sections provided (including the Mathematical Practices taught in the unit, including a section on Helping Students Avoid Common Errors. Unit 2: Help Students Avoid Common Errors in Lessons 3, 5, 7, 9, 10, and 14 (p.159AA). Use each unit’s Test A as pre- and post-test to demonstrate student growth and to guide instruction. SCIENCE LINKS: FOSS Kit Balance and Motion Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheets 12 & 13, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Pebbles, Sand and Silt Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.2 Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 15, 2.OA.1 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 17, 2.OA.1 Investigation 3, Math Extension, Student Sheets 18 & 19, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Insects Investigation 4, Math extension, Student Sheet 19, 2.OA.1 4|Page 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Common Core Content 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction with 100 to solve one and two step word problems, involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions. 2.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies by end of grade 2 know from memory all sums of two one digit numbers. 2 NBT.1 Understand that the three digits of a three digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens and ones. 2.NBT.2 Count within 1000; skipcount by 5s, 10s, and 100s. 2.NBT.3 Read and write numbers to 1000 using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. 2.NBT.4 Compare two three-digit numbers based on meanings of the hundreds, tens, and ones digits, using >, =, < symbols to record the results of comparisons. 2.NBT.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 2. NBT.6 Add up to four two digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. Big Ideas Use Place Value (Lessons 1-5) Add 2-Digit Numbers (Lessons 6-10) Money and Fluency for Addition Within 100 (Lessons 11-15) CCSS Mathematical Practices Habits of Mind/ Interaction To address the Common Core Mathematical Practices, select those you will use during this unit. Habits of Mind: Make Sense Justify Why Generalize Regularity, Patterns, Structure Mathematical Representations Metacognition and Reflection Connections Mistakes and Stuck points Persevere and Seek More Habits of Interaction: Private Reasoning Time Listen to Understand Explain Genuine Questions Multiple Pathways Compare the Logic of our Ideas Critique and Debate Formative Assessments Summative Assessments Use Unit 2 Test A as a Pre-test Unit 2 Test Form A Quick Quiz 1 and Fluency Check 4 (after Lesson 5) Use Unit 2 Performance Assessment from Assessment Guide. (Use as needed). Quick Quiz 2 and Fluency Check 5 (after Lesson 10) Quick Quiz 3 and Fluency Check 6 (after Lesson 15) Formative Assessment Check Understanding-at the end of each MX lesson-use as needed PARCC (optional) Report Card Represents and solves addition and subtraction one and two step word problems within 100. 2.OA.1 Uses mental strategies to add and subtract within 20. 2.OA.2 Identifies, models and compares the digits and their values in the ones, tens, and hundreds place. 2.NBT.1-4 Uses place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract within 1000. 2.NBT.5-9 Solves two-step word problems using money. 2.MD.8 for ex: If you have 2 dimes and 3 pennies, how many cents do you have? 5|Page 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 2.NBT.7 Add and subtract within 1000, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method. Math Reasoning is the Authority 2.NBT.8 Mentally add 10 or 1000 to a given number 100-900, and mentally subtract 10 or 100 from a given number 100-900. 2 NBT.9 Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work, using place value and the properties of operations. 2.MD.8 Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies, using $ and ¢ symbols appropriately. Unit 2 Vocabulary: Cent symbol (¢) Decade Decimal point Dime Dollar Dollar symbol ($) Error Expanded form Equal to (=) Greater than (>) Hundreds Less than (<) Number name Ones Penny Sum Teen Numbers Unit 2 Strategies: Expanded form New groups above method New groups below method Quick tens Quick hundreds Skip count Show all totals method Literature Links: Count on Pablo by Barbara deRubertis More or Less by Stuart J. Murphy 6|Page 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Unit 3: Lengths and Shapes December 1, 2014 – January 9, 2015 Learning Progression and Big Ideas In Grade 2, students will: Use rulers to measure lengths to the nearest whole number unit. Build line plots to display measurement data. Recognize and draw shapes with specific attributes. TEACHER TIPS: Plan to teach the STEM Investigation Lesson 5: Design Challenge Rolling Wheels (Find on K-5 STEM Swift and K-5 Science Share Point Sites.) Consider using the Arts Impact lessons (See teaching resources on district website.) Remember to use Quick Practice daily in addition to Daily Routines to practice/assess 2.OA.2. SCIENCE LINKS: FOSS Kit Balance and Motion Investigation 3, Math Extension, Student Sheets 17 & 18, 2.MD.1-5 FOSS Kit Pebbles, Sand and Silt Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.2 Common Core Content 2.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. By the end of Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers. 2.NBT.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 2.NBT.6 Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operation. Big Ideas Length and Shapes (Lessons 1-5) Estimate, Measure, and Make Line Plots (Lessons 6-9) CCSS Mathematical Practices Habits of Mind/Interaction To address the Common Core Mathematical Practices, select those you will use during this unit. Habits of Mind: Make Sense Justify Why Generalize Regularity, Patterns, Structure Formative Assessments Summative Assessments Use Unit 3 Test A as a Pre-test Unit 3 Test Form A Quick Quiz 1 and Fluency 7 (after Lesson 5) Use Unit 3 Performance Assessment from Assessment Guide. (Use as needed). Quick Quiz 2 and Fluency 8 (after Lesson 9) Report Card Uses mental strategies to add and subtract within 20. 2.OA.2 Measures, estimates and compares lengths in standard units and relates addition and subtraction to lengths. 2.MD.1-6 PARCC (optional) 7|Page 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 2.MD.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes. 2MD.2 Measure the length of an object twice using lengths for the two measurements; describe how the two measurements relate to the size of the unit chosen. Mathematical Representations Metacognition and Reflection Connections Mistakes and Stuck points Persevere and Seek More Formative Assessment Check Understanding-at the end of each MX lesson-use as needed Identifies and draws shapes given specified attributes. 2.G.1 2.MD.3 Estimate lengths using units of inches, feet, centimeters and meters. 2.MD.4 Measure to determine how much longer one object is than another expressing the length difference in terms of a standard length unit. 2.MD.9 Generate measurement data by measuring lengths of several objects to the nearest whole unit, or by making repeated measurements of the same object. Show the measurements by making a line plot where the horizontal scale is marked off in whole number units. 2.G.1 Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes such as a given numbers of angles or a given number of equal faces. Identify triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons and cubes. Habits of Interaction: Private Reasoning Time Listen to Understand Explain Genuine Questions Multiple Pathways Compare the Logic of our Ideas Critique and Debate Math Reasoning is the Authority 8|Page 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Unit 3 Vocabulary: 2-dimensional 3-dimensional Angle Centimeter Cube Decimeter Unit 3 Strategies: Partner lengths Face Foot Height Hexagon Horizontal Inch Length Line plot Line segment Meter Opposite sides Pentagon Quadrilateral Rectangle Rectangular prism Right angle Square Triangle Vertical View Width Yard Literature Links: A Cloak for a Dreamer by Aileen Friedman Racing Around by Stuart J. Murphy 9|Page 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Unit 4: Subtract 2-Digit Numbers January 12 – March 6, 2015 Learning Progression and Big Ideas In Grade 2, students will: Compute differences within 1000 using place value and the relationship between addition and subtraction Become fluent with subtraction within 100 Find totals of mixed coins and bills TEACHER TIPS: Remember to use Quick Practice daily in addition to Daily Routines to practice/assess 2.OA.2. SCIENCE LINKS: FOSS Kit Balance and Motion Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheets 12 & 13, 2.OA.1 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Pebbles, Sand and Silt Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.2 Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 15, 2.OA.1 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 17, 2.OA.1 Investigation 3, Math Extension, Student Sheets 18 & 19, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Insects Investigation 4, Math extension, Student Sheet 19, 2.OA.1 Common Core Content 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one-and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions. 2.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. 2.NBT.1 Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones. Big Ideas Totals of Mixed Coins and Bills (Lessons 1-2) Multidigit Subtraction Strategies (Lessons 3-11) CCSSMathematical Practices Habits of Mind/Interaction To address the Common Core Mathematical Practices, select those you will use during this unit. Habits of Mind: Make Sense Justify Why Generalize Formative Assessments Use Unit 4 Test A as a Pre-Test Quick Quiz 1 and Fluency Check 9 (after lesson 2) Quick Quiz 2 and Fluency Check 10 (after Lesson 11) Summative Assessments Unit 4 Test Form A Use Unit 4 Performance Assessment from Assessment Guide. (Use as needed). Report Card Represents and solves addition and subtraction one and two step word problems within 100. 2.OA.1 Uses mental strategies to add and subtract within 20. 2.OA.2 10 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 a. 100 can be thought of as a bundle of ten tens—called a “hundred”. b. The numbers 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 refer to one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine hundreds (and 0 tens and 0 ones). 2.NBT.4 Compare two three-digit numbers based on meanings of the hundreds, tens, and ones digits using >, =, < symbols to record the results of comparisons. 2.NBT.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/ or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 2.NBT.6 Add up to four three-digit numbers using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 2.NBT.7 Add and subtract within 1000, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/ or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method. Understand that in adding or subtracting three-digit numbers, one adds or subtracts hundreds and hundreds, tens and tens, and ones and ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose or decompose tens or hundreds. Word Problems: Addition and Subtraction Within 100 (Lessons 12-23) Regularity, Patterns, Structure Mathematical Representations Metacognition and Reflection Connections Mistakes and Stuck points Persevere and Seek More Habits of Interaction: Private Reasoning Time Listen to Understand Explain Genuine Questions Multiple Pathways Compare the Logic of our Ideas Critique and Debate Math Reasoning is the Authority Quick Quiz 3 and Fluency Check 11 (after Lesson 23) Formative Assessment Check for Understanding at end of MX lessons PARCC (optional) Uses place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract within 1000. 2.NBT.5-9 Solves word problems using money. 2.MD.8 for ex: If you have 2 dimes and 3 pennies, how many cents do you have? 2 NBT.9 Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work using place value and the properties of operations. 11 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 2.MD.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes. 2.MD.3 Estimate lengths using units of inches, feet, centimeters, and meters. 2.MD.4 Measure to determine how much longer one object is than another, expressing the length difference in terms of a standard length unit. 2.MD.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths that are given in the same units and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. 2.MD.8 Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies, using $ and cents symbols appropriately. Unit 4 Vocabulary: Difference Quarter Unit 4 Strategies: Adding Up Method Break Apart Change Unknown Count On Expanded Method Start Unknown Ungroup Ungroup First Method Literature Links: Henry Hikes to Fitchburg by D. B. Johnson Tightwad Tod by Daphne Skinner 100th Day Worries by Margery Cuyler and Arthur Howard Shark Swimathon by Stuart J. Murphy Hannah’s Collections by Marthe Jocelyn 12 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Unit 5: Time, Graphs and Word Problems March 9 – April 10, 2015 Learning Progression and Big Ideas In Grade 2, students will: Tell and write time to the nearest 5 minutes Draw and use picture graphs. Draw and use both horizontal and vertical bar graphs and relate the scale to a number line diagram. TEACHER TIPS: Remember to use Quick Practice daily in addition to Daily Routines to practice/assess 2.OA.2. Report Card competency 2.G.3 (partitioning circles and rectangles) is not assessed on the unit test, but you may choose to assess based on class work, formative assessments from lessons and anecdotal notes.) SCIENCE LINKS: FOSS Kit Balance and Motion Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheets 12 & 13, 2.OA.1 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Pebbles, Sand and Silt Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.2 Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 15, 2.OA.1 Investigation 1, Math Extension, Do Rock Math, page 33, 2.MD.10 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 17, 2.OA.1 Investigation 3, Math Extension, Student Sheets 18 & 19, 2.OA.1 Investigation 4, Math Extension, Student Sheet 20, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Insects Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.1 Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 15, 2.MD.10 Investigation 3, Math Extension, Student Sheet 18, 2.MD.10 Investigation 4, Math extension, Student Sheet 19, 2.OA.1 13 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Common Core Content Big Ideas 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one-and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions. Time (Lessons 1-2) 2.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. By end of Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers. Bar Graphs (Lessons 5-10) 2.NBT.2 Count within 1000; skip-count by 5s, 10s, and 100s. 2.NBT.4 Compare two three-digit numbers based on meanings of the hundreds, tens, and ones digits using >, =, < symbols to record the results of comparisons. 2.NBT.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/ or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 2.NBT.6 Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value ad properties of operations. 2.MD.7 Tell and write time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest five minutes, using a.m. and p.m. Picture Graphs (Lessons 3-4) CCSSMathematical Practices Habits of Mind/ Interaction To address the Common Core Mathematical Practices, select those you will use during this unit. Habits of Mind: Make Sense Justify Why Generalize Regularity, Patterns, Structure Mathematical Representations Metacognition and Reflection Connections Mistakes and Stuck points Persevere and Seek More Habits of Interaction: Private Reasoning Time Listen to Understand Explain Genuine Questions Multiple Pathways Compare the Logic of our Ideas Critique and Debate Formative Assessments Summative Assessments Use Unit 5 Test A as a Pre-test Unit 5 Test Form A Quick Quiz 1 and Fluency Check 12 (after Lesson 2) Use Unit 5 Performance Assessment from Assessment Guide. (Use as needed). Quick Quiz 2 and Fluency Check 13 (after Lesson 4) Quick Quiz 3 and Fluency Check 14 (after Lesson 10) Formative Assessment Check for Understanding at end of MX lessons PARCC (optional) Report Card Represents and solves addition and subtraction one and two step word problems within 100. 2.OA.1 Uses mental strategies to add and subtract within 20. 2.OA.2 Tells and writes time to the nearest 5 minutes using digital and analog clocks, using A.M and P.M. 2.MD.7 Draws, reads, compares and interprets a picture graph & bar graph. 2.MD.10 14 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 2.MD.10 Draw a picture graph and a bar graph (with single-unit scale) to represent a data set with up to four categories. Solve simple put-together, take-apart, and compare problems using information presented in a bar graph. Partitions circles and rectangles into 2, 3, or 4 equal shares and describes the shares. 2.G.3 (Not assessed on unit test, but you may choose to assess based on class work, formative assessments from lessons and anecdotal notes.) Math Reasoning is the Authority 2.G.3 Partitions circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, half of, a third of etc.. and describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, four fourths. Recognize that equal shares of identical wholes need not have the same shape. Unit 5 Key Vocabulary: AM Analog clock Bar graph Clock Data Data Survey Data Table Digital Clock Equal Shares Fewer Fewest Graph Half Halves Horizontal Horizontal bar graph Hour Hand Less Minute Hand More Picture Graph PM Scale Sort Table Title Vertical Vertical bar Literature Links: How Do You Know What Time It Is? by Robert E. Wells 15 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Unit 6: 3 Digit Addition and Subtraction April 13 – May 15, 2015 Learning Progression and Big Ideas In Grade 2, students will: Extend base-ten understanding to 1000 Compute sums and differences within 1000 using place value TEACHER TIPS: May want to revisit fluency with teen numbers. Remember to use Quick Practice daily in addition to Daily Routines to practice/assess 2.OA.2. SCIENCE LINKS: FOSS Kit Balance and Motion Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheets 12 & 13, 2.OA.1 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Pebbles, Sand and Silt Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.2 Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 15, 2.OA.1 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 17, 2.OA.1 Investigation 3, Math Extension, Student Sheets 18 & 19, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Insects Investigation 3, Math Extension, Student Sheet 17, 2.NBT.2 Investigation 4, Math Extension, Student Sheet 19, 2.OA.1 Common Core Content Big Ideas 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one-and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions. Understanding Numbers to 1,000 (Lessons 1-5) 2.NBT.1 Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Adding to 1,000 (Lessons 6-8) 3-Digit Subtraction (Lessons 9-12) CCSSMathematical Practices Habits of Mind/Interaction To address the Common Core Mathematical Practices, select those you will use during this unit. Habits of Mind: Make Sense Justify Why Generalize Formative Assessments Summative Assessments Use Unit 6 Test A as a Pre-test Unit 6 Test Form A Quick Quiz 1 and Fluency Check 15 (after Lesson 5) Use Unit 1 Performance Assessment from Assessment Guide. (Use as needed). Quick Quiz 2 and Fluency Check 16 (after Lesson 8) Report Card Represents and solves addition and subtraction one and two step word problems within 100. 2.OA.1 16 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 2.NBT.2 Count within 1000; skip-count by 5s, 10s, and 100s. 2.NBT.3 Read and write numbers to 1000 using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. 2.NBT.4 Compare two three-digit numbers based on meanings of the hundreds, tens, and ones digits using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons. 2.NBT.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 2.NBT.7 Add and subtract within 1000, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/ or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method. Understand that in adding or subtracting three-digit numbers, one adds or subtracts hundreds and hundreds, tens and tens, and ones and ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose or decompose tens or hundreds. 3-Digit Addition and Subtraction Lessons 13-15 Regularity, Patterns, Structure Mathematical Representations Metacognition and Reflection Connections Mistakes and Stuck points Persevere and Seek More Habits of Interaction: Private Reasoning Time Listen to Understand Explain Genuine Questions Multiple Pathways Compare the Logic of our Ideas Critique and Debate Math Reasoning is the Authority Quick Quiz 3 and Fluency Check 17 (after Lesson 12) Quick Quiz 4 and Fluency Check 18 (after Lesson 15) Formative Assessment Check for Understanding at end of MX lessons PARCC (optional) Uses mental strategies to add and subtract within 20. 2.OA.2 Identifies, models and compares the digits and their values in the ones, tens, and hundreds place. 2.NBT.1-4 Uses place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract within 1000. 2.NBT.5-9 2.NBT.8 Mentally add 10 or 1000 to a given number 100-900, and mentally subtract 10 or 100 from a given number 100-900. 2 NBT.9 Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work, using place value and the properties of operations. 17 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 2.MD.8 Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies, using $ and cents symbols appropriately. Unit 6 Vocabulary: Unit 6 Strategies: Decade Number Hundreds New Groups Above Ones One Thousand New Groups Below Opposite Operations Show all totals Ungroup Tens Literature Links: A Place for Zero by Angeline Sparagna LoPresti Earth Day—Hooray! By Stuart J. Murphy The 329th Friend by Marjorie Weinman Sharmat 18 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 Unit 7: Arrays, Equal Shares and Adding or Subtracting Lengths May 18 – June 11, 2015 Learning Progression In Grade 2, students will: Continue to use fraction language to describe partitions of shapes into equal shares Relate addition and subtraction to length TEACHER TIPS: Introduce students to written form of fractions. Remember to use Quick Practice daily in addition to Daily Routines to practice/assess 2.OA.2. SCIENCE LINK: FOSS Kit Balance and Motion Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheets 12 & 13, 2.OA.1 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Pebbles, Sand and Silt: Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 14, 2.OA.2 Investigation 1, Math Extension, Student Sheet 15, 2.OA.1 Investigation 2, Math Extension, Student Sheet 17, 2.OA.1 Investigation 3, Math Extension, Student Sheets 18 & 19, 2.OA.1 FOSS Kit Insects Investigation 4, Math Extension, Student Sheet 19, 2.OA.1 Common Core Content 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one-and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions. 2.OA.3 Determine whether a group of objects (up to 20) has an odd or even number of members lessons 6,7,21 Big Ideas Arrays and Equal Shares (Lessons 1-2) Relate Addition and Subtraction to Length (Lessons 3-6) CCSSMathematical Practices Habits of Mind/Interaction To address the Common Core Mathematical Practices, select those you will use during this unit. Habits of Mind: Make Sense Justify Why Generalize Formative Assessments Summative Assessments Use Unit 7 Test A as a Pre-test Unit 7 Test Form A Quick Quiz 1 and Fluency Check 19 (after Lesson 2) Use Unit 1 Performance Assessment from Assessment Guide. (Use as needed). Quick Quiz 2 and Fluency Check 20 (after Lesson 6) Report Card Represents and solves addition and subtraction one and two step word problems within 100. 2.OA.1 19 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 2.OA.4 Use addition to find the total number of objects arranged in rectangular arrays with up to 5 rows and up to 5 columns; write an equation to express the total as a sum of equal addends. 2.NBT.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 2.NBT.6 Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. 2.MD.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes. 2.MD.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings (such as drawings of rulers) and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. 2.MD.6 Represent whole numbers as lengths from 0 on a number line diagram with equally spaced points corresponding to the numbers 0, 1, 2, …, and represent whole-number sums and differences within 100 on a number line. Regularity, Patterns, Structure Mathematical Representations Metacognition and Reflection Connections Mistakes and Stuck points Persevere and Seek More Habits of Interaction: Private Reasoning Time Listen to Understand Explain Genuine Questions Multiple Pathways Compare the Logic of our Ideas Critique and Debate Math Reasoning is the Authority Formative Assessment Check for Understanding at end of MX lessons PARCC (optional) Uses mental strategies to add and subtract within 20. 2.OA.2 Optional: End of Year MX Assessment May or June 2015 Work with equal groups of objects to gain foundations for multiplication. (even/odd, arrays) 2.OA. 3-4 Measures, estimates and compares lengths in standard units and relates addition and subtraction to lengths. 2.MD.1-6 Partitions a rectangle into same-sized squares and counts total of squares. 2.G.2 Partitions circles and rectangles into 2,3, or 4 equal shares and describes the shares. 2.G.3 20 | P a g e 7/1/14 2014-15 Mathematics Curriculum Map – Grade 2 2.G.2 Partition a rectangle into rows and columns of same-size squares and count to find the total number of them. 2.G.3 Partition circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, four fourths. Recognize that equal shares of identical wholes need not have the same shape. Unit 7 Vocabulary: Array Column Diagram Fourths Half Halves Thirds Fourths Number line Row Thirds Literature Links: Keep Your Distance! by Gail Herman 21 | P a g e 7/1/14