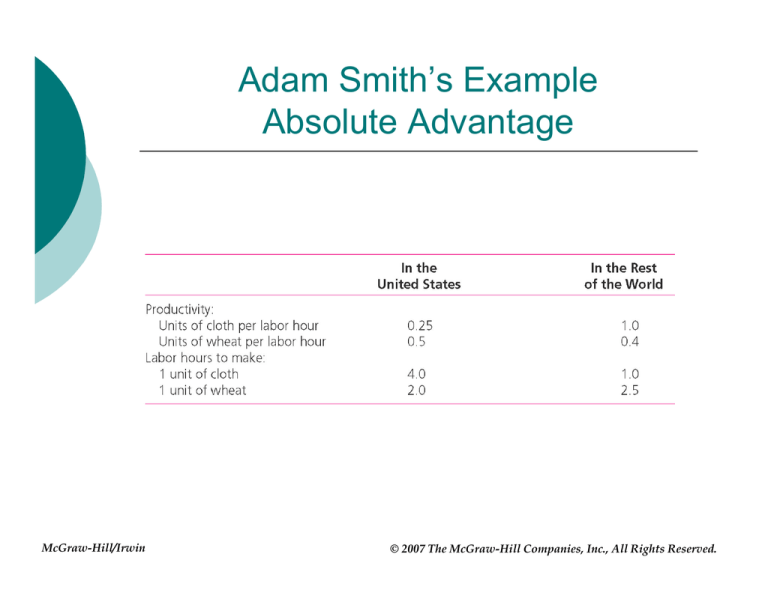
Adam Smith’s Example
Absolute Advantage
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Ricardo’s Theory of Trade
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Ricardo focused on labor productivity (or
resource productivity more generally) for
different products in different countries.
Comparative advantage
A country will export products that it can produce
at a low opportunity cost (in terms of other
goods that could be produced within the
country).
A country will import products that it would
otherwise produce at a high opportunity cost.
Basis for trade: Relative differences in labor
(resource) productivity.
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Ricardo’s Example:
Comparative Advantage
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Ricardo’s Example:
No-Trade Relative Prices
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Figure 3.1 – The Gains from Trade, Shown
for Ricardo’s Constant-Cost Case
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Absolute Advantage Does Matter
for Wage Rates
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.





