ECTS Guide Power Electronic Converters and Applications
advertisement
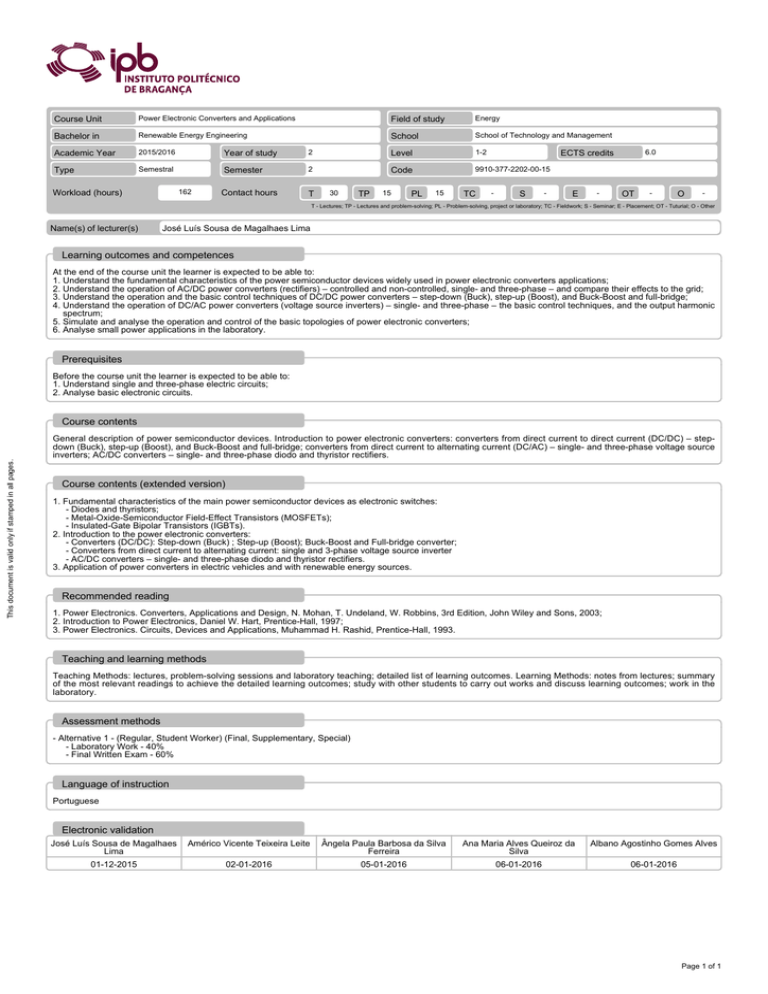
Course Unit Power Electronic Converters and Applications Bachelor in Renewable Energy Engineering Academic Year 2015/2016 Type Semestral 162 Workload (hours) Field of study Energy School School of Technology and Management Year of study 2 Level 1-2 Semester 2 Code 9910-377-2202-00-15 Contact hours T 30 TP 15 PL 15 TC 6.0 ECTS credits - S - E - OT - O - T - Lectures; TP - Lectures and problem-solving; PL - Problem-solving, project or laboratory; TC - Fieldwork; S - Seminar; E - Placement; OT - Tuturial; O - Other Name(s) of lecturer(s) José Luís Sousa de Magalhaes Lima Learning outcomes and competences At the end of the course unit the learner is expected to be able to: 1. Understand the fundamental characteristics of the power semiconductor devices widely used in power electronic converters applications; 2. Understand the operation of AC/DC power converters (rectifiers) – controlled and non-controlled, single- and three-phase – and compare their effects to the grid; 3. Understand the operation and the basic control techniques of DC/DC power converters – step-down (Buck), step-up (Boost), and Buck-Boost and full-bridge; 4. Understand the operation of DC/AC power converters (voltage source inverters) – single- and three-phase – the basic control techniques, and the output harmonic spectrum; 5. Simulate and analyse the operation and control of the basic topologies of power electronic converters; 6. Analyse small power applications in the laboratory. Prerequisites Before the course unit the learner is expected to be able to: 1. Understand single and three-phase electric circuits; 2. Analyse basic electronic circuits. This document is valid only if stamped in all pages. Course contents General description of power semiconductor devices. Introduction to power electronic converters: converters from direct current to direct current (DC/DC) – stepdown (Buck), step-up (Boost), and Buck-Boost and full-bridge; converters from direct current to alternating current (DC/AC) – single- and three-phase voltage source inverters; AC/DC converters – single- and three-phase diodo and thyristor rectifiers. Course contents (extended version) 1. Fundamental characteristics of the main power semiconductor devices as electronic switches: - Diodes and thyristors; - Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs); - Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs). 2. Introduction to the power electronic converters: - Converters (DC/DC): Step-down (Buck) ; Step-up (Boost); Buck-Boost and Full-bridge converter; - Converters from direct current to alternating current: single and 3-phase voltage source inverter - AC/DC converters – single- and three-phase diodo and thyristor rectifiers. 3. Application of power converters in electric vehicles and with renewable energy sources. Recommended reading 1. Power Electronics. Converters, Applications and Design, N. Mohan, T. Undeland, W. Robbins, 3rd Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2003; 2. Introduction to Power Electronics, Daniel W. Hart, Prentice-Hall, 1997; 3. Power Electronics. Circuits, Devices and Applications, Muhammad H. Rashid, Prentice-Hall, 1993. Teaching and learning methods Teaching Methods: lectures, problem-solving sessions and laboratory teaching; detailed list of learning outcomes. Learning Methods: notes from lectures; summary of the most relevant readings to achieve the detailed learning outcomes; study with other students to carry out works and discuss learning outcomes; work in the laboratory. Assessment methods - Alternative 1 - (Regular, Student Worker) (Final, Supplementary, Special) - Laboratory Work - 40% - Final Written Exam - 60% Language of instruction Portuguese Electronic validation José Luís Sousa de Magalhaes Lima Américo Vicente Teixeira Leite Ângela Paula Barbosa da Silva Ferreira Ana Maria Alves Queiroz da Silva Albano Agostinho Gomes Alves 01-12-2015 02-01-2016 05-01-2016 06-01-2016 06-01-2016 Page 1 of 1