1 ECE 202: Ideal Transformers Objectives The Ideal Transformer
advertisement
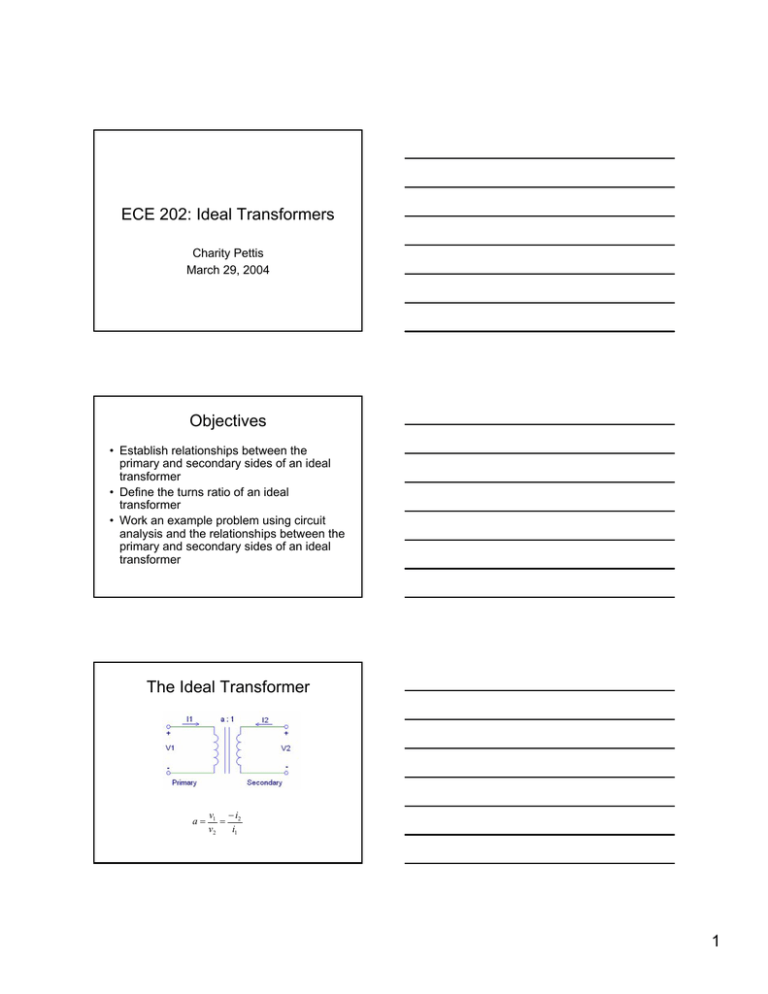
ECE 202: Ideal Transformers Charity Pettis March 29, 2004 Objectives • Establish relationships between the primary and secondary sides of an ideal transformer • Define the turns ratio of an ideal transformer • Work an example problem using circuit analysis and the relationships between the primary and secondary sides of an ideal transformer The Ideal Transformer a= v1 − i2 = v2 i1 1 Idealizations 1. The coupling coefficient is one. k= M =1 L1 L2 2. The mutual and self-inductances are very large. M , L1 , and L2 → ∞ a= v1 − i2 = v2 i1 Development V1 = sL1 I1 + sMI 2 V2 = sMI1 + sL2 I 2 V1 sL1 I1 + sMI 2 = MV2 M ( sMI1 + sL2 I 2 ) V1 sL1 I1 + sMI 2 1 = = MV2 L2 ( sL1 I1 + sMI 2 ) L2 V1 M = = V2 L2 L1 L2 = L2 L1 L2 2 Recall that a= V1 ( s ) V2 ( s ) From the previous slide V1 = V2 L1 L2 The self - inductance of a coil is L = N 2P where N is the numbers of turns in the coil, and P is the permeance. V1 = V2 N12 P N1 = =a N 22 P N 2 Development V1 = sL1 I1 + sMI 2 V1 sL I + sMI 2 = 11 =0 sM sM L1 I1 + I 2 = 0 M L1 I1 = − I 2 M L1 L1 = = M L1 L2 a=− L1 =a L2 I2 I1 The Impedance Transformation Property The impedance transforma tion property states Z in ( s ) = a 2 Z ( s ) We can verify this by Z in ( s ) = V (s) V1 ( s ) aV2 ( s ) = a 2 Z ( s ) = = a 2 2 I1 ( s ) − I 2 ( s ) − I 2 (s) a 3 Example 1 1 Z ( s ) = 10Ω // s (0.1F ) 10 10 s = 10 Z ( s) = 10 s + 1 10 + s Z in ( s) = a 2 Z ( s) 10 1000 Z in ( s ) = (10) 2 = s +1 s +1 Example 2 Step 1: Find Z in ( s ). Step 2 : Use voltage division to find V1. Z in ( s ) = a 2 Z ( s ) Z ( s ) = Rload = 10Ω Zin( s ) = (10) 2 (10Ω) = 1kΩ V1 = Z in ( s)Vs Rs + Z in ( s) V1 = (1kΩ)Vs 1 = Vs (1kΩ + 1kΩ) 2 Example 3 Step 1: Find the turns ratios a1 and a2 . a1 = N1 100 = = 10 Na1 10 a2 = Na2 2 = =2 N2 1 4 Step 2: Break the Circuit into manageable pieces. From the impedance transforma tion property Z a ( s ) = a22 Z ( s ). Z a ( s ) = a22 Rload Z a ( s ) = ( 2) 2 (5Ω) Z a ( s ) = 20Ω Step 3: Find the equivalent impedance Z a ' ( s ) = Ra // Z a ( s ) Z a ' (s) = Ra Z a Ra + Z a Z a ( s ) = 20Ω Za ' ( s ) = (20Ω)(20Ω) = 10Ω (20Ω + 20Ω) Step 4 : Find Z in (s ). Z in ( s ) = a12 Z a ' ( s ) Z in ( s ) = (10) 2 (10Ω) = 1kΩ 5 Step 5 : Find V1 and I1. Zin( s ) = 1kΩ Zin( s )Vs ( s ) V1 = Zin( s ) + Rs V1 = V1 Zin( s) 1 Vs ( s) I1 = 2 = 0.0005Vs ( s) (1kΩ) I1 = (1kΩ)Vs ( s ) 1 = Vs ( s ) (1kΩ + 1kΩ) 2 Step 6 : Find Va and I a 2 . V1 10 1 1 Va = Vs ( s ) 10 2 Va = 0.05Vs ( s ) Va = I a1 = aI1 I a1 = 10(0.0005Vs ( s )) I a1 = 0.005Vs ( s ) Ia2 = 20Ω (0.005Vs ( s )) (20Ω + 20Ω) = 0.0025Vs ( s ) Ia2 = Ia2 Ra I a1 Ra + Z a ( s ) Step 7 : Find V2 and I 2 . Va a 0.05Vs ( s ) V2 = = 0.025Vs ( s ) 2 V2 = I 2 = − aI a 2 I 2 = −2(0.0025Vs ( s )) I 2 = −0.005Vs ( s ) 6 Example 4 100 = 10 10 Z in = (10) 2 (10Ω) a= Z in = 1kΩ V1 = (10Ω)(1kΩ) I s ≈ 10 I s 1.01kΩ 7