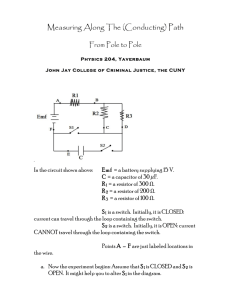
AP Physics 1 Learning Guide Unit 12: DC Circuits Essential Questions:

AP Physics 1 Learning Guide
Unit 12: DC Circuits
Essential Questions:
What is the main advantage of parallel circuits versus series circuits?
What is the significance of a
Wheatstone bridge?
Key Vocabulary:
Series Circuit
Parallel Circuit
Equivalent Resistance
EMF
Internal Resistance
Terminal Voltage
Kirchhoff’s 1 st Rule (Junction)
Kirchhoff’s 2 nd Rule (Loop)
RC Circuit
Time Constant
Galvanometer
Ammeter
Voltmeter
Potentiometer Circuit
Wheatstone bridge
Learning Targets:
AP.PHYS.11.12.1
Determine the equivalent resistance of resistors arranged in series or in parallel or the equivalent resistance of a series ‐ parallel combination
AP.PHYS.11.12.2
Use Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s rules to determine the current through each resistor and the voltage drop across each resistor in a single loop or multi ‐ loop dc circuit
AP.PHYS.11.12.3
Distinguish between the emf and the terminal voltage of a battery and calculate the terminal voltage given the emf, internal resistance of the battery, and external resistance in the circuit
AP.PHYS.11.12.4
Determine the equivalent capacitance of capacitors arranged in series or in parallel or the equivalent capacitance of a series ‐ parallel combination.
AP.PHYS.11.12.5
Determine the charge on each capacitor and the voltage drop across each capacitor in a circuit where capacitors are arranged in series, parallel or a series parallel combination.
AP.PHYS.11.12.6
Calculate the time constant of an RC circuit.
Determine the charge on the capacitor and the potential difference across the capacitor at a particular moment of time and the current through the resistor at a particular moment in time.
AP.PHYS.11.12.7
Describe the basic operation of a galvanometer and calculate the resistance which must be added to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter or a voltmeter .
AP.PHYS.11.12.8
Describe how a slide wire potentiometer can be used to determine the emf of a source of the emf.
Given the emf of a standard cell, use the slide wire potentiometer to calculate the emf of the unknown.
AP.PHYS.11.12.9
Describe how a Wheatstone bridge circuit can be used to determine the resistance of an unknown resistor.
Given three known resistors and a Wheatstone bridge circuit, calculate the resistance of an unknown resistor.