AC DC Conversion
advertisement
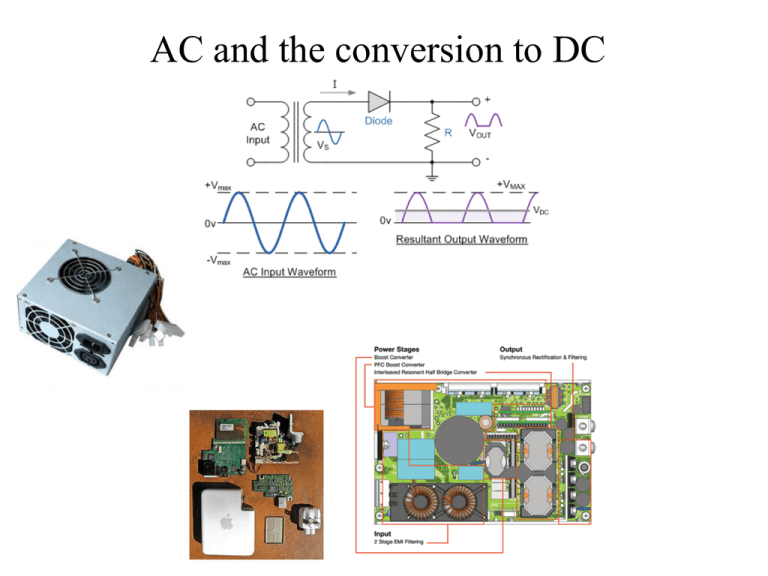
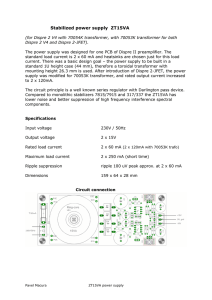
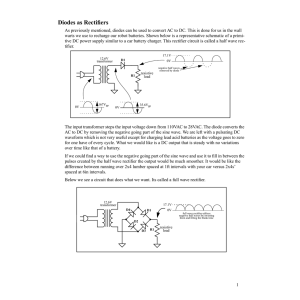
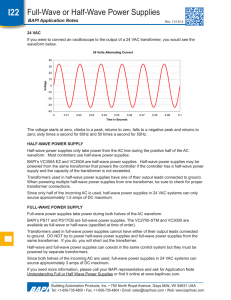
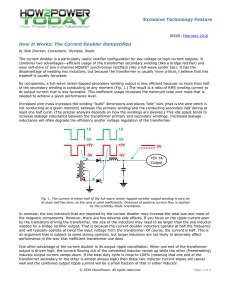
AC and the conversion to DC Direct Current. (a) DC Sources. (b) DC Flow. (c) Graphic Representation of DC. Alternating Current. Voltage that varies in amplitude and polarity as a function of time AC Power Distribution. AC Wave Shapes. (a) Sine Wave. (b) Square Wave. (c) Pulse Wave. (d) Triangular Wave. (e) Sawtooth Wave. (f) Irregular Wave. Sine Wave Characteristics Transformers only work with Alternating Current because . Where is the magnitude of the EMF in volts and ΦB is the magnetic flux (strength) through the circuit Transformer Action. A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field through the secondary winding. This varying magnetic field induces a varying electromotive force (EMF), or "voltage", in the secondary winding. This effect is called inductive coupling. If a load is connected to the secondary, current will flow in the secondary winding and electrical energy will be transferred from the primary circuit through the transformer to the load. In an ideal transformer, the induced voltage in the secondary winding (Vs) is in proportion to the primary voltage (Vp), and is given by the ratio of the number of turns in the secondary (Ns) to the number of turns in the primary (Np) as follows: Transformer Action. Center-Tapped Utility Pole Transformer. DC Power Supply. (a) Block Diagram. (b) Built-In Subsystem. (c) Stand-Alone Unit. Half-Wave Rectifier. (a) Basic Circuit. (b) Positive Input Half-Cycle Operation. (c) Negative Input Half-Cycle Operation. (d) Input/Output Waveforms. (e) Half-Wave Output Minus Diode Barrier Voltage. Half-Wave Rectifier. Percent of Ripple Out of a Filter. V peak (ripple) VRMS (ripple) 1 Peak to Peak ripple 2 0.707 V peak (ripple) Vavg (ripple) Vmid ( Peak to Peak ) % ripple VRMS of ripple 100 Vavg of ripple Full-Wave Center-Tapped Rectifier. (a) Basic Circuit. (b) Positive Input Half-Cycle Operation. (c) Negative Input Half-Cycle Operation. Input/Output Waveforms of a Full-Wave Center-Tapped Rectifier. Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier. (a) Basic Circuit. (b) Positive Half-Cycle Operation. (c) Negative Half-Cycle Operation. Capacitive Filtering of a Half-Wave Rectifier Output. Capacitive Filtering of a Full-Wave Rectifier Output. Function of a Regulator. Zener Diode Regulator.