Chapter 14 Review
advertisement

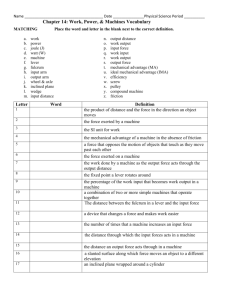
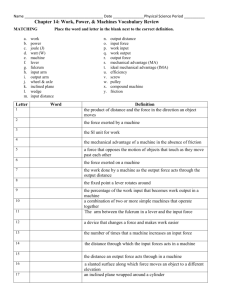
Chapter 14 Review Name Period Physical Science Fill in the blank/Short Answer/True or False LT 1 1. In science, work is done when a(n) moves. LT 1 force acts on an object in the direction the object 2. Why isn’t work being done on a barbell when a weight lifter is holding the barbell over his head? It isn’t moving, distance = zero LT 2 3. In science, work that is done on an object can be described as the force acting on the object multiplied by the distance . LT 2 4. The unit for work is the Joule . LT 2 5. Circle the letter of the amount of work done when a 1 newton force moves an object 1 meter. A. 1 newton/second B. 1 joule C. 1 watt D. 1 newton per meter LT 3 6. True or False: Power is the rate of doing work. LT 3 7. In order to do work faster, more LT 3 8. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about power. power is required. A. Power and work are always equal. B. You can increase power by doing a given amount of work in a shorter period of time. C. When you decrease the force acting on an object, the power increases. D. When you do less work in a given time period, the power decreases. LT 4 9. Write a word equation describing how to calculate power. Power equals work divided by time. LT 4 10. The unit for power is the watt . LT 4 11. Circle the letter of the expression that is equivalent to one watt. LT 2 A. one newton per meter B. one joule per meter C. one newton per second D. one joule per second 12. How much work does a 100 W light bulb do in 45 seconds? Work = power x time = 100 W x 45 seconds = 4500 J LT 6 13. True or False: A machine can make work easier to do by changing the size of the force needed, the direction of a force or the distance over which a force acts. 14. The force exerted by a machine is the ____output_____ force. The force exerted on the machine is the _____input___ force. LT 8 15. The number of times a machine increases an input force is the mechanical advantage of the machine. LT 8 16. Actual mechanical advantage describes the relationship between input force and output force. 17. The percentage of input work that becomes output work is the _____efficiency_____ of the machine. LT 8 18. How do you determine the input and output distances on a lever? Input distance = distance between the input force and the fulcrum, Output distance = distance between the output force and the fulcrum LT 5 19. List the 6 types of simple machines. Screw, lever, wheel and axle, pulley, wedge, inclined plane LT 5 20. A screwdriver used to pry the lid off a paint can is an example of a(n) lever . LT 5 21. The fixed point that a lever rotates around in called the . LT 5 one. 22. What characteristics distinguish levers as first, second and third class? Give an example of each First class has the fulcrum in the middle. Ex. Teeter totter fulcrum Second class has load (output force) in the middle. Ex. Wheelbarrow Third class has input force in the middle. Ex. rake LT 5 23. True or False: All second class levers have an ideal mechanical advantage greater than one, because the input distance is longer than the output distance. LT 5 24. Describe a wheel and axle. A lever that rotates in a circle. Combination of 2 wheels of different sizes. LT 5 25. A slanted surface along which a force moves an object to a different elevation is called a(n) inclined plane . LT 5 26. Describe a screw. An inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder. LT 5 27. A simple machine consisting of a rope fitted into a groove in a wheel is a(n) pulley . LT 7 28. True or False: A compound machine is a combination of two or more simple machines that operate together. Problems LT 4 29. A light bulb does 100 J of work in 2.5 seconds. How much power does it have? Power = W/t = 100 J/ 2.5 s= 40 J/s or 40 Watts LT 4 30. A man exerts 700 N of force to move a piece of furniture 4 m. If it takes him 2 seconds to move the furniture, how much power does it require? Power = W/t = Fd/t = (700 N x 4 m)/2 sec = 1400 W LT 4 31. A hair curling iron uses 13 W of power. How long must it operate to do 1,040 J of work? P = Work/t so t = Work/P t = 1040 J/ 13 W = 80 sec LT 4 32. A 4 W night light is left on for 8 hours each night. How much work does it do per night? Work = Pt = 4 W x 8 hr x 3600 s/hr = 115200 J LT 9 33. What is the actual mechanical advantage of the lever below? 270 N (resistance/output) 90 N (effort/input) AMA = Output force / input force = 270 N / 90 N = 3 LT 9 34. What is the length of the incline plane below if the ideal mechanical advantage is 25? 25 = L / 45 h = 45 m Length = 25 x 45 = 1125 m LT 9 35. What is the ideal mechanical advantage of each pulley? IMA = 3 IMA = 3 IMA = 4 36. Circle the pulley that would require the least input force to lift the weight. (Assume all weights are 100N.) The last one (IMA = 4)