Science
advertisement

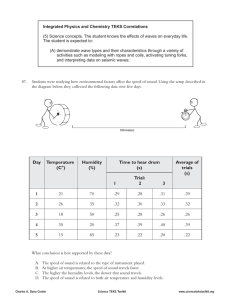
Science Course: IPC Unit: Waves / Properties of Matter TEKS/Prerequisites Guiding Questions/ Specificity 5(G) explore the characteristics and behaviors of energy transferred by waves, including acoustic, seismic, light, and waves on water as they superpose on one another, bend around corners, reflect off surfaces, are absorbed by materials, and change direction when entering new materials 3) Scientific processes. The student uses critical thinking, scientific reasoning, and problem solving to make informed decisions. The student is expected to: Guiding Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 3(E) describe connections between physics and chemistry and future careers How do waves affect everybody’s lives for good and for bad? How does sound affect your daily life? How does sound travel? Why is light the only form of electromagnetic energy you can see? Specificity: 1. 2. Transverse vs. compression waves Relate the velocity of the wave to the frequency and wavelength. Measure the amplitude of a wave Guiding Questions: 1. What determines if something will sink or float in a fluid? Assessment One tuning fork is struck and placed next to an identical fork. The two forks do not touch. The second tuning fork starts to vibrate because of A interference B the Doppler effect C resonance D machine Answer: C Designated Six Weeks: Fourth Grading Period Days to teach: 33 Instructional days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Transverse Wave Activities: Longitudinal Wave a. Medium Amplitude b. Crest Exemplar Lesson: Waves TEKS 5G Trough Vibrations in Matter d. Exemplar Lesson: Wave Properties TEKS 5G e. Polarizing Filter f. Making Music g. Blocking Noise Pollution Doppler Effect h. Radio Frequencies Pitch i. Wave Generation – Coil Spring Wavelength A diver on a springboard can increase the height of a jump by repeatedly flexing the knees with a rhythm that matches the springboard’s natural frequency. This is an example of Frequency Diffraction United Streaming.com – Elements of Physics: Waves: Sound and Electromagnetism https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= _dl_-DsOEi4 http://www5.unitedstreaming.com/vi deos/11302/f6d32134-f0b5-ea9b36ac05a938421c89.pdf Interference Decibel At 0 degrees Celsius, sound travels through air at a speed of 330m/s. If a sound wave is produced with a wavelength of 0.10m, what is the wave’s frequency? All Exemplar Lessons are located on the Google Drive: High School IPC Refraction Resonance A. Interference B. Reflection C. Resonance D. Polarization Answer: C Textbook: Physics + Chemistry, McGraw Hill, 2014 Safari Montage c. Sonar Electromagnetic Spectrum Volume Revised Spring 2015 Exemplar Lesson: Electromagnetic Spectrum TEKS 5G Resources/ Weblinks ELPS: http://ritter.tea.state.tx.us/rul es/tac/chapter074/ch074a.ht ml a. (4F) Visuals/Video b. (4F) Manipulative (2G) Draw & Write Making Sound Waves http://www.school-forchampions.com/science/sound_from _string_or_wire.htm Sound Waves and Sources http://paws.kettering.edu/~drussell/d emos.html Wave Refraction http://www.wiley.com/college/strahl er/0471480533/animations/ch19_ani mations/animation2.html APP: Decibel 10th Science Course: IPC Unit: Waves / Properties of Matter TEKS/Prerequisites Guiding Questions/ Specificity (6) Science concepts. The student knows that relationships exist between the structure and properties of matter. The student is expected to: 2. 3. 6(C) analyze physical and chemical properties of elements and compounds such as color, density, viscosity, buoyancy, boiling point, freezing point, conductivity, and reactivity What can cause the viscosity of a fluid to change? How does the Bernoulli principle relate to how airplanes are able to fly? Specificity: 1. Identify the properties of and calculate density. Assessment Designated Six Weeks: Fourth Grading Period Days to teach: 33 Instructional days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS Density What is the density of a 5 gram object which displaces 15 mL of water? The size of object is 3cm by 2 cm by 4 cm. It weighs 10 grams. What is the density of this object? Activity: Safari Montage Mass a. Buoyancy Archimedes Relate density to buoyancy 3. Examine viscosity: Effects of temperature on viscosity Effects of viscosity on velocity of an object Partner pairs to write a question and trade to work the problem. Exemplar Lesson: Marble buoyancy (golf balls) TEKS 6C All Exemplar Lessons are located on the Google Drive: High School IPC c. Exemplar Lesson: Density TEKS 6C APPS: I Tunes U – TASA IPC d. Exemplar Lesson: Viscosity TEKS 6C e. Exemplar Lesson: Explore Differences Between Physical and Chemical Properties TEKS 6C Buoyant Force Bernoulli ELPS: http://ritter.tea.state.tx.us/rul es/tac/chapter074/ch074a.ht ml a. b. c. Properties of Matter Revised Spring 2015 Stephen Murray Resources (Google Drive) b. Density 2. Resources/ Weblinks (4D) Anticipation Guides (4F) Manipulatives (2D) KWL APP: Physical Sci Interactive Glossary - Matter and Energy Science Course: IPC Unit: Waves / Properties of Matter TEKS/Prerequisites Guiding Questions/ Specificity (7) Science concepts. The student knows that changes in matter affect everyday life. (6) Science concepts. The student knows that relationships exist between the structure and properties of matter. The student is expected to: 6(A) examine differences in physical properties of solids, liquids, and gases as explained by the arrangement and motion of atoms, ions, or molecules of the substances and the strength of the forces of attraction between those particles; 6(B) relate chemical properties of substances to the arrangement of their atoms or molecules; 6(C) analyze physical and chemical properties of elements and compounds such as color, density, viscosity, buoyancy, boiling point, freezing point, conductivity, and reactivity Guided Questions: How are physical changes different from chemical changes? What chemical & physical properties should students be able to measure? Specificity: Analyze a phase change diagram Pure substances – Elements and compounds Mixtures Heterogeneous mixture Homogeneous mixture Solutions (colloids and suspensions Assessment Designated Six Weeks: Fourth Grading Period Days to teach: 33 Instructional days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies/ELPS When copper and oxygen chemically unite, they form — Element F an ion G a gas H a compound J a mixture Answer: H Ion Compound Textbook: Physics + Chemistry, McGraw Hill, 2014 http://www.webelements.com/ Molecule Isotope Atom b. Have students illustrate the molecules of a solid, liquid, and gas in their journal. List the characteristics of each state under the picture and give examples. http://education.jlab.org/atomtour/ http://www.greatneck.k12.ny.us/GN PS/SHS/dept/science/tringali/tab_3/ sub_tabs/documents/Folder2forpubli shing.pdf Physical Property Compare and contrast a homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture. Describe the arrangement of the molecules that make up a solid and liquid, how are they different? Chemical Property Conductivity c. States of Matter Lab (Phase Diagram of Ice) Reactivity d. Lab: Chemical and Physical Properties (exemplar lesson) Boiling Point e. Atomic Structure models Freezing Point f. Color and label periodic table based on properties. Solid g. Element Research Liquid Gas Periodic Table Atomic Mass Atomic Number Revised Spring 2015 Activities: a. Introduce scientists that contribute to modern periodic table Resources/ Weblinks h. Discussion of scientists that contributed to early chemistry and the atom ELPS: http://ritter.tea.state.tx.us/rul es/tac/chapter074/ch074a.ht ml (4f) Graphic Organizer (4f) Manipulative Safari Montage Stephen Murray Resources (google drive) APP: Nova Elements