Junior Cert Physics Definitions
advertisement

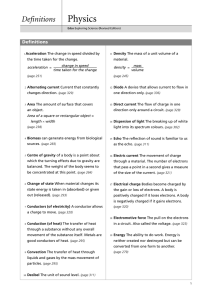
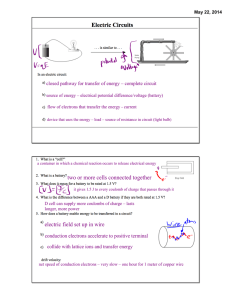
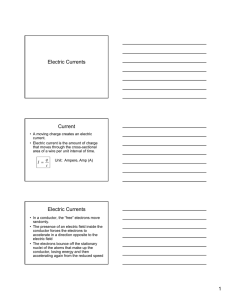
Junior Cert Physics Definitions • • • • • • Volume - space an object occupies Mass - amount of matter in a substance Density = mass / volume Energy - ability to do work Force - anything that causes a change in velocity Pressure = force / area • Lever - rigid body free to turn about a fixed point called a fulcrum • Moment - turning effect of a force, = force x distance • Momentum - mass x velocity • Law of Lever - when a lever is balanced the sum of the moments on the L.H.S. = sum of the moments on the R.H.S. • Centre of Gravity - point at which all the bodies weight appears to act • Weight = mass x gravity • • • • • • Hooke’s Law – extension of an elastic material is directly proportional to the applied force producing the extension Newton’s law – If no force acts on a body then a body in motion will continue at a constant speed in a straight line Displacement - shortest distance between two points, straight line Speed = distance / time Velocity - speed in a given direction i.e 50m/s north acceleration = change in velocity / time • • • • Law of conservation of energy - energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed from one form to another Friction - is a force between any two materials in contact with each other which opposes their motion Work = force x distance Pressure in a liquid depends on depth and density • • Temperature is a measure of the hotness of a body Heat – is a form of energy that moves from hotter to colder bodies Heat travels by • – – – • Conduction through a solid, no movement of the substance Convection through liquids and gases, movement of particles Radiation ( can travel through vacuum ), by means of waves Latent heat - is the heat needed to change the state of a substance without changing the temperature i.e ice melting, boiling water • • • Increased pressure - increases boiling point A body will float in a liquid if it is less dense Power is the amount of work done per second • • • • • Potential difference - difference in charge so that current will flow Current – is the flow of charge (electrons) Amp. No. electrons per second Ohm’s Law - at a constant temperature Voltage = Current x resistance ( V = I x R ) ESB unit - kilowatt hour kilowatts x hours Fuse – a thin piece of wire with a low melting point that breaks the circuit if the current is too high • • • • • Resistor – controls the amount of current in a circuit Ohms The EMF of a battery – the pull of the electrons in a circuit- electromotive force A body becomes positively charged if it looses electrons and negatively charged if it gains electrons. Insulator – is a substance that holds charge A conductor – is a material that allows charge to flow through it. • • • • Direct current (D.C) – the flow of charge in one direction only (battery) Alternating current (A.C) – current that changes direction (mains) A diode – device that allows current to flow in one direction only Light emitting diode (LED) – gives out light when current flows through it • • • Light dependent resistor (LDR) – a variable resistor whose resistance changes with the amount of light that falls on it. Switch – device to complete / break a circuit Insulator – does not allow heat / electricity to flow through them • • • Echo – Reflected sound from a solid object Ultra sound – sound of very high pitch, not heard by humans Refraction - bending of light as it passes from one transparent medium to another • • Luminous body – creates its own light, Sun Non-luminous body – Reflects light • • • • • • • • • Energy forms Kinetic - any moving object Potential - due to position / condition stretched elastic / spring Sound - vibrating objects drum Radiant - light and heat sun Chemical - between the bonds of elements Nuclear - in the nucleus of an atom Internal - potential and kinetic energy of molecules Electric - object that needs to be plugged in radio / tv • • • Dispersion - breaking up of white light into seven colours ( spectrum ) Opisometer - measures short curved lines Power = I x V = I2 x R