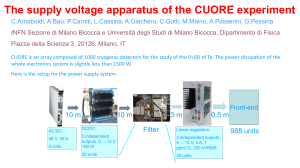
Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High
advertisement

Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance IC Design Flow M. Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni Electronics Department, Politecnico di Torino April, 8-9 2000 Summary. Summary Introduction: noise in VLSI circuits IR drop and causes, scale and consequences Proposed methodology to face these problems Power Supply Model Noise cost function Conclusions M. 1 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Introduction. Introduction: noise in VLSI circuits Technology scaling down leads to: increasing chip size increasing clock frequency increasing interconnect density noise jeopardizes UDSM circuits functionality: crosstalk electromigration ground bounce M. 2 IR drop Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F IR drop and L dI/dt . IR drop causes Transistor and interconnection scaling down causes increased gate number w/o area change greater number of gates in a row growing current on power supply lines increased line resistance increased GND and VDD area for electromigration rise of M. 3 IR drop Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F IR drop and L dI/dt . causes Transistor sizes scaling down causes: increased frequency of the clock signal higher gate switching activity higher electromigration risk decreased clock rise time: higher for on chip and package inductances M. 4 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F IR drop and L dI/dt . IR drop and influences on Power Supply Higher sensibility of gates to noise spikes: delay, charge alteration, reduced Crosstalk towards neighbor lines EMI problems towards neighbor circuits Ground bounce injected into the substrate M. 5 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F IR drop and L dI/dt . Simulations IR drop influence: simulations vdd vdd gnd vdd gnd gnd vdd gnd M. 6 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F IR drop and L dI/dt . Simulations IR drop: simulation parameters AND2 TSPC, 0.25 m, 2.5V, 1Ghz Growing number of cells: from 200 up to 600 Different parasitic inductance conditions: on chip distributed (0.2pH), package (1pH – 10pH) Distributed parasitic resistance function of electromigration sizing M. 7 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F IR drop and L dI/dt . Simulations IR drop: simulations results 3.5 200 gates 400 gates 600 gates Noise Overshoot [V] 3 2.5 2 1.5 0.2pH, Dist. 1pH, Pack. 10pH, Pack 1 0.5 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 Noise Width [ps] M 8 . Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Methodology. Verification or prediction? Verification of noise failures has expensive time-to-market aftereffects Countermeasures are strongly joined to designer intervention It’s basic to develop design tools facing early in the design sequence the potential noise generation M. 9 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Methodology. Noise Cell Views and Cost Function Layout HDL Delay NOISE COST FUNCTION Power FLOOR M. 10 T PLANN I THMS L VIEW DE ING AND PLAC OR Noise Tolerance Cell View CEL Interconnect Density SC Netlist RI Noise Injection Cell View PT ION Area G L A N E M E Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Methodology. Methodology: instruments Synergy among tools related to different design phases is needed: transistor sizing optimization tool gate noise tolerance analysis cell model with noisy power supply references row of cells model: the influences between the cell and its environment M. 11 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Power Supply Model: uniform sizing I p i-1 I p1 Is i-1 I s1 Z1 Z i-1 V1 I p i+1 I pi Is i I si+1 I sN Vi-1 Z i Vi+1 Zi+1 Vi+1 The maximum current is I pN I sN+1 ZN VN ZN+1 !#" while the worst overvoltage is M. 12 %$ & ' ( ) *+ '-, . & /"0 ( #" Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Uniform sizing Uniform sizing, noise prediction Maximum noise overvoltage is known from the number of cells inserted on the line, or vice-versa As a drawback the area of a GND line is: 1 243+576 98;:=< 6 ?> @ ACB M. 13 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Optimized dimensioning Area optimization without noise worsening Area waste due to worst current value used to dimension the whole line Ideal sizing: GND and VDD line width for cell D proportional to the maximum current at point D Real sizing: a controlled and optimized line segmentation is proposed M. 14 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Optimized dimensioning VDD Optimized dimensioning N cells M N cells M N cells M N cells M N cells M GND node 0 row1 g(M-1)=M-1 row2 GND VDD node N M. 15 node N wm -> Rm N M cells N M cells N M N cells cells M ∆w= N M cells node 0 wmax - wmin g(M-1) Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Optimized dimensioning Optimized dimensioning: gain and loss A E The area gain is F 2HG > @ ACB . F > @ and the noise loss due to increased resistance is: E ' I J @ K L M K where T K M. 16 @ K L @ . NM U F K 8 R S QP K L V J F =" K M J > @ ACB M K F W R J J O J J O XQ> @ XY R F J S[Z P Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Optimized dimensioning Optimized dimensioning: overvoltage control Losses at node N when optimizing for area: N parametric Τ ∆Α ∆Ν 2 cells for block m 20 cells for block m 100 cells for block m area gain w_min = TEC_MIN M. 17 W_MIN w_min = w_MAX Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Optimized dimensioning Optimized dimensioning: design parameters Using a good number of segments with increasing dimensions the number of cells does not influence the loss in noise safety. The designer has control on area and noise, varying number of gates in a row number of segments having different width width at the line endpoints M. 18 > @ ACB XQ> @ Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Noise Reduction Overshoot [V] Noise reduction: distributed capacitors 0.8 0.75 0.7 0.65 0.6 0.55 0.5 0.45 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0 Maximum overvoltage versus distributed capacitors 200 gates 400 gates 600 gates 200 400 600 800 1000 Distributed capacitance [fF] M. 19 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Noise reduction Decreased current to shrink resistance Isi = Ip + Isi+1 a) Ip Isi Isi+1 l gate b) Isi = (Ip - Ic) + Isi+1 Ip c) Isi Ic Isi+1 l gate l cap M. April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F 20 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance Power Supply Model. Noise reduction Distributed capacitors: loss and gain Noise overshoot variation \ ]0^`_?a \ c< " \b F U V 8 -< " b O F V U O b #" W 8;:=< 6 \ 8 c< " Z b Area variation 1 2d3e5f6 \ ] ^hgHi \ c< " \b F 1 243+5f6 8 c< " b . ! " F 8;:=< 6 8 -< " b . W " F b Z \ M. 21 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Power Supply Model. Noise reduction Distributed capacitors design parameters If the line width is chosen between W =" F b Z J 8 :=< 6 8 -< " b j > j " 8 :< 6 8;:=< 6 8 -< " b and each cell in the library is connected to an optimized capacitor, a gain in noise and in area is assured with respect to the case w/o capacitors. M. 22 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Future model developments. Future model developments conjunction of optimized dimensioning and of distributed capacitors insertions " QS " P and QS P clock skew modeling in the current superposition and overvoltage evaluation package influence on row model extension to S.O.C. designs M. 23 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Noise Cost Function. Noise Cost Function A Noise Cost Function to be introduced in a placement algorithm is influenced as shown before by Noise overvoltage Power supply lines area Electromigration Number of cells in a row Distributed optimized capacitors Number of optimized segments M. 24 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F Conclusion. Conclusions The aim is to create a NOISE COST FUNCTION to be inserted in a placement algorithm it is based on: a cell description with noise characteristics a cell environment description with noise generation parameters it is of basic impact to face early in the design sequence the potential noise aftereffects M. 25 Graziano, M. Delaurenti, G. Masera, G. Piccinini, M. Zamboni.Power Supply Design Parameters Prediction for High Performance April,IC 8-9Design 2000 F