Powerpoint Slides

PHY132H1F
Introduction to Physics II
Lecture 15, November 2, 2009
Today, Ch. 32
• Drawing Circuit
Diagrams
• Kirchhoff’s Laws
• Energy and Power in
Circuits
• Resistors connected in
Series
Review of last day’s final
In Class Discussion
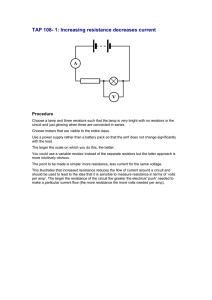
Question. A wire connects the positive and negative terminals of a battery.
Two identical wires connect the positive and negative terminals of an identical battery. Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the currents I a
I d at points a to d.
to
A.
I c
B.
I a
C.
I c
= I d
= I b
=
I d
> I a
> I c
>
I a
> I b
= I d
=
I b
D. I a
E.
I a
= I
> I b b
= I
> I c c
= I
= I d d
Recall from last week…
Resistance and Ohm’s Law
The resistance of a long, thin conductor of length L and cross=sectional area
A is
The SI unit of resistance is the ohm. 1 ohm = 1 Ω = 1 V/A.
The current through a conductor is determined by the potential difference Δ V along its length:
Ohm’s Law
• Ohm’s law is limited to those materials whose resistance R remains constant—or very nearly so—during use.
• The materials to which Ohm’s law applies are called ohmic .
• The current through an ohmic material is directly proportional to the potential difference. Doubling the potential difference doubles the current.
• Metal and other conductors are ohmic devices.
1
Real life:
Circuit Diagrams
A circuit diagram:
In Class Question 1.
Which of these diagrams represent the same circuit?
Tactics: Using Kirchhoff ’ ’ s loop Tactics: Using Kirchhoff ’ ’ s loop law
2
EXAMPLE 32.1 A single resistor
QUESTION:
EXAMPLE 32.1 A single resistor
EXAMPLE 32.1 A single resistor
EXAMPLE 32.1 A single resistor circuit
In Class Question 2.
What is ∆ V across the unspecified circuit element?
In Class Question 3.
Does the potential increase or decrease when traveling through this element in the direction assigned to I?
The power supplied by a battery is
The units of power are J/s, or W.
The power dissipated by a resistor is
Or, in terms of the potential drop across the resistor
3
In Class Question 4. Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the powers P dissipated in resistors a to d.
a to P d
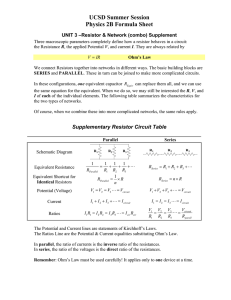
• Resistors that are aligned end to end, with no junctions between them, are called series resistors or, sometimes, resistors “in series.”
• The current
I is the same through all resistors placed in series.
• If we have
N resistors in series, their equivalent resistance is
The behavior of the circuit will be unchanged if the
N series resistors are replaced by the single resistor R eq
.
In Class Question 5.
What is the potential at points a to e ?
4