Examples and HWx - Spring Branch ISD
advertisement

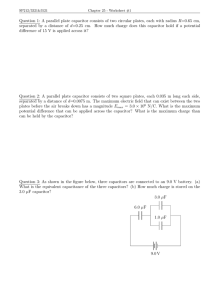
AP Physics C Capacitors – Examples and Homework Examples: 1. Calculate the work needed to place 4 protons at the corners of a square 1nm on a side. 2. A parallel plate capacitor has square plates 10cm on a side separated by 1mm. a. Find the capacitance. b. If the capacitor is charged to 12V, how much charge is transferred from one plate to the other? c. How large would the plates have to be for it to have a capacitance of 1F? 3. A parallel plate capacitor has square plates 14cm on a side separated by 2mm and is charged to 12V. The plate separation is then increased to 3.5mm. a. What is the charge on the capacitor? b. Calculate the original energy stored. c. How does the energy change when the separation is increased? 4. A parallel plate capacitor has square plates 10cm on a side separated by 4mm. There is a dielectric between them with κ = 2. a. What is the capacitance without the dielectric? b. What is the capacitance when the dielectric fills the space between the plates? c. What is the capacitance if a 3mm dielectric is put in the 4mm gap? Homework: 5. A capacitor has a charge of 30 µC. The potential difference between the conductors is 400V. What is the capacitance? [7.5 x 10-8 F] 6. a. If a parallel plate capacitor has a 0.15 mm separation, what must its area be for it to have a capacitance of 1F? [1694915 m2] b. If the plates are square, what is the length of their sides? [1301.89 m] 7. a. A 3 µF capacitor is charged to 100V. How much energy is stored in the capacitor? [0.015 J] b. How much additional energy is required to charge the capacitor from 100 to 200V? [0.045 J] 8. A parallel plate capacitor has square plates 1 m on a side. The plates are initially separated by a distance of 1 mm. a. What is the capacitance? [8.85 x 10-9 F] b. If you connect the capacitor to a 12V battery, how much charge is stored on the plates? [1.62 x 10-7 J] c. If you increase the separation of the plates to 2 mm while it is still connected to the battery, what changes, and what are the new values? [C = 4.425 x 10-9 F, Q = 5.31 x 10 -8 C] d. How much energy is stored in the capacitor? [3.186 x 10-7 J] e. If you now disconnect the capacitor from the battery and move the plates back to a 1 mm separation, what is the voltage between the plates? [6 V] f. How much energy is stored in the capacitor now? [1.593 x 10-7 J] 9. a. A coaxial cable acts like a cylindrical capacitor. If the coaxial cable bringing you your favorite TV shows is 30m long, with the radius of the inner conductor being 1 mm, and the radius of the outer conductor being 0.5 cm, what is the capacitance of the cable? [1.037 x 10-9 F] b. If it is connected to a voltage source of 5 V, how much charge is stored in the cable? [5.183 x 10-9 C] c. How much energy is stored in the cable? [1.296 x 10-8 J] 10. Find the energy stored in a 20pF capacitor when it is charged to 5µC. How much additional energy is required to increase the charge from 5 to 10µC? [0.625 J, 1.875 J] 11. A parallel-plate capacitor with a plate area of 2m2 and a separation of 1.0mm is charged to 100V. a. What is the electric field between the plates? [100000 V/m] b. What is the energy per unit volume in the space between the plates? [0.04425 J/m3] c. Find the total energy by multiplying your answer to part (b) by the total volume between the plates. [8.85 x 10-5 J] d. Find the capacitance C. [1.77 x 10-8 F] e. Calculate the total energy from U = 0.5 CV2, and compare your answer with your result for part (c). [8.85 x 10-5J] 12. A parallel-plate capacitor with plates of area 500cm2 is charged to a potential difference V and is then disconnected from the voltage source. When the plates are moved 0.4 cm farther apart, the voltage between the plates increases by 100V. a. What is the charge Q on the positive plate of the capacitor? [1.11 x 10-8 C] b. How much does the energy stored in the capacitor increase due to the movement of the plates? [5.53 x 10-7J ] 13. An electric field of 2x104 V/m exists between the plates of a circular parallel-plate capacitor that has a plate separation of 2mm. a. What is the voltage across the capacitor? [40V] b. What plate radius is required if the stored charge is 10µC? [4.24 m] 14. A Geiger tube consists of a wire of radius 0.2mm and length 12cm and a coaxial cylindrical shell conductor of the same length and a radius of 1.5cm. a. Find the capacitance, assuming that the gas in the tube has a dielectric constant of 1. [1.55 x 10-12 F] b. Find the charge per unit length on the wire when the potential difference between the wire and shell is 1.2kV. [1.55 x 10-8 C/m] 15. A parallel-plate capacitor is made by placing polyethylene (κ = 2.3) between two sheets of aluminum foil. The area of each sheet is 400cm2, and the thickness of the polyethylene is 0.3mm. Find the capacitance. [2.71 x 10-9 F] 16. A parallel-plate capacitor has plates separated by a distance s. The space between the plates is filled with two dielectrics, one of thickness 0.25s and dielectric constant κ1, the other with thickness 0.75s and dielectric constant κ2. Find the capacitance of this capacitor in terms of C0, the capacitance with no dielectrics. [(4C0 κ1 κ2)/( κ2 + 3 κ1)]