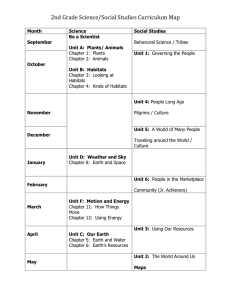
Habitats - Aldo Leopold Nature Center

Habitats
Grades PreK-2
Description
Discover how each organism meets its basic needs for food, water, shelter and space in order to survive. Through a hike, activities and a puppet show, we’ll investigate the prairie, pond and forest habitats of the Nature Center and the life each supports. Pond dipping included when possible.
Objectives
This program is aligned with many National and State Standards (Grades K-2). Please see the next page for more details.
1.
Use our five senses to discover and explore three habitats (Forest, Prairie, and Wetland).
2.
Describe one adaptation of a plant in the forest, prairie and pond habitats.
3.
Describe one adaptation of an animal in the forest, prairie and pond habitats.
4.
Observe and describe two seasonal changes.
5.
Recognize signs of animal activity in the habitats.
Vocabulary
* Adaptation
* Camouflage
* Carnivore
* Compare
* Diurnal
* Forest
* Habitat
* Herbivore
* Hibernate
* Migrate
* Nocturnal
* Observe
* Omnivore
* Prairie
* Predator
* Prey
* Survival
* Wetland
NGSS: Next Generation Science Standards WMAS: Wisconsin’s Model Academic Standards
FOSS: Full Option Science Standards CC: Common Core Page 1 of 5
Outline
Habitats
Grades PreK-2
I. Introduction
Naturalists will welcome the students and introduce Aldo Leopold and his connection to the environment. They will then introduce the topic of habitats and highlight the habitats they will visit while at the Aldo Leopold Nature Center (ALNC).
II. Habitats as a Home
Naturalists will perform a puppet show and use study mounts to highlight the importance of a habitat, how it can be home to many different animals, and what animals can be found in the different habitats the students will explore.
NGSS: K-ESS3-1, K-LS1-1,
1-LS1-2, 2LS4-1
III. Terrestrial Habitat Investigation
WMAS: Science – F CC: K.MD.A.2
Groups will use a Venn diagram worksheet to record plants and animals seen while exploring ALNC’s three habitats (Prairie, Woodland and Wetland). Using this diagram, students will compare and contrast plant and animals they discover, observe seasonal changes that are occurring, and also discuss how the plants and animals are adapted to living in the different habitats.
WMAS: Science – A, F CC: K.CC, K.MD.A.2 NGSS: K-LS1-1, 1-LS1-2,
1-LS3-1, 2-LS4-1
IV. Wetland Habitat Exploration
Students will head to the pond to use nets to search for aquatic insects and other animals. Using magnifying lenses and identification card or books, students will then identify the organisms they have caught and discuss their behavior and the importance of the pond to their survival.
WMAS: Science – C, F NGSS: K-LS1-1, 1-LS3-1,
2-LS4-1
V. Conclusion
CC: RI.K.1, RI.1.1, K.CC,
K.MD.A.2
Naturalists will review what was found in the habitats, their importance, and highlights of the trip with the students.
PLEASE NOTE: Some activities may change or be moved indoors due to inclement weather.
Alternate activities may include:
1.
Worm Game
Using different colored yarn as worms, students will learn about the importance of camouflage to an animal’s survival. The worms are hidden throughout a defined area and students try to find as many pieces as they can. They will then compare and discuss the number of each color of worm they found and how this pertains to camouflage.
2.
Indoor Pond Dip
Similar to the Aquatic Habitat Exploration above, except Naturalists will pre-dip from our pond and bring samples of aquatic organisms and plants indoors to be explored in the case of inclement weather.
NGSS: Next Generation Science Standards WMAS: Wisconsin’s Model Academic Standards
FOSS: Full Option Science Standards CC: Common Core Page 2 of 5
Standards Met
Habitats
Grades PreK-2
Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
K. Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems: Animals, Plants, and Their Environment
K-LS1-1. Use observations to describe patterns of what plants and animals (including humans) need to survive.
LS1.C: Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms – All animals need food in order to live and grow. They obtain their food from plants or from other animals.
Plants need water and light to live and grow.
K-ESS3-1. Use a model to represent the relationship between the needs of different plants or animals (including humans) and places they live.
K -ESS3.A: Natural Resources – all living things need water, air and resources from the land and they live in places that have the things they need.
Science and Engineering Practices:
Analyzing and Interpreting Data – Analyzing data in K-2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to collecting, recording, and sharing observations.
Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Information – Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information in K-2 builds on prior experiences and uses observations and texts to communicate new information.
Crosscutting Concepts:
Patterns – Patterns in the natural and human designed world can be observed and used as evidence.
Systems and System Models – Systems in the natural and designed world have parts that work together.
1. Structure, Function, and Information Processing
1-LS3-1. Make observations to construct an evidence-based account that young plants and animals are like, but not exactly like, their parents.
LS3.A: Inheritance of Traits – Young animals are very much, but not exactly, like their parents.
LS3.B: Variation of Traits – Individuals of the same kind of plant or animal are recognizable as similar but can also vary in many ways.
Science and Engineering Practices:
Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Information – Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information in K-2 builds on prior experiences and uses observations and tests to communicate new information.
Scientific Knowledge is Based on Empirical Evidence – Scientists look for patterns and order when making observations about the world.
NGSS: Next Generation Science Standards WMAS: Wisconsin’s Model Academic Standards
FOSS: Full Option Science Standards CC: Common Core Page 3 of 5
Habitats
Grades PreK-2
(NGSS Continued)
Crosscutting Concepts:
Patterns – Patterns in the natural world can be observed, used to describe phenomena, and used as evidence.
Structure and Function – The shape and stability of structures of natural and designed objects are related to their function.
2. Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems
2-LS4-1: Make Observations of plants and animals to compare the diversity of life in different habitats.
LS4.D: Biodiversity and Humans – There are many different kinds of living things in any area, and they exist in different places on land and in water.
Science and Engineering Practices:
Planning and Carrying Out Investigations – Make Observations to collect data which can be used to make comparisons.
Scientific Knowledge is Based on Empirical Evidence – Scientists look for patterns and order when making observations about the world.
Crosscutting Concepts:
Structure and Function – The shape and stability of structures of natural and designed objects are related to their function.
Wisconsin’s Model Academic Standards (WMAS)
Standards for Science
Standard A: Students will understand there are unifying themes: systems, order, organization, and interactions; evidence, models, and explanations; constancy, change and measurement; evolution, equilibrium, and energy; form and function among scientific disciplines.
Standard C: Students will investigate using scientific methods and tools, revise their personal understanding to accommodate knowledge, and communicate these understandings to others.
Standard F: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the characteristics and structures of living things, the process of life, and how living things interact with one another and their environment.
NGSS: Next Generation Science Standards WMAS: Wisconsin’s Model Academic Standards
FOSS: Full Option Science Standards CC: Common Core Page 4 of 5
Habitats
Grades PreK-2
Common Core (CC)
ELA/Literacy
RI.K.1: With prompting and support, ask and answer questions about key details in a text.
RI.1.1: Ask and answer questions about key details in a text.
Mathematics
K.CC: Counting and Cardinality
K.MD.A.2: Directly compare two objects with measurable attributes in common, to see which object has more or less of that attribute, and discuss the difference.
NGSS: Next Generation Science Standards WMAS: Wisconsin’s Model Academic Standards
FOSS: Full Option Science Standards CC: Common Core Page 5 of 5