ELECTRICAL CURRENT
advertisement

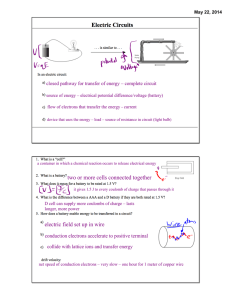
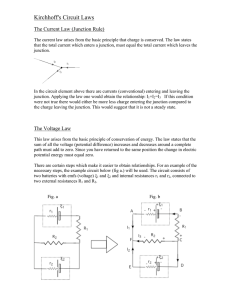
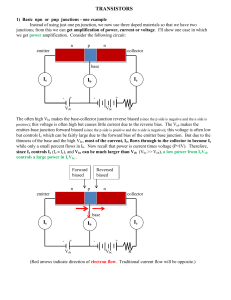
A physical model of current Defining and describing current Lesson 1: ELECTRICAL CURRENT Announcements HW 1 Current due Tuesday Photoelectric Lab simulation due today 5pm by email to mperkins@ortn.edu No pity, no excuses, no sob stories… NO MERCY!!!! Exam: Electrostatics – Monday 3/4/2013 Lesson 1: Introduction to Current AP Physics B Objectives III.C.1. Current, Resistance, & Power a) Students should understand the definition of electric current, so they can relate the magnitude and direction of the current to the rate of flow of positive and negative charge. Student Objectives Students will be able to 1) Define electric current. 2) Calculate the electric current in a circuit. 3) Apply conservation of charge to junctions in wires. A physical model of electrical current Current is the flow of electrical charge from one point to another…specifically positive charge! Charges flow in response to an electric field. What are charge carriers? In a normal electrical circuit with metal wire, it is the electrons that are the “charge carriers”. So if the electrons move one way, which way does the current move? How is current created? Current is created when an electric field exists in a conductor. The loosely held electrons in the conductor respond to the electric force, and move opposite the direction of the field. To sustain the current, the electric field must be sustained. Batteries and capacitors do a good job of providing an electric field. What do we mean by conservation of current? Charge cannot be created or destroyed. The flow of charge cannot be created or destroyed, either. Current cannot be created or destroyed. Mathematical definition of current Current is defined as the flow of positive charge. I = Q/t I: current in Amperes or Amps (A) Q: charge in Coulombs (C) t: time in seconds Sample Problem 1.1: How many electrons per hour flow past a point in a circuit if it bears 11.4 mA of direct current? If the electrons are moving north, in which direction is the current? Mathematical definition of current conservation A point where wire branches meet is called a junction. The sum of currents entering a junction equals the sum of currents leaving the junction. Iin = Iout or Iin – Iout= 0 Sample Problem 1.2: Find the missing currents a) 8A 15 A ? b) 2A 4A ? Sample Problem 1.3: Find the missing current.