Regimen: Classical CMF (IV) for Early Breast Cancer
advertisement

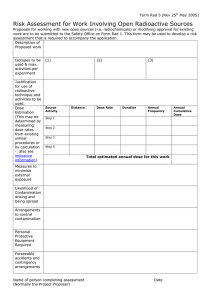
Regimen: Indication Adjuvant treatment for early breast cancer in patients who are unsuitable for anthracycline based chemotherapy Regimen detail Administration Classical CMF (IV) for Early Breast Cancer Day 1&8 1&8 1&8 Drug Cyclophosphamide Methotrexate Fluorouracil (5-FU) Dose 600mg/m2 40mg/m2 600mg/m2 Route IV IV IV Fluorouracil, methotrexate and cyclophosphamide are given by slow intravenous bolus into the side arm of a fast flowing drip of 0.9% sodium chloride. Cyclophosphamide may be given in 250-500ml 0.9% sodium chloride over 30 minutes Frequency Every 28 days Maximum 6 cycles Extravasation Fluorouracil and methotrexate are inflammatants (Group 2) Cyclophosphamide is a neutral agent (Group 1) Premedication Not usually required. Emetogenicity This regimen has moderate emetogenic potential – refer to local protocol Additional recommended supportive medication Mouthwashes as per local policy Loperamide 4mg po stat then 2mg prn for diarrhoea Consider folinic acid (calcium folinate/leucovorin) rescue 15mg po 6 hourly x 6 doses, starting 24 hours post methotrexate D1&D8 (only for patients with severe toxicities such as mucositis, sore eyes, diarrhoea, severe renal impairment or “third – space” fluid collection) Pre- treatment evaluation FBC LFT U&E (inc. SrCr) Baseline - results valid for 4 weeks Baseline - results valid for 4 weeks Baseline - results valid for 4 weeks Regular investigation FBC LFT U&E (inc SrCr) Clinical Assessment Pre D1 – results valid for 72 hours, Pre D1 – results valid for 7 days Pre D1 – results valid for 7 days Clinically assess patient prior to each cycle, particularly focusing on whether the patient has developed stomatitis or haemorrhagic cystitis Controlled document Last printed 02/12/2010 Document No Version Number ASWCS10 BR016 1.1.a *ONLY VALID ON DATE OF PRINTING* Page 1 of 4 within range, authorisation to administer must be given by prescriber/consultant Dose modifications • Haematological toxicity ≥ 1 x 109/l ≥100 x 109/l ≥ 80ml/min <1.5 x ULN <2.5 x ULN Neutrophil count Platelet count Creatinine Clearance Bilirubin ALT Standard limits for administration to go ahead – if blood results not Reduce the dose of methotrexate if the patient has a pleural effusion or ascites (Is this done empirically or is there a defined dose reduction?) Delay 1 week if neutrophils <1.0 x 109/l and/or platelets <100 x 109/l. Dose reduction should be considered if myelosuppression results in delay of subsequent courses. In adjuvant treatment, dose reduction and delays can compromise outcome. GCSF should be considered if more than one delay and/or before dose reduction. Contact relevant consultant. • • Renal impairment Hepatic impairment CrCl (ml/min) >80 60-80 50-59 30-50 10-30 Cyclophosphamide dose 100% 100% 100% 100% 75% Methotrexate dose 100% 65% 50% 50% Contraindicated <10 50% Contraindicated Bilirubin ALT < 1.5 x ULN 1.5 – 3 x x ULN or <2.5 x ULN 2.5 - 5 x ULN Fluorouracil (5FU) dose 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% Consider dose reduction Cyclophosphamide dose Methotrexate dose Fluorouracil (5FU) dose 100% 100% 100% 100%* 75% 67% Consider dose >5x reduction / use > 3x ULN Contraindicated Contraindicated ULN alternative regimen* * Cyclophosphamide is not recommended in patients if bilirubin > 1.5 x ULN or AST/ALT >2–3xULN, but exposure to active metabolites may not be increased and therefore a dose reduction may not be necessary. Consultant decision • NCI Common Toxicity Criteria Controlled document Last printed 02/12/2010 Toxicity Febrile neutropenia Definition ANC <0.5 x 109/l plus fever requiring IV antibiotics +/hospitalisation Stomatitis & for Grade III painful Mucositis erythema or ulcers requiring rehydration resolving to Grade I or less painless ulcers of mild soreness Other Grade III/IV toxicity toxicities (except alopecia) Dose adjustment 20% reduction of cyclophosphamide only 20% dose reduction of methotrexate and fluorouracil. Consider folinic acid rescue (see above) Continue with 20% dose reduction of suspected causative agent(s) Document No Version Number ASWCS10 BR016 1.1.a *ONLY VALID ON DATE OF PRINTING* Page 2 of 4 provided toxicity has resolved to Grade I or less If further toxicity occurs, an additional reduction may be made after discussion with consultant. • Defer treatment for any grade III/IV non-haematological toxicity (excluding alopecia) • If a delay of more than 3 weeks is required for recovery, or more than 2 dose reductions are necessary, the patient should discontinue treatment Adverse effects – the contents of the table indicate the adverse effects that should be included in consent to treatment forms Rare or Serious Side Effects Frequently occurring Side Effects Grade 3/4 febrile neutropenia Nausea and vomiting Myelosuppression Fatigue Risk of second malignancy e.g. Long term risk of early menopause, leukaemia reduced fertility Cardiac toxicity Stomatitis and mucositis Teratogenicity Diarrhoea Other side effects include: alopecia (partial), loss of appetite, taste disturbance, skin sensitivity, gritty eyes, blurred vision, nail changes, bladder irritation (including haemorrhagic cystitis), allergic reactions and altered liver and kidney function. Significant drug interactions – Co-trimoxazole/trimethoprim – Avoid if possible – enhances antifolate effect. If essential, monitor FBC regularly. NSAIDs – Monitor renal function and FBC if used concomitantly as may reduce renal excretion of methotrexate (increased risk in renal impairment). Probenecid – avoid – increases methotrexate toxicity 3-4 fold. Antibacterials – Monitor FBC – penicillins, tetracyclines, sulphonamides, doxycycline and ciprofloxacin may reduce methotrexate clearance. For full details consult product literature/ reference texts Comments Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) deficiency can result in severe toxicity secondary to reduced fluorouracil metabolism – avoid use in patients with known DPD deficiency Cardiotoxicity has been associated with fluoropyrimidine therapy, with adverse events being more common in patients with a prior history of coronary artery disease. Caution must be taken in patients with a history of significant cardiac disease, arrhythmias or angina pectoris. Methotrexate accumulates in 3rd space fluids (pleural effusions, ascites) leading to prolonged elimination time and potentially increased toxicity. Consider folinic acid rescue (as above) starting 24 hours after each dose. Methotrexate can cause acute or chronic interstitial pneumonitis, which is often associated with blood eosinophilia. Monitor patients for dyspnoea, cough (especially dry, non-productive) and fever. Deaths have been reported. Cumulative Doses References None • Fisher B, Brown AM, Dimitrov NV, Poisson R, Redmond C, Margolese RG, et al. Two months of doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide with and without interval reinduction therapy compared with 6 months of cyclophosphamide, Controlled document Last printed 02/12/2010 Document No Version Number ASWCS10 BR016 1.1.a *ONLY VALID ON DATE OF PRINTING* Page 3 of 4 • • • • • • • • • • • Document title Document number Approval date Written by Checked by Authorised by Review date Document reviewed by Version number Summary of changes Controlled document Last printed 02/12/2010 methotrexate, and fluorouracil in positive-node breast cancer patients with tamoxifen-nonresponsive tumors: results from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-15. J Clin Oncol. 1990; 8:1483-96. Tancini G, Bonadonna, G, Valagussa P, Marchini S and Veronesi U. Adjuvant CMF in breast cancer: comparative 5-year results of 12 versus 6 cycles. J Clin Oncol. 1983;1:2-10. Bonadonna G, Brusamolino E, Valagussa P, Rossi A, Brugnatelli L, Brambilla C et al. Combination chemotherapy as adjuvant treatment in operable breast cancer. N Engl JMed 1976;294:405-10. Bonadonna G, Valagussa P, Rossi A, Tancini G, Brambilla C, Zambetti M et al. Ten year experience with CMF-based adjuvant chemotherapy in resectable breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.1985;5:95-115. Daniels S. North London Cancer Network, Dose adjustment of cytotoxics for hepatic impairment [internet]. accessed 16/04/2009 available at http://www.bopawebsite.org/tiki-download_file.php?fileId=621 Daniels S. North London Cancer Network, Dose adjustment of cytotoxics for renal impairment [internet]. 16/04/2009 available at http://www.bopawebsite.org/tiki-download_file.php?fileId=620 Baxter K, editor. Stockley’s Drug Interactions. Pharmaceutical Press; 2009. Accessed on line on 06/05/09 available at https://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/ Summary of Product Characteristics Fluorouracil 50mg/ml injection (Hospira) [internet] accessed 16/04/2009 available from http://emc.medicines.org.uk/document.aspx?documentId=636 Summary of Product Characteristics Methotrexate 100mg/ml injection (Hospira) [internet] accessed 16/04/2009 available at http://emc.medicines.org.uk/document.aspx?documentId=11588 Summary of Product Characteristics Cyclophosphamide 500mg injection (Baxter) [internet] accessed 11/11/2009 available from http://www.ecomm.baxter.com/ecatalog/loadResource.do?bid=44228 Allwood M, Stanley, A, Wright P, editors. The cytotoxics handbook. 4th ed. Radcliffe Medical Press 2002. Trissel LA. Handbook of Injectable Drugs. 15th ed. American Society for Health-Systems Pharmacists 2009. Accessed on line on 06/05/09 available at http://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/hid/current/ Classical CMF (IV) for Breast Cancer ASWCS10 BR016 Jeremy Braybrooke, Consultant Medical Oncologist, BHOC, and Chair, ASWCS Drugs and Therapeutics Committee Becky Bagnall, Consultant Pharmacist, NBT Jeremy Braybrooke, Chair, ASWCS Drug+Therapeutics Committee 15/10/2011 Jeremy Braybrooke Digitally signed by Jeremy Braybrooke DN: cn=Jeremy Braybrooke, o, ou, email=james.carr@aswcs.nhs.uk, c=GB Date: 2010.12.02 15:59:59 Z Becky Bagnall Digitally signed by Becky Bagnall DN: cn=Becky Bagnall, o, ou, email=james.carr@aswcs.nhs. uk, c=GB Date: 2010.12.02 16:00:32 Z Digitally signed by Jeremy Braybrooke cn=Jeremy Braybrooke, o, ou, Jeremy Braybrooke DN: email=james.carr@aswcs.nhs.uk, c=GB Date: 2010.12.02 16:01:09 Z 1.1.a Version Document No Version Number ASWCS10 BR016 1.1.a *ONLY VALID ON DATE OF PRINTING* Page 4 of 4